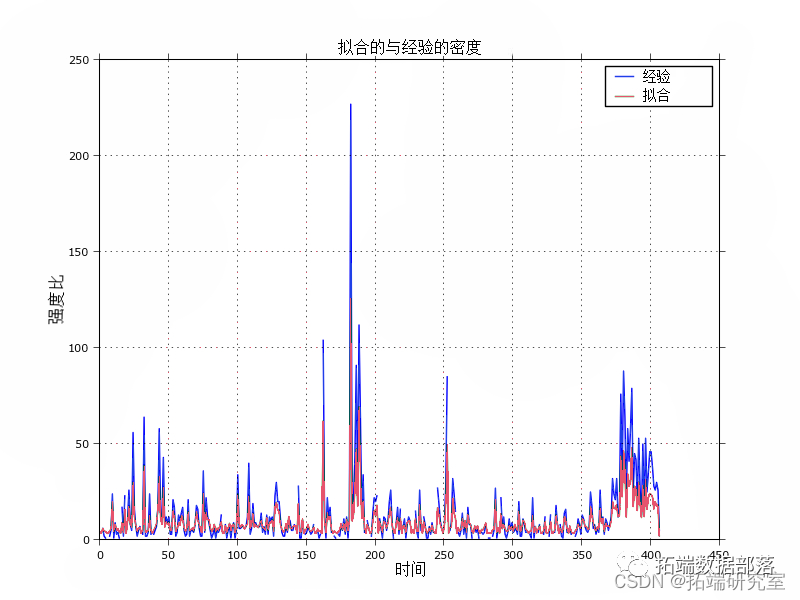
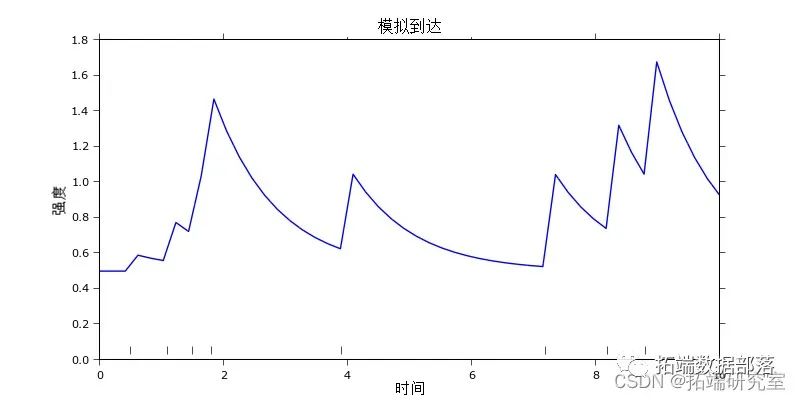
原文链接:http://tecdat.cn/?p=6145
在本文中,我们用SAS进行泊松,零膨胀泊松和有限混合Poisson模型分析(点击文末“阅读原文”获取完整代码数据)。
泊松模型
proc fmm data = tmp1 tech = trureg;
model majordrg = age acadmos minordrg logspend dist = truncpoisson;
probmodel age acadmos minordrg logspend;
/*
Fit Statistics
-2 Log Likelihood 8201.0
AIC (smaller is better) 8221.0
AICC (smaller is better) 8221.0
BIC (smaller is better) 8293.5
Parameter Estimates for 'Truncated Poisson' Model
Standard
Component Effect Estimate Error z Value Pr > |z|
1 Intercept -2.0706 0.3081 -6.72 <.0001
1 AGE 0.01796 0.005482 3.28 0.0011
1 ACADMOS 0.000852 0.000700 1.22 0.2240
1 MINORDRG 0.1739 0.03441 5.05 <.0001
1 LOGSPEND 0.1229 0.04219 2.91 0.0036
Parameter Estimates for Mixing Probabilities
Standard
Effect Estimate Error z Value Pr > |z|
Intercept -4.2309 0.1808 -23.40 <.0001
AGE 0.01694 0.003323 5.10 <.0001
ACADMOS 0.002240 0.000492 4.55 <.0001
MINORDRG 0.7653 0.03842 19.92 <.0001
LOGSPEND 0.2301 0.02683 8.58 <.0001
*/
*** HURDLE POISSON MODEL WITH NLMIXED PROCEDURE ***;
proc nlmixed data = tmp1 tech = trureg maxit = 500;
parms B1_intercept = -4 B1_age = 0 B1_acadmos = 0 B1_minordrg = 0 B1_logspend = 0
B2_intercept = -2 B2_age = 0 B2_acadmos = 0 B2_minordrg = 0 B2_logspend = 0;
eta1 = B1_intercept + B1_age * age + B1_acadmos * acadmos + B1_minordrg * minordrg + B1_logspend * logspend;
exp_eta1 = exp(eta1);
p0 = 1 (1 + exp_eta1);
eta2 = B2_intercept + B2_age * age + B2_acadmos * acadmos + B2_minordrg * minordrg + B2_logspend * logspend;
exp_eta2 = exp(eta2);
if majordrg = 0 then _prob_ = p0;
else _prob_ = (1 - p0) * exp(-exp_eta2) * (exp_eta2 ** majordrg) ((1 - exp(-exp_eta2)) * fact(majordrg));
ll = log(_prob_);
model majordrg ~ general(ll);
run;
/*
Fit Statistics
-2 Log Likelihood 8201.0
AIC (smaller is better) 8221.0
AICC (smaller is better) 8221.0
BIC (smaller is better) 8293.5
Parameter Estimates
Standard
Parameter Estimate Error DF t Value Pr > |t|
B1_intercept -4.2309 0.1808 1E4 -23.40 <.0001
B1_age 0.01694 0.003323 1E4 5.10 <.0001
B1_acadmos 0.002240 0.000492 1E4 4.55 <.0001
B1_minordrg 0.7653 0.03842 1E4 19.92 <.0001
B1_logspend 0.2301 0.02683 1E4 8.58 <.0001
============
B2_intercept -2.0706 0.3081 1E4 -6.72 <.0001
B2_age 0.01796 0.005482 1E4 3.28 0.0011
B2_acadmos 0.000852 0.000700 1E4 1.22 0.2240
B2_minordrg 0.1739 0.03441 1E4 5.05 <.0001
