树的介绍
树是一种非线性的数据结构,即树从一个节点出发可能有多个后继节点。
树的基本术语
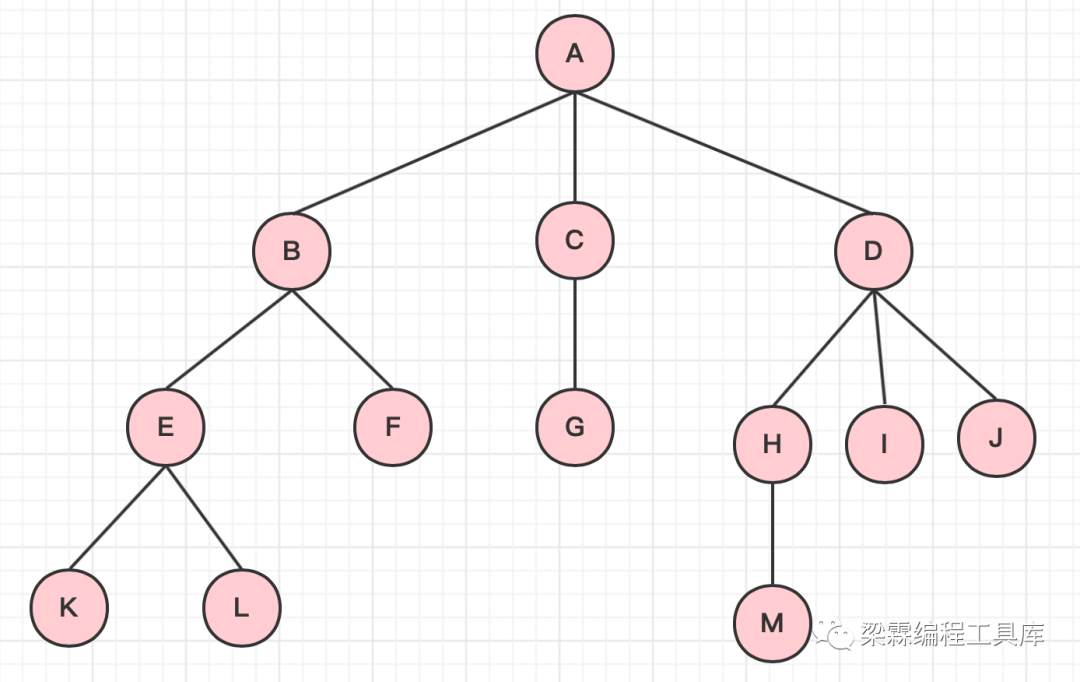
节点: A、B、C等元素都是节点,节点不仅包含了数据元素,还包含了指向子树的分支。
节点的度:节点拥有的子树的个数或者分支的个数,比如节点A有三个子树,因此节点A的度为3,节点B有两个子树,因此节点B的度是2
树的度:树中各个节点中度的最大值定义为整颗树的度。比如下面这棵树的度是3
叶子节点:指的是没有子树的节点叫做树的叶子节点,比如下图中的K、L、F、G、M、I、J
内部节点: 指的是除叶子节点意外的其他节点叫内部节点,比如下图中的A、B、C、D、E、H
孩子节点:某一节点的子树称之为改节点的孩子节点,比如A节点的孩子节点是B、C、D
双亲节点:与孩子节点向电影院的节点是双亲节点,比如B节点的双亲是A
兄弟节点:统一节点的孩子节点之间称之为兄弟节点,比如B节点的兄弟节点是C和D
树的高度:从根节点开始所能到达叶子节点中距离最长路径长度称之为树的高度,比如下图的树高是4
二叉树的定义
每个节点最多只能有两个孩子节点,即二叉树中节点的度只可以为0,1,2
子树有左右之分,不能颠倒,分别称之为左孩子和右孩子。
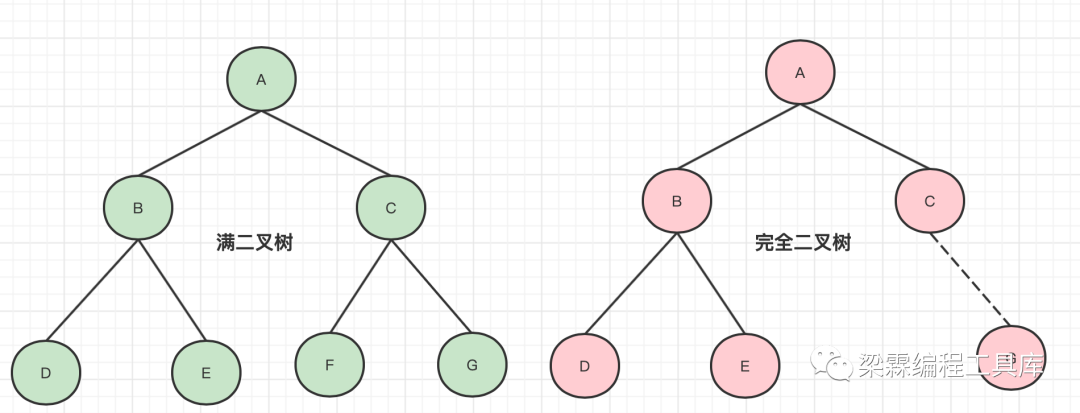
特殊的二叉树
满二叉树:如果二叉树所有的内部节点都有左右孩子节点,并且所有的孩子节点都集中在同一层中,这样的二叉树称之为满二叉树。
完全二叉树:从上到下,从左到右紧密的排布,不跳跃任何一个位置的二叉树就是完全二叉,比如下图中去掉G节点的右边的树就是一颗完全二叉树,满二叉树是一种特殊的完全二叉树。
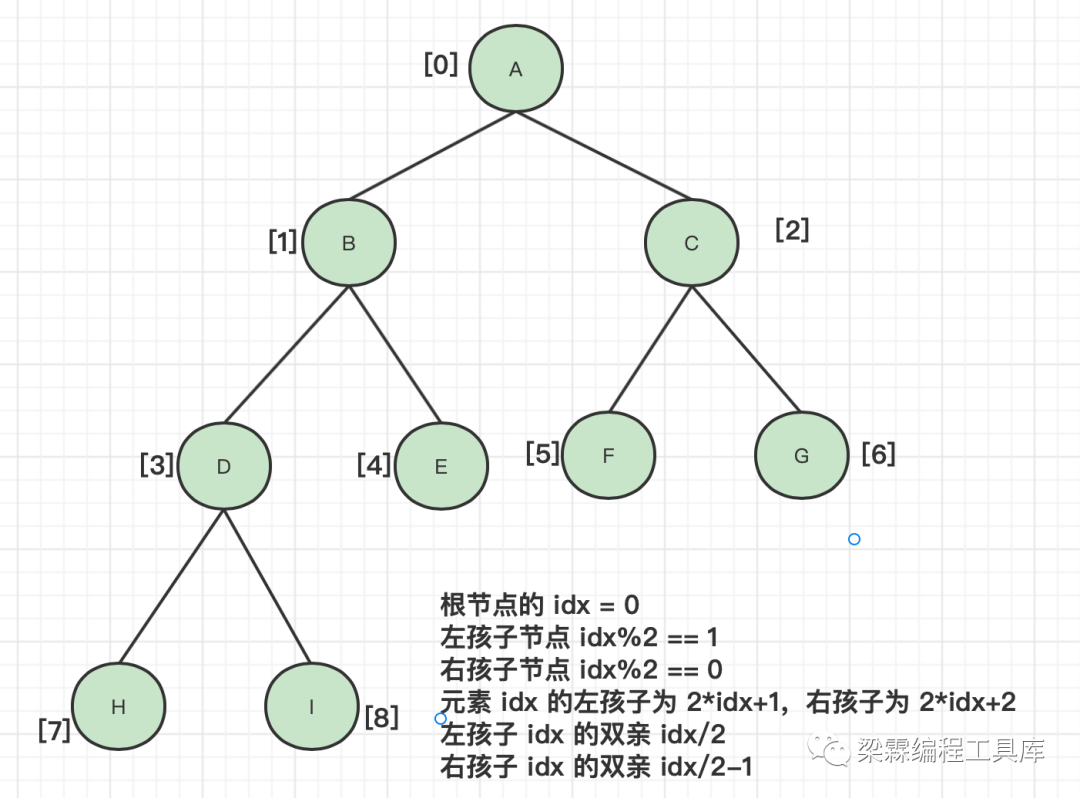
树的顺序存储结构
特点:要求是一颗完全二叉树或者把一颗普通的二叉树补齐虚拟节点保证补齐以后是一颗完全二叉树,然后采用数组的方式进行存储。
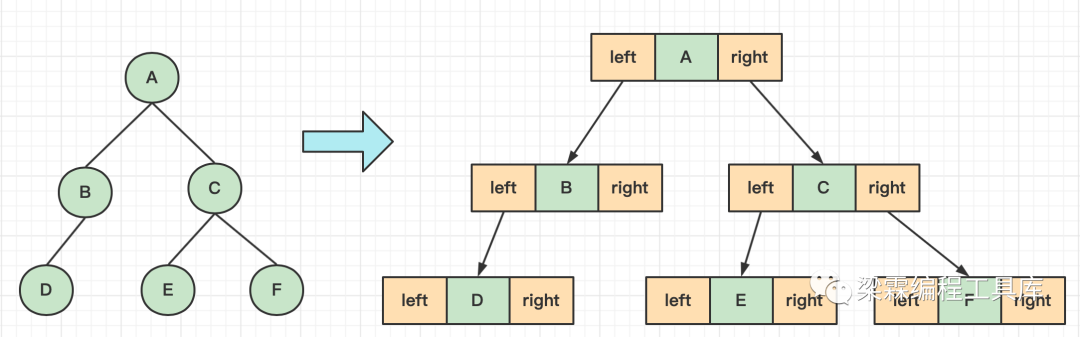
二叉树的链式存储
