
一、问题定义
在有向图G=(V,E)上,对任两个结点u,v∈V,若存在从u到v的路径,那么称v是由u可达的,记作u→v。
给定一张有向图G=(V,E),一对结点u,v∈V,可达性问题即为判定是否有u→v的判定问题。

二、基于索引的方法


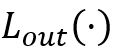 与
与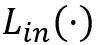 ,使得结点u可达结点v当且仅当
,使得结点u可达结点v当且仅当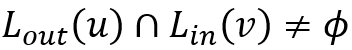 . 在这对结点集合中、用于连接可达结点对的中介结点称为hop. 直观上,我们希望找到尽量少的hop来覆盖所有的可达点对。已有理论工作证明在具有某些结构特征的图上最小两跳标签的总空间上限为
. 在这对结点集合中、用于连接可达结点对的中介结点称为hop. 直观上,我们希望找到尽量少的hop来覆盖所有的可达点对。已有理论工作证明在具有某些结构特征的图上最小两跳标签的总空间上限为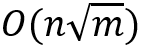 , 其中n为总结点数,m为总边数;并猜想在任意图上两跳标签仍满足此性质。
, 其中n为总结点数,m为总边数;并猜想在任意图上两跳标签仍满足此性质。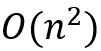 )的贪心算法,可得出空间占用在理论最小值的
)的贪心算法,可得出空间占用在理论最小值的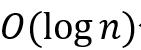 倍之内的两跳标签。这个算法首先需要计算和暂存图的传递闭包,然后对每对可达结点维护一个最大堆,以每个hop能覆盖的它们之间的近似路径比例为键值,每次取堆顶元素放入标签中。
倍之内的两跳标签。这个算法首先需要计算和暂存图的传递闭包,然后对每对可达结点维护一个最大堆,以每个hop能覆盖的它们之间的近似路径比例为键值,每次取堆顶元素放入标签中。

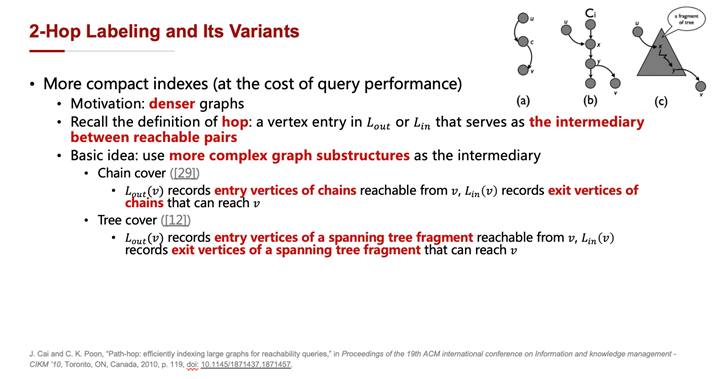
三、不基于索引的方法
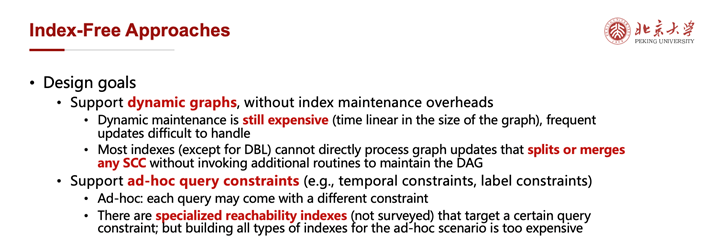
不基于索引的方法主要的设计目标有二:一是基于目前的可达性索引更新效率仍然较低的现实,希望通过去除索引为动态图提供更优的支持;二是基于建立所有可能出现的约束所对应的特化可达性索引(前文未介绍)时间与空间开销过大的现实,希望适应随机出现的查询约束的需求。

四、总结
本文给出了图上可达性的问题定义,并以是否基于索引为分类标准,总结了迄今为止求解图上可达性问题方法的主要技术路线、简要介绍了每种技术对应的重要工作。
参考文献
[1] A. Anagnostopoulos, R. Kumar, M. Mahdian, E.Upfal, and F. Vandin, “Algorithms on evolving graphs,” in Proceedings of the 3rd Innovations in Theoretical ComputerScience Conference on - ITCS ’12, Cambridge, Massachusetts, 2012, pp. 149–160, doi: 10.1145/2090236.2090249.