B2_logspend 0.1229 0.04219 1E4 2.91 0.0036
*/
零膨胀泊松模型
*** ZERO-INFLATED POISSON MODEL WITH FMM PROCEDURE ***;
proc fmm data = tmp1 tech = trureg;
model majordrg = age acadmos minordrg logspend dist = poisson;
probmodel age acadmos minordrg logspend;
run;
/*
Fit Statistics
-2 Log Likelihood 8147.9
AIC (smaller is better) 8167.9
AICC (smaller is better) 8167.9
BIC (smaller is better) 8240.5
Parameter Estimates for 'Poisson' Model
Standard
Component Effect Estimate Error z Value Pr > |z|
1 Intercept -2.2780 0.3002 -7.59 <.0001
1 AGE 0.01956 0.006019 3.25 0.0012
1 ACADMOS 0.000249 0.000668 0.37 0.7093
1 MINORDRG 0.1176 0.02711 4.34 <.0001
1 LOGSPEND 0.1644 0.03531 4.66 <.0001
Parameter Estimates for Mixing Probabilities
Standard
Effect Estimate Error z Value Pr > |z|
Intercept -1.9111 0.4170 -4.58 <.0001
AGE -0.00082 0.008406 -0.10 0.9218
ACADMOS 0.002934 0.001085 2.70 0.0068
MINORDRG 1.4424 0.1361 10.59 <.0001
LOGSPEND 0.09562 0.05080 1.88 0.0598
*/
*** ZERO-INFLATED POISSON MODEL WITH NLMIXED PROCEDURE ***;
proc nlmixed data = tmp1 tech = trureg maxit = 500;
parms B1_intercept = -2 B1_age = 0 B1_acadmos = 0 B1_minordrg = 0 B1_logspend = 0
B2_intercept = -2 B2_age = 0 B2_acadmos = 0 B2_minordrg = 0 B2_logspend = 0;
eta1 = B1_intercept + B1_age * age + B1_acadmos * acadmos + B1_minordrg * minordrg + B1_logspend * logspend;
exp_eta1 = exp(eta1);
p0 = 1 (1 + exp_eta1);
eta2 = B2_intercept + B2_age * age + B2_acadmos * acadmos + B2_minordrg * minordrg + B2_logspend * logspend;
exp_eta2 = exp(eta2);
if majordrg = 0 then _prob_ = p0 + (1 - p0) * exp(-exp_eta2);
else _prob_ = (1 - p0) * exp(-exp_eta2) * (exp_eta2 ** majordrg) fact(majordrg);
ll = log(_prob_);
model majordrg ~ general(ll);
run;
/*
Fit Statistics
-2 Log Likelihood 8147.9
AIC (smaller is better) 8167.9
AICC (smaller is better) 8167.9
BIC (smaller is better) 8240.5
Parameter Estimates
Standard
Parameter Estimate Error DF t Value Pr > |t|
B1_intercept -1.9111 0.4170 1E4 -4.58 <.0001
B1_age -0.00082 0.008406 1E4 -0.10 0.9219
B1_acadmos 0.002934 0.001085 1E4 2.70 0.0068
B1_minordrg 1.4424 0.1361 1E4 10.59 <.0001
B1_logspend 0.09562 0.05080 1E4 1.88 0.0598
============
B2_intercept -2.2780 0.3002 1E4 -7.59 <.0001
B2_age 0.01956 0.006019 1E4 3.25 0.0012
B2_acadmos 0.000249 0.000668 1E4 0.37 0.7093
B2_minordrg 0.1176 0.02711 1E4 4.34 <.0001
B2_logspend 0.1644 0.03531 1E4 4.66 <.0001
*/
点击标题查阅往期内容