public class BTNode {public int val;public String info;public BTNode left;public BTNode right;public BTNode(){val = 0;info = "";left = right = null;}public BTNode(int val,String info){this.val = val;this.info = info;}@Overridepublic String toString() {return "BTNode{" +"val=" + val +", info='" + info + '\'' +'}';}}
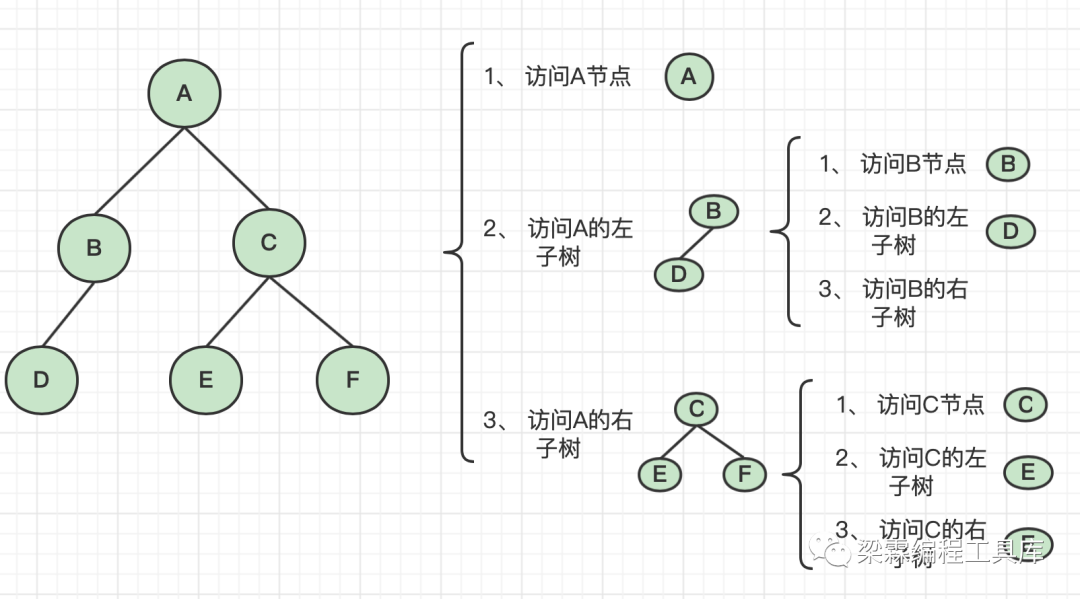
二叉树的先序遍历算法(链式存储)
先序遍历的遍历顺序是先访问根节点,然后访问左子树,最后访问右子树的过程。
遍历结果: A,B,D,C,E,F
先序遍历递归版本代码实现
public class Main {public static void main(String[] args) {BTNode root = create();preOrder(root);}public static void preOrder(BTNode root){if(root == null){return;}System.out.println(root);//递归调用左边preOrder(root.left);//递归调用右边preOrder(root.right);}public static BTNode create(){BTNode a = new BTNode(0,"A");BTNode b = new BTNode(1,"B");BTNode c = new BTNode(2,"C");BTNode d = new BTNode(3,"D");BTNode e = new BTNode(4,"E");BTNode f = new BTNode(5,"F");a.left = b;a.right = c;b.left = d;c.left = e;c.right = f;return a;}}