[2] A. D. Zhu, W. Lin, S. Wang, and X. Xiao, “Reachability queries on large dynamic graphs: a totalorder approach,” in Proceedings ofthe 2014 ACM SIGMOD International Conference on Management of Data,Snowbird Utah USA, Jun. 2014, pp. 1323–1334, doi: 10.1145/2588555.2612181.
[3] E. Cohen, E. Halperin, H. Kaplan, and U. Zwick, “Reachability and Distance Queries via 2-Hop Labels,” SIAM J. Comput., vol. 32, no. 5, pp. 1338–1355, Jan. 2003, doi: 10.1137/S0097539702403098.
[4] Haixun Wang, Hao He, Jun Yang, P. S. Yu, and J. X.Yu, “Dual Labeling:Answering Graph Reachability Queries in Constant Time,” in 22nd International Conference on DataEngineering (ICDE’06), Atlanta, GA, USA, 2006, pp. 75–75, doi: 10.1109/ICDE.2006.53.
[5] H. He, H. Wang, J. Yang, and P. S. Yu, “Compact reachability labeling for graph-structureddata,” in Proceedings ofthe 14th ACM international conference on Information and knowledge management -CIKM ’05, Bremen, Germany,2005, p. 594, doi: 10.1145/1099554.1099708.
[6] H. V. Jagadish, “A compression technique to materialize transitiveclosure,” ACM Trans.Database Syst., vol. 15, no. 4, pp. 558–598, Dec. 1990, doi: 10.1145/99935.99944.
[7] H. Wei, J. X. Yu, C. Lu, and R. Jin, “Reachability querying: an independent permutationlabeling approach,” Proc. VLDB Endow.,vol. 7, no. 12, pp. 1191–1202, Aug. 2014, doi: 10.14778/2732977.2732992.
[8] H. Wei, J. X. Yu, C. Lu, and R. Jin, “Reachability querying: an independent permutationlabeling approach,” The VLDB Journal,vol. 27, no. 1, pp. 1–26, Feb. 2018, doi: 10.1007/s00778-017-0468-3.
[9] H. Yildirim, V. Chaoji, and M. J. Zaki, “DAGGER: A Scalable Index for Reachability Queries inLarge Dynamic Graphs,” arXiv:1301.0977 [cs], Jan. 2013, Accessed: Mar. 20, 2021.[Online]. Available: http://arxiv.org/abs/1301.0977.
[10] H. Yıldırım, V. Chaoji, and M. J. Zaki, “GRAIL: a scalable index for reachability queries invery large graphs,” The VLDB Journal,vol. 21, no. 4, pp. 509–534, Aug. 2012, doi: 10.1007/s00778-011-0256-4.
[11] H. Yildirim, V. Chaoji, and M. J.Zaki, “GRAIL: scalable reachability index for large graphs,” Proc. VLDBEndow., vol. 3, no. 1–2, pp. 276–284, Sep. 2010, doi: 10.14778/1920841.1920879.
[12] J. Cai and C. K. Poon, “Path-hop:efficiently indexing large graphs for reachability queries,” in Proceedingsof the 19th ACM international conference on Information and knowledgemanagement - CIKM ’10, Toronto, ON, Canada, 2010, p. 119, doi: 10.1145/1871437.1871457.
[13] J. Cheng, J. X. Yu, X. Lin, H. Wang,and P. S. Yu, “Fast Computation of Reachability Labeling for Large Graphs,” in Advancesin Database Technology - EDBT 2006, vol. 3896, Y. Ioannidis, M. H. Scholl,J. W. Schmidt, F. Matthes, M. Hatzopoulos, K. Boehm, A. Kemper, T. Grust, andC. Boehm, Eds. Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer Berlin Heidelberg, 2006, pp.961–979.
