
本文首发于Ressmix个人站点:https://www.tpvlog.com
本章,我将在上一章的项目基础上,实现库存服务的缓存与数据库的双写一致性。在开始之前,我们先来回顾下什么是双写一致性。在《系统整体架构》一章中,我画过下面这一张图:
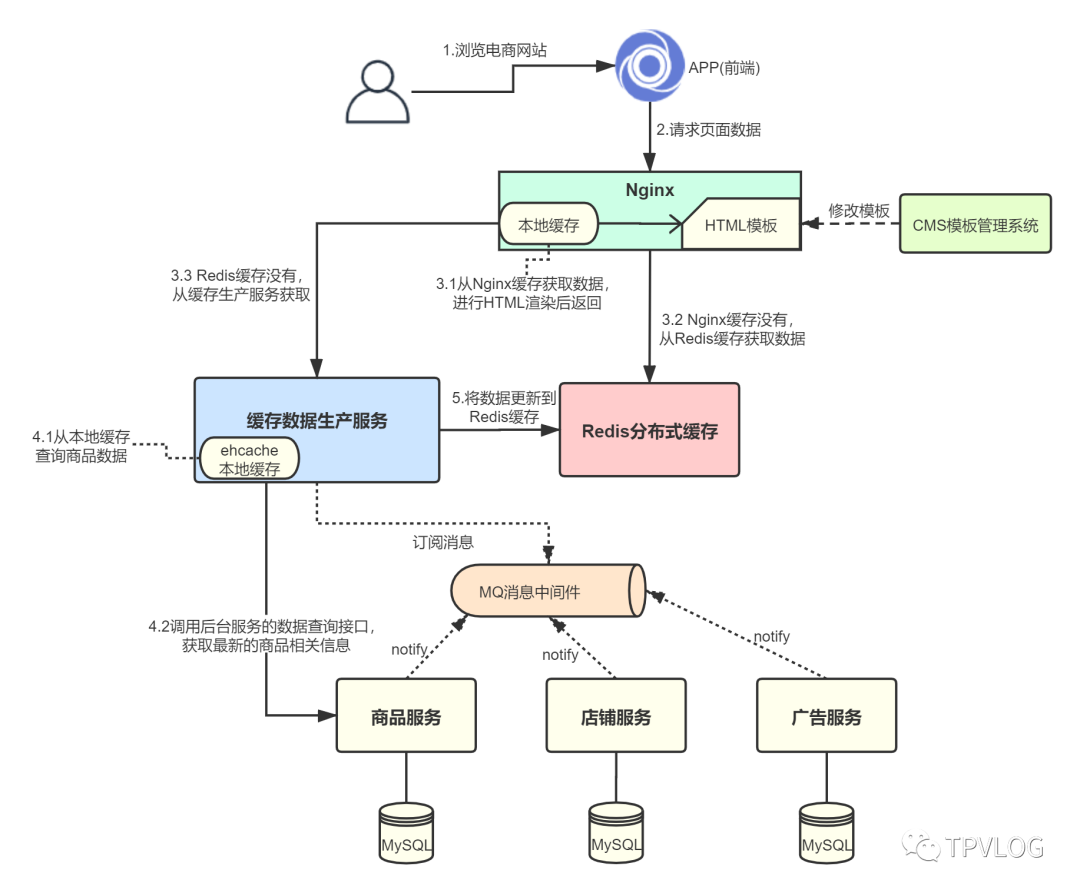
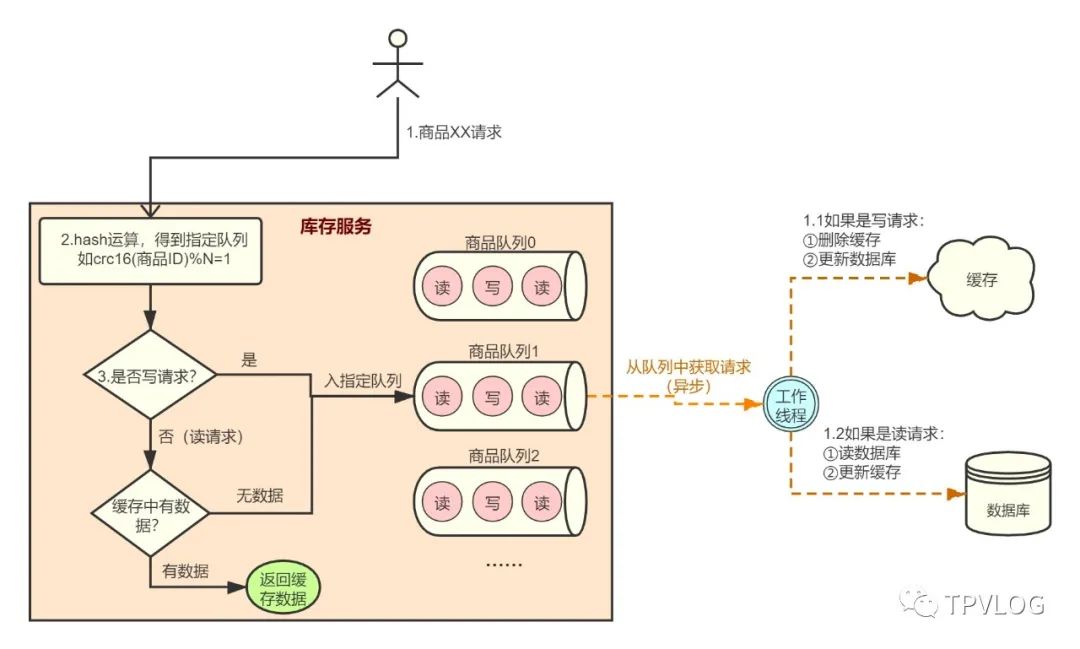
库存属于商品信息中对实时性要求非常高的数据,我画在了图的最右侧。库存服务的大体实现逻辑是:
当请求查询商品库存时,如果Redis缓存中不存在,则从数据库查询,然后写入Redis缓存,最后返回客户端;
当请求修改商品库存时,采用Cache Aside模式,先删除缓存,然后更新数据库。
采用Cache Aside模式时,存在高并发场景下的缓存一致性问题,读者可以先去看看我写的这篇文章——《分布式理论之高性能:分布式缓存》,然后回头来看本章,我将在本章中通过代码实现这种缓存一致性方案。
实现商品库存的缓存与数据库双写一致性,几个核心要点如下:
用内存队列保存同一商品的库存读写请求,每个处理线程关联一个内存队列;
对读请求和写请求进行封装,并提供统一的处理接口;
读请求去重优化,也就是说如果队列中已经有读请求,则当前读请求hang一会儿;
一、内存队列
首先,库存服务应用启动后,需要初始化一个线程池,线程池中的每一个线程去监听一个自己的内存队列。后续会从这个内存队列里消费读请求和写请求:
1.1 线程池
我这边直接使用J.U.C中的工具类进行内存队列的设计编码,对J.U.C不了解的童鞋可以先去学习下我的《透彻理解Java并发编程系列》。另外,如果要追求更高的性能,读者也可以自行尝试使用Disruptor(https://github.com/LMAX-Exchange/disruptor)这个高性能队列。
首先,我们创建10个固定线程数的线程池,每个工作线程负责监听一个内存队列:
1 /**
2 * 请求处理线程池,线程池中的每个线程监听一个任务
3 *
4 * @author ressmix
5 */
6@Component
7public class RequestProcessorThreadPool {
8
9 private ExecutorService executor;
10
11 private final int size = 10;
12
13 @PostConstruct
14 private void init() {
15 // 10个线程的线程池
16 executor = new ThreadPoolExecutor(size, size, 0L, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS,
17 new ArrayBlockingQueue<Runnable>(1024), Executors.defaultThreadFactory());
18
19 // 提交10个任务
20 RequestQueue requestQueue = RequestQueue.getInstance();
21 for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
22 // requestQueue内部保存着队列
23 ArrayBlockingQueue<Request> queue = new ArrayBlockingQueue<Request>(128);
24 requestQueue.addQueue(queue);
25
26 // 提交任务,每个任务关联一个队列
27 executor.submit(new RequestProcessorTask(queue));
28 }
29 }
30}
1.2 请求队列
请求队列为单例类,内部包含ArrayBlockingQueue列表,也就是我们的内存队列:
1 /**
2 * 请求队列,单例类
3 *
4 * @author ressmix
5 */
6public class RequestQueue {
7
8 private static final RequestQueue instance = new RequestQueue();
9
10 /**
11 * 内存队列
12 */
13 private final List<ArrayBlockingQueue<Request>> queues = new ArrayList<ArrayBlockingQueue<Request>>();
14
15 private RequestQueue() {
16 }
17
18 public static RequestQueue getInstance() {
19 return instance;
20 }
21
22 /**
23 * 添加一个内存队列
24 *
25 * @param queue
26 */
27 public void addQueue(ArrayBlockingQueue<Request> queue) {
28 this.queues.add(queue);
29 }
30
31 /**
32 * 根据索引,获取一个内存队列
33 */
34 public ArrayBlockingQueue<Request> getQueue(int idx) {
35 return this.queues.get(idx);
36 }
37
38 /**
39 * 内存队列大小
40 */
41 public int size() {
42 return queues.size();
43 }
44}
1.3 请求处理任务