先序遍历非递归版本代码实现
当我们访问到父节点的时候,其实我们在这个时候同时遇见了父节点的左孩子和右孩子,但先序遍历要求先处理了左孩子,再处理右孩子,因此此时我们应该先将右孩子入栈,等访问玩左孩子以后,通过出栈操作可以访问右孩子。
public class Main2 {public static void main(String[] args) {BTNode root = create();preOrderNoCur(root);}public static void preOrderNoCur(BTNode root){if(root == null){return;}Stack<BTNode> stack = new Stack<>();//初始化stack.push(root);//遍历while(!stack.empty()){BTNode p = stack.pop();System.out.println(p);if(p.right!=null){stack.push(p.right);}if(p.left!=null){stack.push(p.left);}}}public static BTNode create(){BTNode a = new BTNode(0,"A");BTNode b = new BTNode(1,"B");BTNode c = new BTNode(2,"C");BTNode d = new BTNode(3,"D");BTNode e = new BTNode(4,"E");BTNode f = new BTNode(5,"F");a.left = b;a.right = c;b.left = d;c.left = e;c.right = f;return a;}}
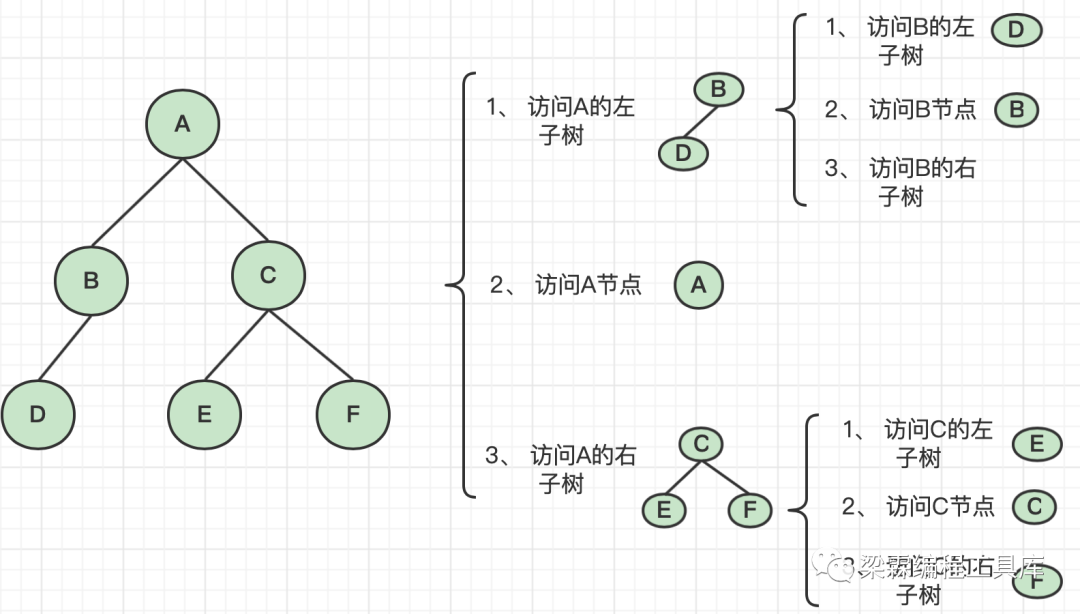
二叉树的中序遍历算法(链式存储)
中序遍历的遍历顺序是先访问左子树,然后访问根,最后访问右子树的过程。
遍历结果:D、B、A、E、C、F
中序遍历递归版本代码实现