[14] J. Cheng, J. X. Yu, X. Lin, H. Wang,and P. S. Yu, “Fast computing reachability labelings for large graphs with highcompression rate,” in Proceedings of the 11th international conference onExtending database technology Advances in database technology - EDBT ’08,Nantes, France, 2008, p. 193, doi: 10.1145/1353343.1353370.
[15] J. Cheng, S. Huang, H. Wu, and A.W.-C. Fu, “TF-Label: a topological-folding labeling scheme for reachabilityquerying in a large graph,” in Proceedings of the 2013 internationalconference on Management of data - SIGMOD ’13, New York, New York, USA,2013, p. 193, doi: 10.1145/2463676.2465286.
[16] J. Su, Q. Zhu, H. Wei, and J. X. Yu,“Reachability Querying: Can It Be Even Faster?,” IEEE Trans. Knowl. DataEng., vol. 29, no. 3, pp. 683–697, Mar. 2017, doi: 10.1109/TKDE.2016.2631160.
[17] L. Chen, A. Gupta, and M. E. Kurul,“Stack-based Algorithms for Pattern Matching on DAGs,” p. 12, 2005.
[18] L. Li, W. Hua, and X. Zhou, “HD-GDD:high dimensional graph dominance drawing approach for reachability query,” WorldWide Web, vol. 20, no. 4, pp. 677–696, Jul. 2017, doi: 10.1007/s11280-016-0407-z.
[19] L. Roditty and U. Zwick, “ImprovedDynamic Reachability Algorithms for Directed Graphs,” SIAM J. Comput.,vol. 37, no. 5, pp. 1455–1471, Jan. 2008, doi: 10.1137/060650271.
[20] L. Zhu, B. Choi, B. He, J. X. Yu, andW. K. Ng, “A Uniform Framework for Ad-Hoc Indexes to Answer ReachabilityQueries on Large Graphs,” in Database Systems for Advanced Applications,vol. 5463, X. Zhou, H. Yokota, K. Deng, and Q. Liu, Eds. Berlin, Heidelberg:Springer Berlin Heidelberg, 2009, pp. 138–152.
[21] M. Starnini, A. Baronchelli, A.Barrat, and R. Pastor-Satorras, “Random walks on temporal networks,” Phys.Rev. E, vol. 85, no. 5, p. 056115, May 2012, doi: 10.1103/PhysRevE.85.056115.
[22] N. Sengupta, A. Bagchi, M. Ramanath,and S. Bedathur, “ARROW: Approximating Reachability Using Random Walks OverWeb-Scale Graphs,” in 2019 IEEE 35th International Conference on DataEngineering (ICDE), Macao, Macao, Apr. 2019, pp. 470–481, doi: 10.1109/ICDE.2019.00049.
[23] Q. Lyu, Y. Li, B. He, and B. Gong,“DBL: Efficient Reachability Queries on Dynamic Graphs (Complete Version),”arXiv:2101.09441 [cs], Jan. 2021, Accessed: Mar. 24, 2021. [Online]. Available:http://arxiv.org/abs/2101.09441.
[24] R. Agrawal, A. Borgida, and H. V.Jagadish, “Efficient management of transitive relationships in large data andknowledge bases,” in Proceedings of the 1989 ACM SIGMOD internationalconference on Management of data - SIGMOD ’89, Portland, Oregon, UnitedStates, 1989, pp. 253–262, doi: 10.1145/67544.66950.
[25] R. Jin and G. Wang, “Simple, fast, andscalable reachability oracle,” Proc. VLDB Endow., vol. 6, no. 14, pp.1978–1989, Sep. 2013, doi: 10.14778/2556549.2556578.
[26] R. Jin, N. Ruan, S. Dey, and J. Y. Xu,“SCARAB: scaling reachability computation on large graphs,” in Proceedingsof the 2012 international conference on Management of Data - SIGMOD ’12,Scottsdale, Arizona, USA, 2012, p. 169, doi: 10.1145/2213836.2213856.
[27] R. Jin, N. Ruan, Y. Xiang, and H. Wang,“Path-tree: An efficient reachability indexing scheme for large directedgraphs,” ACM Trans. Database Syst., vol. 36, no. 1, pp. 1–44, Mar. 2011,doi: 10.1145/1929934.1929941.
