大家好,我是小寒。
今天来分享 9 个 python 常用技巧,如果觉得不错,点赞,转发安排起来。
一、列表推导
greenhouse = ['boat orchid', 'bird\'s nest fern', 'dancing-lady orchid',
'nun\'s hood orchid', 'pennywort', 'snake plant',
'maidenhair fern', 'chinese ground orchid',
'vanilla orchid', 'tiger orchid', 'pothos']
[print(plant) for plant in greenhouse if 'orchid' in plant];
二、单行 if 语句
与前面的技巧一样,单行 if 可以帮助你,使代码更简洁。
此代码将单行 if 与列表推导结合起来,在植物是兰花的情况下输出 1,否则输出 0。
[1 if 'orchid' in plant else 0 for plant in greenhouse]
输出为:
[1, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0]
三、将 lambda 函数 应用于 DataFrame 列
pandas DataFrame 是一种可以保存表格数据的结构。 lambda
是一个关键字,它提供了对表中的值执行操作的快捷方式。
import pandas as pd
data = pd.DataFrame({'plant': greenhouse,
'height_(cm)': [50, 20, 15, 40, 50,
60, 45, 50, 50, 20, 20],
'condition': ['full sun', 'shade', 'partial sun', 'partial sun', 'partial sun',
'full sun', 'shade', 'partial sun', 'full sun', 'partial sun', 'full sun'],
'water_(cm/week)': [2.5, 4, 2.5, 2.5, 3,
0.5, 4.5, 2.5, 2, 2.5, 2.5],
'music': ['bach', 'bach', 'beyonce', 'bach', 'cardi b',
'nicki', 'bach', 'bach', 'vivaldi', 'cardi b', 'bach']})
输出为:
plant height_(cm) condition water_(cm/week) music