R语言和Python用泊松过程扩展:霍克斯过程Hawkes Processes分析比特币交易数据订单到达自激过程时间序列

左右滑动查看更多

两类有限混合Poisson模型
*** TWO-CLASS FINITE MIXTURE POISSON MODEL WITH FMM PROCEDURE ***;
proc fmm data = tmp1 tech = trureg;
model majordrg = age acadmos minordrg logspend dist = poisson k = 2;
run;
/*
Fit Statistics
-2 Log Likelihood 8136.8
AIC (smaller is better) 8166.8
AICC (smaller is better) 8166.9
BIC (smaller is better) 8275.7
Parameter Estimates for 'Poisson' Model
Standard
Component Effect Estimate Error z Value Pr > |z|
1 Intercept -2.4449 0.3497 -6.99 <.0001
1 AGE 0.02214 0.006628 3.34 0.0008
1 ACADMOS 0.000529 0.000770 0.69 0.4920
1 MINORDRG 0.05054 0.04015 1.26 0.2081
1 LOGSPEND 0.2140 0.04127 5.18 <.0001
2 Intercept -8.0935 1.5915 -5.09 <.0001
2 AGE 0.01150 0.01294 0.89 0.3742
2 ACADMOS 0.004567 0.002055 2.22 0.0263
2 MINORDRG 0.2638 0.6770 0.39 0.6968
2 LOGSPEND 0.6826 0.2203 3.10 0.0019
Parameter Estimates for Mixing Probabilities
Standard
Effect Estimate Error z Value Pr > |z|
Intercept -1.4275 0.5278 -2.70 0.0068
AGE -0.00277 0.01011 -0.27 0.7844
ACADMOS 0.001614 0.001440 1.12 0.2623
MINORDRG 1.5865 0.1791 8.86 <.0001
LOGSPEND -0.06949 0.07436 -0.93 0.3501
*/
*** TWO-CLASS FINITE MIXTURE POISSON MODEL WITH NLMIXED PROCEDURE ***;
proc nlmixed data = tmp1 tech = trureg maxit = 500;
B2_intercept = -8 B2_age = 0 B2_acadmos = 0 B2_minordrg = 0 B2_logspend = 0
eta1 = B1_intercept + B1_age * age + B1_acadmos * acadmos + B1_minordrg * minordrg + B1_logspend * logspend;
exp_eta1 = exp(eta1);
prob1 = exp(-exp_eta1) * exp_eta1 ** majordrg fact(majordrg);
eta2 = B2_intercept + B2_age * age + B2_acadmos * acadmos + B2_minordrg * minordrg + B2_logspend * logspend;
exp_eta2 = exp(eta2);
prob2 = exp(-exp_eta2) * exp_eta2 ** majordrg fact(majordrg);
eta3 = B3_intercept + B3_age * age + B3_acadmos * acadmos + B3_minordrg * minordrg + B3_logspend * logspend;
exp_eta3 = exp(eta3);
p = exp_eta3 (1 + exp_eta3);
_prob_ = p * prob1 + (1 - p) * prob2;
ll = log(_prob_);
model majordrg ~ general(ll);
run;
/*
Fit Statistics
-2 Log Likelihood 8136.8
AIC (smaller is better) 8166.8
AICC (smaller is better) 8166.9
BIC (smaller is better) 8275.7
Parameter Estimates
Standard
Parameter Estimate Error DF t Value Pr > |t|
B1_intercept -2.4449 0.3497 1E4 -6.99 <.0001
B1_age 0.02214 0.006628 1E4 3.34 0.0008
B1_acadmos 0.000529 0.000770 1E4 0.69 0.4920
B1_minordrg 0.05054 0.04015 1E4 1.26 0.2081
B1_logspend 0.2140 0.04127 1E4 5.18 <.0001
============
B2_intercept -8.0935 1.5916 1E4 -5.09 <.0001
B2_age 0.01150 0.01294 1E4 0.89 0.3742
B2_acadmos 0.004567 0.002055 1E4 2.22 0.0263
B2_minordrg 0.2638 0.6770 1E4 0.39 0.6968
B2_logspend 0.6826 0.2203 1E4 3.10 0.0020
============
B3_intercept -1.4275 0.5278 1E4 -2.70 0.0068
B3_age -0.00277 0.01011 1E4 -0.27 0.7844
B3_acadmos 0.001614 0.001440 1E4 1.12 0.2623
B3_minordrg 1.5865 0.1791 1E4 8.86 <.0001
B3_logspend -0.06949 0.07436 1E4 -0.93 0.3501
*/

点击文末“阅读原文”
获取全文完整代码数据资料。
本文选自《用SAS进行泊松,零膨胀泊松和有限混合Poisson模型分析》。
点击标题查阅往期内容


文章转载自拓端数据部落,如果涉嫌侵权,请发送邮件至:contact@modb.pro进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,墨天轮将立刻删除相关内容。