[28] R. Jin, Y. Xiang, N. Ruan, and H.Wang, “Efficiently answering reachability queries on very large directedgraphs,” in Proceedings of the 2008 ACM SIGMOD international conference onManagement of data - SIGMOD ’08, Vancouver, Canada, 2008, p. 595, doi: 10.1145/1376616.1376677.
[29] R. Jin, Y. Xiang, N. Ruan, and D.Fuhry, “3-HOP: a high-compression indexing scheme for reachability query,” in Proceedingsof the 35th SIGMOD international conference on Management of data - SIGMOD ’09,Providence, Rhode Island, USA, 2009, p. 813, doi: 10.1145/1559845.1559930.
[30] R. R. Veloso, L. Cerf, W. M. Junior,and M. J. Zaki, “Reachability Queries in Very Large Graphs: A Fast RefinedOnline Search Approach.” OpenProceedings.org, 2014, doi: 10.5441/002/EDBT.2014.46.
[31] R. Schenkel, A. Theobald, and G.Weikum, “Efficient Creation and Incremental Maintenance of the HOPI Index forComplex XML Document Collections,” in 21st International Conference on DataEngineering (ICDE’05), Tokyo, Japan, 2005, pp. 360–371, doi: 10.1109/ICDE.2005.57.
[32] R. Schenkel, A. Theobald, and G.Weikum, “HOPI: An Efficient Connection Index for Complex XML DocumentCollections,” in Advances in Database Technology - EDBT 2004, vol. 2992,E. Bertino, S. Christodoulakis, D. Plexousakis, V. Christophides, M.Koubarakis, K. Böhm, and E. Ferrari, Eds. Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer BerlinHeidelberg, 2004, pp. 237–255.
[33] S. J. van Schaik and O. de Moor, “Amemory efficient reachability data structure through bit vector compression,”in Proceedings of the 2011 international conference on Management of data -SIGMOD ’11, Athens, Greece, 2011, p. 913, doi: 10.1145/1989323.1989419.
[34] S. Seufert, A. Anand, S. Bedathur, andG. Weikum, “FERRARI: Flexible and efficient reachability range assignment forgraph indexing,” in 2013 IEEE 29th International Conference on DataEngineering (ICDE), Brisbane, QLD, Apr. 2013, pp. 1009–1020, doi: 10.1109/ICDE.2013.6544893.
[35] S. Trißl and U. Leser, “Fast andpractical indexing and querying of very large graphs,” in Proceedings of the2007 ACM SIGMOD international conference on Management of data - SIGMOD ’07,Beijing, China, 2007, p. 845, doi: 10.1145/1247480.1247573.
[36] S. Zhou, P. Yuan, L. Liu, and H. Jin,“MGTag: a Multi-Dimensional Graph Labeling Scheme for Fast ReachabilityQueries,” in 2018 IEEE 34th International Conference on Data Engineering(ICDE), Paris, Apr. 2018, pp. 1372–1375, doi: 10.1109/ICDE.2018.00153.
[37] U. Feige, “A fast randomized LOGSPACEalgorithm for graph connectivity,” Theoretical Computer Science, vol. 169,no. 2, pp. 147–160, Dec. 1996, doi: 10.1016/S0304-3975(96)00118-1.
[38] Y. Chen and Y. Chen, “An EfficientAlgorithm for Answering Graph Reachability Queries,” in 2008 IEEE 24thInternational Conference on Data Engineering, Cancun, Mexico, Apr. 2008,pp. 893–902, doi: 10.1109/ICDE.2008.4497498.
[39] Y. Yano, T. Akiba, Y. Iwata, and Y.Yoshida, “Fast and scalable reachability queries on graphs by pruned labelingwith landmarks and paths,” in Proceedings of the 22nd ACM internationalconference on Conference on information & knowledge management - CIKM ’13,San Francisco, California, USA, 2013, pp. 1601–1606, doi: 10.1145/2505515.2505724.
 相 关 链 接
相 关 链 接