0 boat orchid 50 full sun 2.5 bach
1 bird's nest fern 20 shade 4.0 bach
2 dancing-lady orchid 15 partial sun 2.5 beyonce
3 nun's hood orchid 40 partial sun 2.5 bach
4 pennywort 50 partial sun 3.0 cardi b
5 snake plant 60 full sun 0.5 nicki
6 maidenhair fern 45 shade 4.5 bach
7 chinese ground orchid 50 partial sun 2.5 bach
8 vanilla orchid 50 full sun 2.0 vivaldi
9 tiger orchid 20 partial sun 2.5 cardi b
10 pothos 20 full sun 2.5 bach
假设我们想知道植物是否更喜欢某个德国古典作曲家。
data['music'].apply(lambda x: 1 if x == 'bach' else 0)
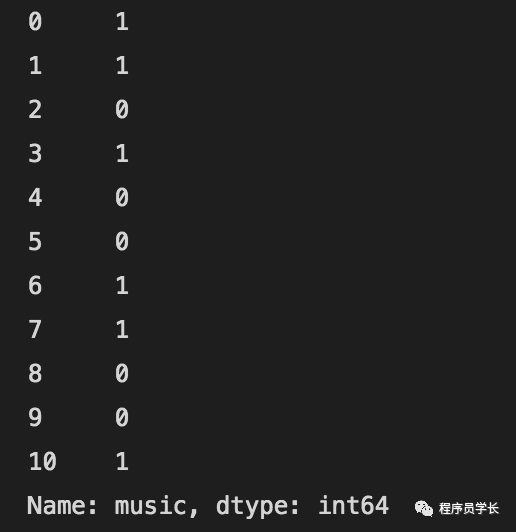
lambda代表一个 “匿名函数”。它允许我们在不创建正式函数的情况下对 DataFrame 中的值执行操作。
四、将条件应用于多列
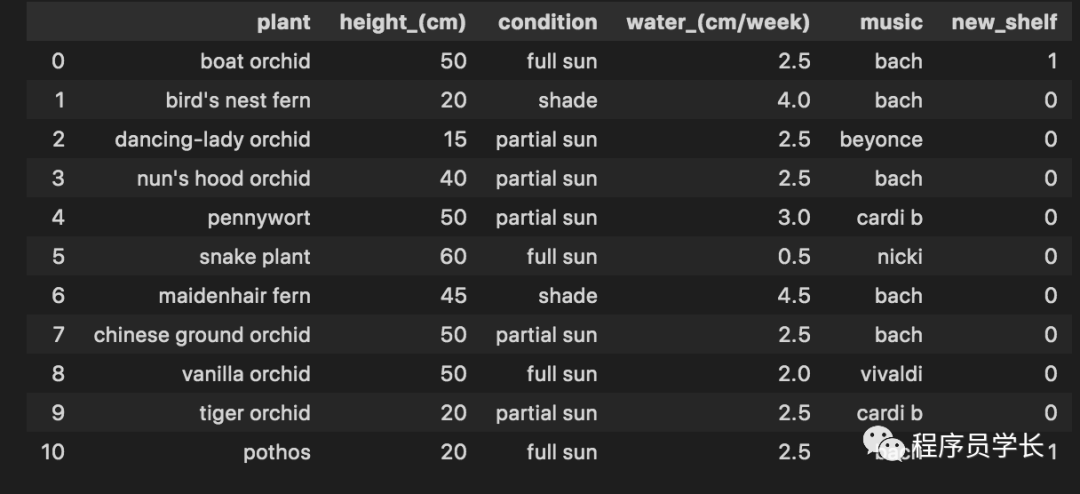
假设我们要确定哪些喜爱巴赫的植物也需要充足的阳光,因此我们可以将它们一起安排在温室中。
def sunny_shelf(col1, col2):
return (1 if ((col1 == 'full sun') & (col2 == 'bach')) else 0)
data['new_shelf'] = data.apply(lambda x: sunny_shelf(x.condition, x.music), axis=1)
import numpy as np
data['new_shelf'] = np.where((data['condition'] == 'full sun')
& (data['music'] == 'bach'), 1, 0)
五、读入 .csv 文件并设置索引
可以通过 read_csv() 函数来读取 csv 格式的数据。
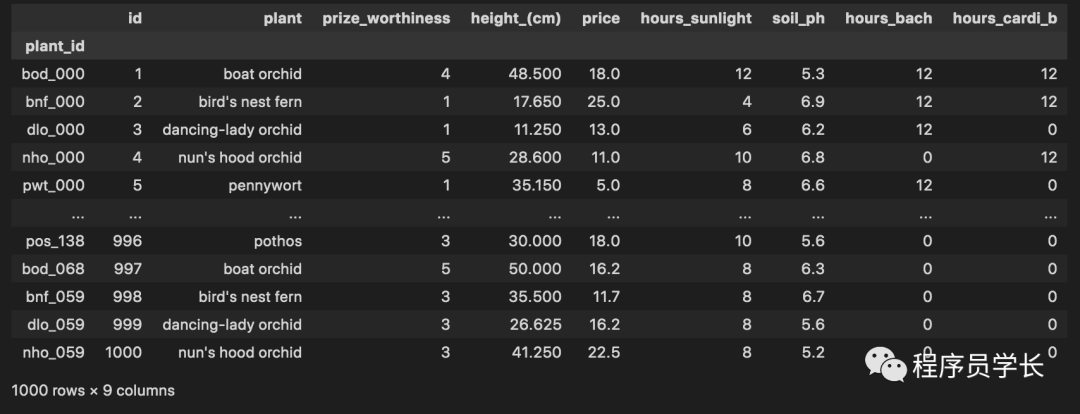
假设 csv 文件中包含一个唯一的植物标识符,我们希望将其用作 DataFrame 中的索引。我们可以使用 index_col 参数进行设置。