public class Main {public static void main(String[] args) {BTNode root = create();inOrder(root);}public static void inOrder(BTNode root){if(root == null){return;}inOrder(root.left);System.out.println(root);inOrder(root.right);}public static BTNode create(){BTNode a = new BTNode(0,"A");BTNode b = new BTNode(1,"B");BTNode c = new BTNode(2,"C");BTNode d = new BTNode(3,"D");BTNode e = new BTNode(4,"E");BTNode f = new BTNode(5,"F");a.left = b;a.right = c;b.left = d;c.left = e;c.right = f;return a;}}
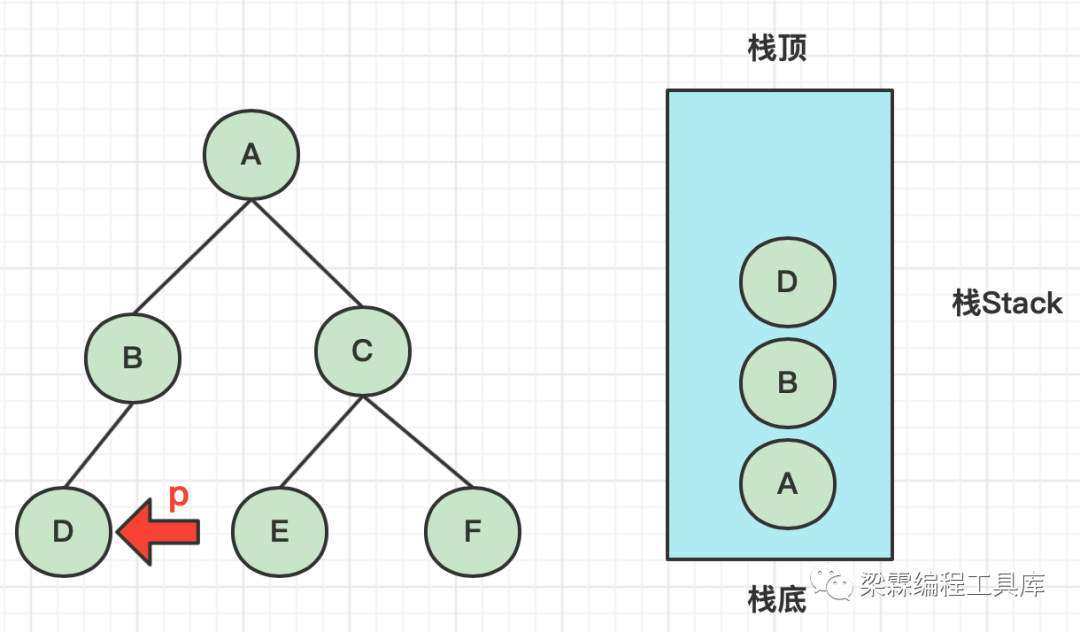
中序遍历非递归版本代码实现
当我们遇见A节点的时候,我们需要先处理A.left,处理完以后再处理A,因此A需要夏安入栈
递归->非递归 : 核心点是当前我们遇见了A,但不能立即处理A,需要先处理A.left再处理A,因此栈具有记忆性特征。
public class Main2 {public static void main(String[] args) {BTNode root = create();inOrderNoCur(root);}public static void inOrderNoCur(BTNode root){if(root == null){return;}Stack<BTNode> stack = new Stack<>();BTNode p = root;while(p!=null || !stack.empty()){if(p!