请求处理任务,会与一个内存队列绑定,并被提交到线程池中,然后由线程池中的一个工作线程监听执行:
1/**
2 * 请求处理任务
3 * @author ressmix
4 */
5public class RequestProcessorTask implements Callable<Boolean> {
6
7 private final ArrayBlockingQueue<Request> queue;
8
9 public RequestProcessorTask(ArrayBlockingQueue<Request> queue) {
10 this.queue = queue;
11 }
12
13 @Override
14 public Boolean call() throws Exception {
15 while (true) {
16 try {
17 // 获取一个请求
18 Request request = queue.take();
19 // 执行
20 request.process();
21 } catch (Exception ex) {
22 ex.printStackTrace();
23 }
24 }
25 }
26}
生产环境,我们也可以使用分布式消息中间件来实现,将同一个商品的读写请求全部发送到一个队列(或主题)中,然后有一个消费者订阅该队列(主题),线性处理每一个请求。
之所以采用内存队列,另外一个考量点是内存队列比分布式MQ的性能更高,因为不涉及服务间的调用以及消息持久化。但也要注意,分布式环境下一个好的内存队列的设计是比较复杂的,需要综合考虑性能、线程安全、异常处理等方方面面的设计,特别是生产环境会部署多个对等服务,所以使用内存队列,必须保证对同一个商品的请求,路由到同一个服务节点。
二、请求封装
接着,我们需要封装两种类型的请求:商品库存查询请求和商品库存更新请求。先定义一个Request
接口:
1public interface Request {
2 void process();
3 Long getProductId();
4}
2.1 查询请求
查询请求主要做两件事:
从数据库查询商品库存;
更新Redis缓存中的商品库存。
1/**
2 * 商户库存查询请求:
3 * 1.从数据库查询商品库存
4 * 2.更新缓存
5 */
6public class ProductInventoryQueryRequest implements Request {
7
8 /**
9 * 商品库存信息
10 */
11 private ProductInventory productInventory;
12
13 /**
14 * 商品库存服务
15 */
16 private ProductInventoryService productInventoryService;
17
18 public ProductInventoryQueryRequest(ProductInventory productInventory, ProductInventoryService productInventoryService) {
19 this.productInventory = productInventory;
20 this.productInventoryService = productInventoryService;
21 }
22
23 @Override
24 public void process() {
25 // 1.从数据库查询
26 ProductInventory productFromDB = productInventoryService.queryProductInventory(productInventory.getProductId());
27 if (productFromDB == null) {
28 return;
29 }
30 // 2.更新缓存
31 productInventoryService.setCachedProductInventory(productFromDB);
32 }
33
34 @Override
35 public Long getProductId() {
36 return this.productInventory.getProductId();
37 }
38}
2.2 更新请求
更新请求主要做两件事:
删除缓存中的商品库存;
更新商品库存至数据库。
1/**
2 * 商户库存更新请求:
3 * 1.删除缓存
4 * 2.更新数据库
5 */
6public class ProductInventoryUpdateRequest implements Request {
7
8 /**
9 * 商品库存信息
10 */
11 private ProductInventory productInventory;
12
13 /**
14 * 商品库存服务
15 */
16 private ProductInventoryService productInventoryService;
17
18 public ProductInventoryUpdateRequest(ProductInventory productInventory, ProductInventoryService productInventoryService) {
19 this.productInventory = productInventory;
20 this.productInventoryService = productInventoryService;
21 }
22
23 @Override
24 public void process() {
25 // 1.删除缓存