data = pd.read_csv('greenhouse.csv', index_col='plant_id')
六、格式化价格
'${:,.2f}'.format(data['price'].sum())
输出为:
'$16,126.66'
七、创建数据透视表
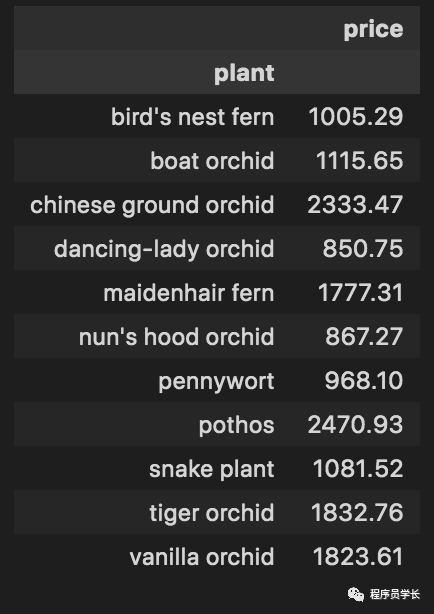
接下来,假设我们想查看每个植物物种的花费。我们可以使用 pd.pivot_table() 或 .groupby()进行聚合。
pd.pivot_table(data, index='plant', values='price', aggfunc=np.sum)
或者
data[['plant','price']].groupby(by='plant').sum()
我们还可以使用任一方法指定多级数据透视表。
data['orchid'] = data['plant'].apply(lambda x: 1 if 'orchid' in x else 0)
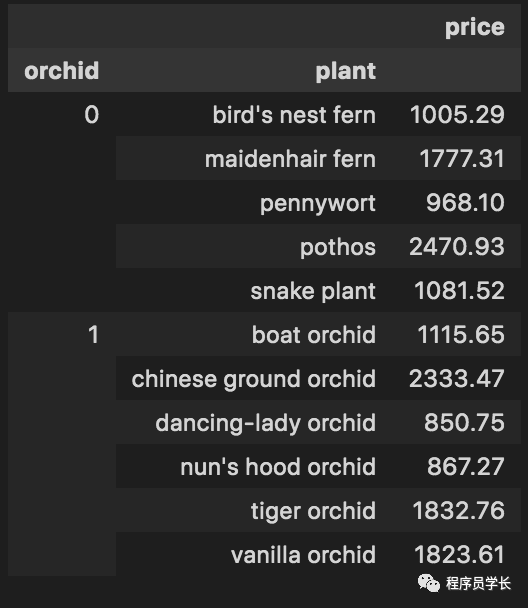
piv = pd.pivot_table(data2, index=['orchid', 'plant'], values='price', aggfunc=np.sum)
piv0 = data[['orchid','plant','price']].groupby(by=['orchid','plant']).sum()
八、计算占总数的百分比
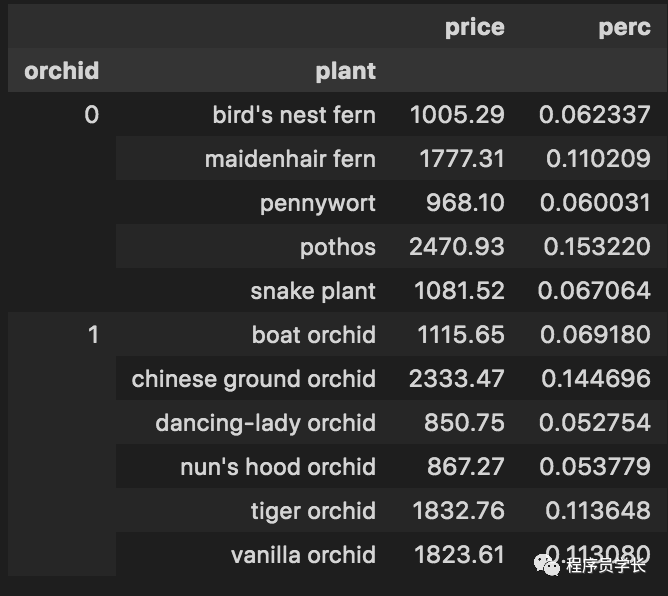
好奇每种植物对温室总成本的贡献?将每个值除以所有行的总和,并将该输出分配给名为 “perc” 的新列:
piv['perc'] = piv['price'].div(piv['price'].sum(axis=0))
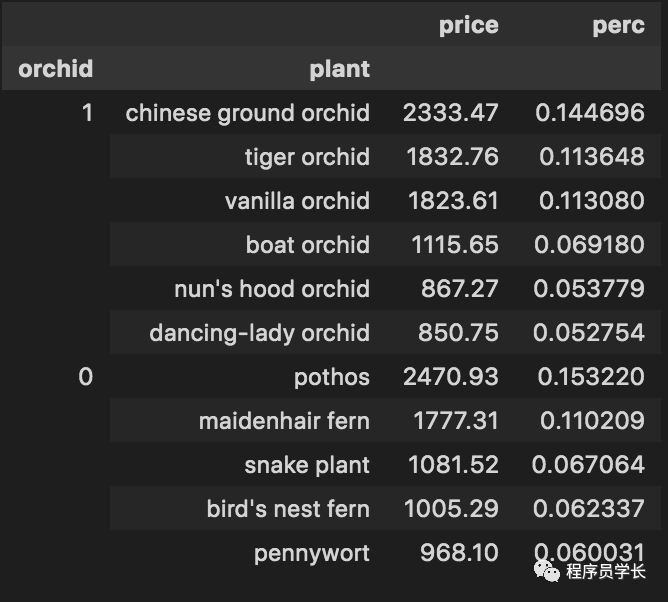
九、 按多列排序
piv.sort_values(['orchid','price'], ascending=False)
最后
—
「进群方式:加我微信,备注 “python”」

往期回顾






如果对本文有疑问可以加作者微信直接交流。进技术交流群的可以拉你进群。

文章转载自程序员学长,如果涉嫌侵权,请发送邮件至:contact@modb.pro进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,墨天轮将立刻删除相关内容。