=null){stack.push(p);p = p.left;}else{p = stack.pop();System.out.println(p);p = p.right;}}}public static BTNode create(){BTNode a = new BTNode(0,"A");BTNode b = new BTNode(1,"B");BTNode c = new BTNode(2,"C");BTNode d = new BTNode(3,"D");BTNode e = new BTNode(4,"E");BTNode f = new BTNode(5,"F");a.left = b;a.right = c;b.left = d;c.left = e;c.right = f;return a;}}
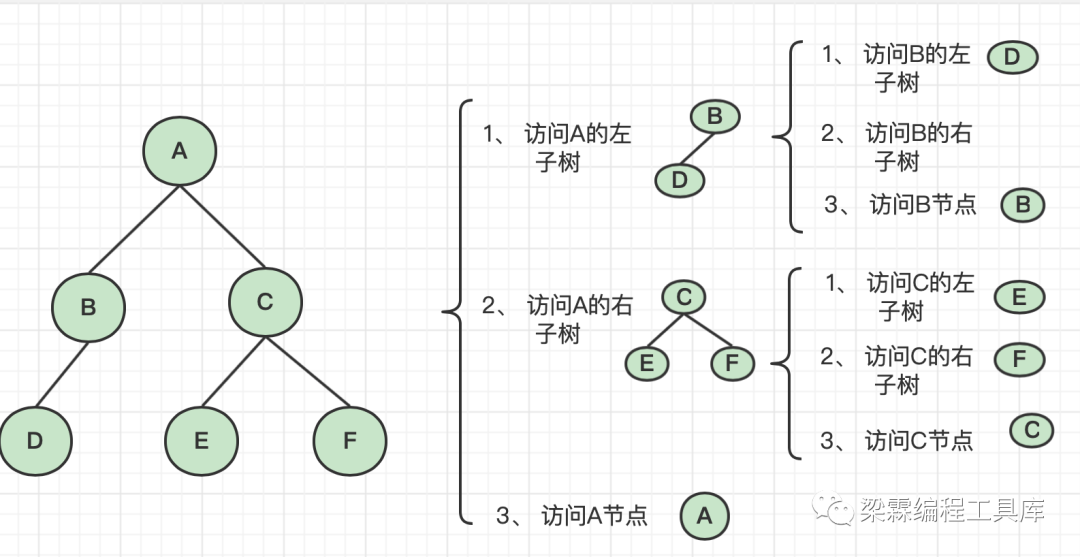
二叉树的后序遍历算法(链式存储)
后序遍历的遍历顺序是先访问左子树,然后访问右子树,最后访问根的过程。
遍历结果:D、B、E、F、C、A
后序遍历递归版本代码实现
public class Main {public static void main(String[] args) {BTNode root = create();postOrder(root);}public static void postOrder(BTNode root){if(root == null){return;}postOrder(root.left);postOrder(root.right);System.out.println(root);}public static BTNode create(){BTNode a = new BTNode(0,"A");BTNode b = new BTNode(1,"B");BTNode c = new BTNode(2,"C");BTNode d = new BTNode(3,"D");BTNode e = new BTNode(4,"E");BTNode f = new BTNode(5,"F");a.left = b;a.right = c;b.left = d;c.left = e;c.right = f;return a;}}