26 boolean result = productInventoryService.removeCachedProductInventory(productInventory);
27
28 // 2.更新数据库
29 if (result) {
30 productInventoryService.updateProductInventory(productInventory);
31 }
32 }
33
34 @Override
35 public Long getProductId() {
36 return this.productInventory.getProductId();
37 }
38}
2.3 库存Bean
1/**
2 * 商品库存Bean
3 */
4public class ProductInventory {
5
6 private Long id;
7
8 /**
9 * 商品id
10 */
11 private Long productId;
12 /**
13 * 库存数量
14 */
15 private Long inventoryCnt;
16
17 public ProductInventory() {
18 }
19
20 public ProductInventory(Long productId, Long inventoryCnt) {
21 this.productId = productId;
22 this.inventoryCnt = inventoryCnt;
23 }
24}
三、服务实现
接着,我们来看下库存服务和缓存服务的实现,主要就是针对数据库和Redis的增删改查操作。
3.1 库存服务
1/**
2 * 商品库存服务接口
3 *
4 * @author ressmix
5 */
6public interface ProductInventoryService {
7
8 /**
9 * 根据商品id,查询数据库中的商品库存
10 *
11 * @param productId 商品id
12 * @return 商品库存
13 */
14 ProductInventory queryProductInventory(Long productId);
15
16 /**
17 * 更新数据库中的商品库存
18 *
19 * @param productInventory 商品库存
20 */
21 int updateProductInventory(ProductInventory productInventory);
22
23 /**
24 * 根据商品id,从缓存查询商品库存
25 *
26 * @param productId 商品id
27 * @return 商品库存
28 */
29 ProductInventory queryCachedProductInventory(Long productId);
30
31 /**
32 * 设置缓存中的商品库存
33 *
34 * @param productInventory 商品库存
35 */
36 Boolean setCachedProductInventory(ProductInventory productInventory);
37
38 /**
39 * 删除商品库存缓存
40 *
41 * @param productInventory 商品库存
42 */
43 Boolean removeCachedProductInventory(ProductInventory productInventory);
44}
45
46
47/**
48 * 商品库存服务实现
49 *
50 * @author ressmix
51 */
52@Service("productInventoryService")
53public class ProductInventoryServiceImpl implements ProductInventoryService {
54
55 private static final Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(ProductInventoryServiceImpl.class);
56
57 @Autowired
58 private RedisDao redisDao;
59
60 @Autowired
61 private ProductInventoryMapper productInventoryMapper;
62
63 @Override
64 public ProductInventory queryProductInventory(Long productId) {
65 ProductInventory result = productInventoryMapper.queryProductInventory(productId);
66 if (result == null || result.getId() == null) {
67 return null;
68 } else {
69 return result;
70 }
71 }
72
73 @Override
74 public int updateProductInventory(ProductInventory productInventory) {
75 return productInventoryMapper.updateProductInventory(productInventory);
76 }
77
78 @Override
79 public ProductInventory queryCachedProductInventory(Long productId) {
