基本概念
ApplicationContext 中的事件处理是通过 ApplicationEvent 类和 ApplicationListener 接口提供的。如果将实现 ApplicationListener 接口的 bean 部署到上下文中,则每次将 ApplicationEvent 发布到 ApplicationContext 时,都会通知该 bean。本质上,这是标准的观察者设计模式。
事件监听三要素
事件(Event):想要自定义一个事件,我们通常会继承Spring的
ApplicationEvent来声明一个事件,ApplicationEvent的父类是Jdk包下的EventObjeck类,Spring做了进一步的封装,且目前我们也正在用Spring框架,这使得我们的开发变得简单,所以我们继承Spring的ApplicationEvent类即可声明一个事件事件监听(Listener):ApplicationListener 通常使用自定义事件的类型进行参数化。这意味着 onApplicationEvent() 方法可以保持类型安全,避免任何向下转换的需要。默认情况下,事件监听器会同步接收事件,也就是说publishEvent()方法(“事件发布的方法”)会阻塞 发布事件(publishEvent):ApplicationContext提供了publishEvent()方法,每次调用该方法时,会将事件发布到ApplicationContext中,ApplicationContext负责通知事件监听(Listener)
事件样例
自定义事件
@Getter@Setter@ToStringpublic class BaseEvent extends ApplicationEvent {private final Person person;public BaseEvent(Object source, Person person) {super(source);this.person = person;}}
自定义监听
@Componentpublic class MyApplicationEventListener implements ApplicationListener<BaseEvent> {/*** Handle an application event.** @param event the event to respond to*/@Overridepublic void onApplicationEvent(BaseEvent event) {Person person = event.getPerson();System.out.println(person);}}
触发 onApplicationEvent() 方法,发布事件
@Componentpublic class PublishEventService {@Resourceprivate ApplicationContext applicationContext;public void pushNotice() {Person person = new Person();person.setAge(18);person.setName("老王");BaseEvent objectBaseEvent = new BaseEvent(this, person);applicationContext.publishEvent(objectBaseEvent);}}
使用注解实现监听
@Componentpublic class MyApplicationAnnotationEventListener {/*** Handle an application event.** @param event the event to respond to*/@EventListenerpublic void onApplicationEvent(BaseEvent event) {Person person = event.getPerson();System.out.println(person);}}
@EventListener注解提供了 事件类的选择,也就是说,监听方法的形参可以不写,具体如下
@Target({ElementType.METHOD, ElementType.ANNOTATION_TYPE})@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)@Documentedpublic @interface EventListener {/*** Alias for {@link #classes}.*/@AliasFor("classes")Class<?>[] value() default {};/*** The event classes that this listener handles.* <p>If this attribute is specified with a single value, the* annotated method may optionally accept a single parameter.* However, if this attribute is specified with multiple values,* the annotated method must <em>not</em> declare any parameters.*/@AliasFor("value")Class<?>[] classes() default {};}
@Componentpublic class MyApplicationAnnotationEventListener {@EventListener(value = BaseEvent.class)public void handle() {System.err.println("ApplicationContext 发布了事件,当前线程:" + Thread.currentThread().getName());}}
还可以通过使用定义SpEL表达式的注释的condition属性来添加额外的运行时筛选,该注释应该与针对特定事件的方法的实际调用相匹配
@Componentpublic class MyApplicationAnnotationEventListener {/*** Handle an application event.** @param event the event to respond to*/@EventListener(condition = "#event.person.age == 18")public void onApplicationEvent(BaseEvent event) {Person person = event.getPerson();System.err.println(person);}}
异步监听
注:上面的【监听三要素】里提到,publishEvent()方法是阻塞的,若事件多时,同步可能不能满足现有业务,Spring也想到这点了,它为我们提供了异步的监听,如下所示
要想使用异步监听,必须先开启异步,我们只需在Springboot启动类添加@EnablAsync注解即可开启异步监听,监听的方法上添加@Async声明方法为异步方法
@Componentpublic class MyApplicationAnnotationEventListener {/*** Handle an application event.** @param event the event to respond to*/@Async@EventListener(condition = "#event.person.age == 18")public void onApplicationEvent(BaseEvent event) {System.out.println("异步监听,当前线程:" + Thread.currentThread().getName());}@EventListener(value = BaseEvent.class)public void handle() {System.out.println("同步监听,当前线程:" + Thread.currentThread().getName());}}
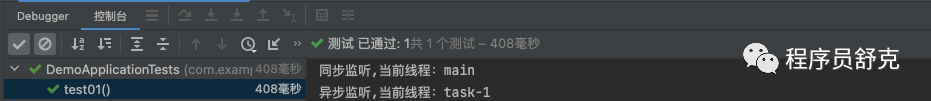
注:观察发现,加了@Async注解的方法为异步方法,当前线程非主线程,注解生效
下一篇文章【Spring事件监听的源码解析】正在准备中...
文章转载自程序员舒克,如果涉嫌侵权,请发送邮件至:contact@modb.pro进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,墨天轮将立刻删除相关内容。