后序遍历非递归版本代码实现
public class Main2 {public static void main(String[] args) {BTNode root = create();postOrderNoCur(root);}public static void postOrderNoCur(BTNode root){if(root == null){return;}Stack<BTNode> stack = new Stack<>();BTNode p = root;//最近一次访问的节点BTNode lastVisitedNode = null;while(p!=null || !stack.empty()){if(p!=null){stack.push(p);p = p.left;}else{p = stack.peek();if(p.right==null || lastVisitedNode == p.right){stack.pop();//说明是从右子树往回走System.out.println(p);//标记最近访问的节点lastVisitedNode = p;// p=null是 为了继续往回走p = null;}else{//说明是从左子树往回走p = p.right;}}}}public static BTNode create(){BTNode a = new BTNode(0,"A");BTNode b = new BTNode(1,"B");BTNode c = new BTNode(2,"C");BTNode d = new BTNode(3,"D");BTNode e = new BTNode(4,"E");BTNode f = new BTNode(5,"F");a.left = b;a.right = c;b.left = d;c.left = e;c.right = f;return a;}}
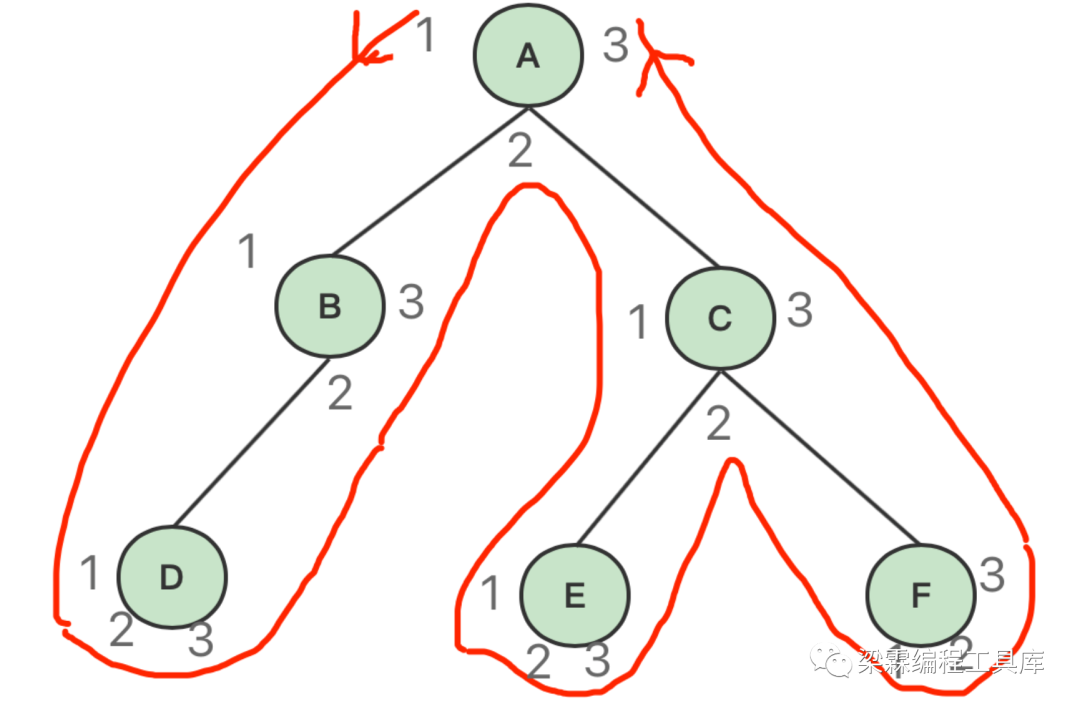
总结以上三种遍历算法的路程流转图