80 String key = "product:inventory:" + productId;
81 String result = redisDao.get(key);
82 if (StringUtils.isBlank(result)) {
83 return null;
84 }
85 Long inventoryCnt = -1L;
86 try {
87 inventoryCnt = Long.valueOf(result);
88 } catch (Exception ex) {
89 log.error("库存数据格式错误:{}", result, ex);
90 return null;
91 }
92 return new ProductInventory(productId, inventoryCnt);
93 }
94
95 @Override
96 public Boolean setCachedProductInventory(ProductInventory productInventory) {
97 try {
98 String key = "product:inventory:" + productInventory.getProductId();
99 redisDao.set(key,String.valueOf(productInventory.getInventoryCnt()));
100 return true;
101 } catch (Exception ex) {
102 log.error("设置商品库存缓存失败:{}", productInventory, ex);
103 }
104 return false;
105 }
106
107 @Override
108 public Boolean removeCachedProductInventory(ProductInventory productInventory) {
109 try {
110 String key = "product:inventory:" + productInventory.getProductId();
111 redisDao.del(key);
112 return true;
113 } catch (Exception ex) {
114 log.error("删除商品库存缓存失败:{}", productInventory, ex);
115 }
116 return false;
117 }
118}
3.2 缓存服务
1public interface RedisDao {
2 <T> void set(String key, T value);
3
4 <T> void set(String key, T value, long expire, TimeUnit timeUnit);
5
6 <T> T get(String key);
7
8 boolean expire(String key, long expire);
9
10 void del(String key);
11
12 void delBatch(Set<String> keys);
13
14 void delBatch(String keyPrefix);
15
16 <T> void setList(String key, List<T> list);
17
18 <T> void setList(String key, List<T> list, long expire, TimeUnit timeUnit);
19
20 <T> List<T> getList(String key, Class<T> clz);
21
22 boolean hasKey(String key);
23
24 long getExpire(String key);
25
26 Set<String> keySet(String keyPrefix);
27
28}
四、路由服务
我们需要一个路由服务对不同类型的请求进行路由,以及封装一些Cacha Aside模式的优化操作。
1/**
2 * 商品路由服务
3 *
4 * @author ressmix
5 */
6@Service("requestAsyncProcessorService")
7public class RequestAsyncProcessorServiceImpl implements RequestAsyncProcessorService {
8 private static final Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(RequestAsyncProcessorServiceImpl.class);
9
10 @Override
11 public void process(Request request) {
12 try {
13 Long productId = request.getProductId();
14 ArrayBlockingQueue<Request> queue = getRoutingQueue(productId);
15 queue.put(request);
16 } catch (Exception ex) {
17 log.error("处理异步请求失败:{}", request, ex);
18 }
19 }
20
21 /**
22 * 获取路由到的内存队列
23 *
24 * @param productId 商品id
25 * @return 内存队列
26 */
27 private ArrayBlockingQueue<Request> getRoutingQueue(Long productId) {
28 RequestQueue requestQueue = RequestQueue.getInstance();
29
30 // 获取productId的hash值
31 int hash = String.valueOf(productId).hashCode();
32 hash = hash ^ (hash >>> 16);
33
34 // 获取队列
35 int index = (requestQueue.size() - 1) & hash;
36 return requestQueue.getQueue(index);
37 }
38}
最后,来看下Controller中的请求封装处理。这里需要注意的是库存查询接口:首先需要把查询请求入队,然后再通过轮询的方式从缓存查,查不到再从数据库查询返回结果。后面我们需要对第一步“入队列”进行优化,避免每次读请求都进入队列:
1@Controller
2public class InventoryController {
3
4 private static final Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(InventoryController.class);
5
6 @Autowired
7 private ProductInventoryService inventoryService;
8
9 @Autowired
10 private RequestAsyncProcessorService requestAsyncProcessorService;
11
12 /**
13 * 查询商品库存
14 * @param productId
15 * @return
16 */
17 @RequestMapping("/getInventory/{productId}")
18 @ResponseBody
19 public ProductInventory getInventory(@PathVariable("productId") Long productId) {
20 ProductInventory result = null;
21 try {
22
23 // 1.入队列,异步处理查询请求
24 Request request = new ProductInventoryQueryRequest(new ProductInventory(productId, -1L), inventoryService);
25 requestAsyncProcessorService.process(request);
26
27 // 2.hang一会儿,尝试从缓存中查询
28 long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
29 long endTime = startTime;
30 while (endTime - startTime < 120L) {
31 result = inventoryService.queryCachedProductInventory(productId);
32 if (result == null) {
33 // 等待20毫秒
34 LockSupport.parkNanos(20 * 1000 * 1000L);
35 endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
36 } else {
37 return result;
38 }
39 }
40
41 // 2.缓存中查不到,从数据库查
42 result = inventoryService.queryProductInventory(productId);
43 } catch (Exception ex) {
44 log.error("getInventory failed", ex);
45 }
46 return result;
47 }
48
49 /**
50 * 更新商品库存
51 * @param productId
52 * @return
53 */
54 @RequestMapping("/updateInventory")
55 @ResponseBody
56 public Response updateInventory(ProductInventory productInventory) {
57 Response response = null;
58 try {
59 // 封装更新请求
60 Request request = new ProductInventoryUpdateRequest(
61 productInventory, inventoryService);
62 // 异步处理
63 requestAsyncProcessorService.process(request);
64 response = new Response(Response.SUCCESS);
65 } catch (Exception e) {
66 response = new Response(Response.FAILURE, e.getMessage());
67 }
68 return response;
69 }
70}
五、总结
本章,我通过代码实现了数据库和缓存的双写一致性解决方案,示例代码保存在Gitee:2.双写一致性实现(https://gitee.com/ressmix/epay/tree/master/2.双写一致性实现/epay-inventory)上,需要的读者可以自行下载参阅。