在二叉树遍历的过程中,不论是先序遍历,中序遍历还是后序遍历,均按照这个流程来进行。
第1次遇见就输出,则是先序遍历;
第2次遇见就输出,则是中序遍历;
第3次遇见就输出,则是后序遍历;
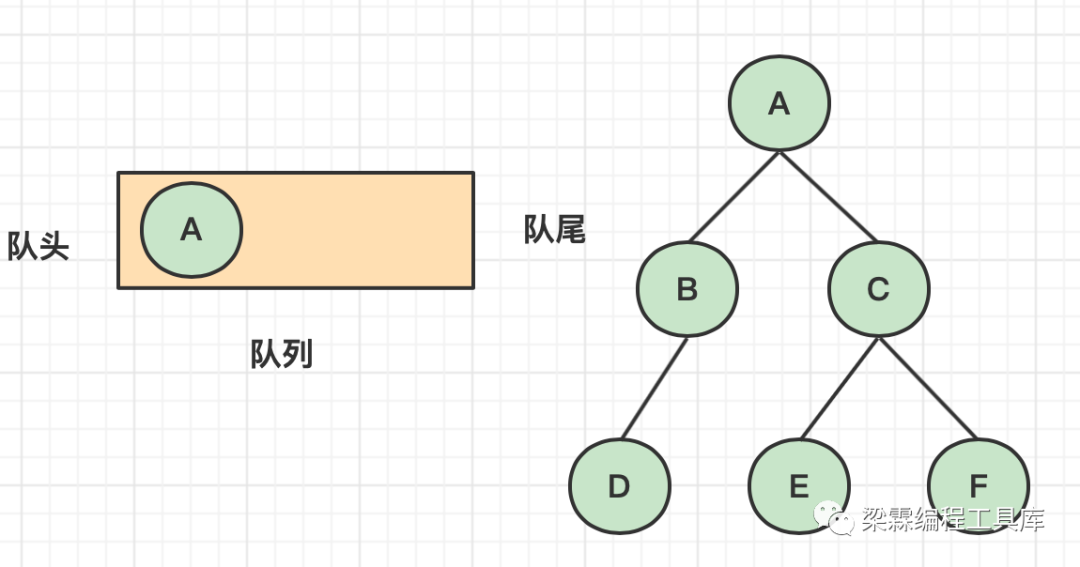
二叉树的层序遍历(链式存储)
层序遍历,顾名思义就是按照二叉树的层次结构一层一层的访问。
下面这个二叉树的层序遍历访问结果是:A、B、C、D、E、F
层序遍历代码实现
public class Main {public static void main(String[] args) {BTNode root = create();layerOrder(root);}public static void layerOrder(BTNode root){if(root == null){return;}Queue<BTNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();//队列初始化queue.offer(root);//层序遍历while (!queue.isEmpty()){BTNode cur = queue.poll();System.out.println(cur);if(cur.left!=null){queue.offer(cur.left);}if(cur.right!=null){queue.offer(cur.right);}}}public static BTNode create(){BTNode a = new BTNode(0,"A");BTNode b = new BTNode(1,"B");BTNode c = new BTNode(2,"C");BTNode d = new BTNode(3,"D");BTNode e = new BTNode(4,"E");BTNode f = new BTNode(5,"F");a.left = b;a.right = c;b.left = d;c.left = e;c.right = f;return a;}}






