
本文首发于Ressmix个人站点:https://www.tpvlog.com
上一章,我讲解了Broker的启动原理,它的本质是内部启动了一个Broker控制器——BrokerController,由它来控制Broker的各种行为,BrokerController内部引用了很多组件,包括接收网络请求的Netty服务器,各种核心功能组件,负责处理请求的线程池,负责执行定时调度任务的后台线程等,如下图:
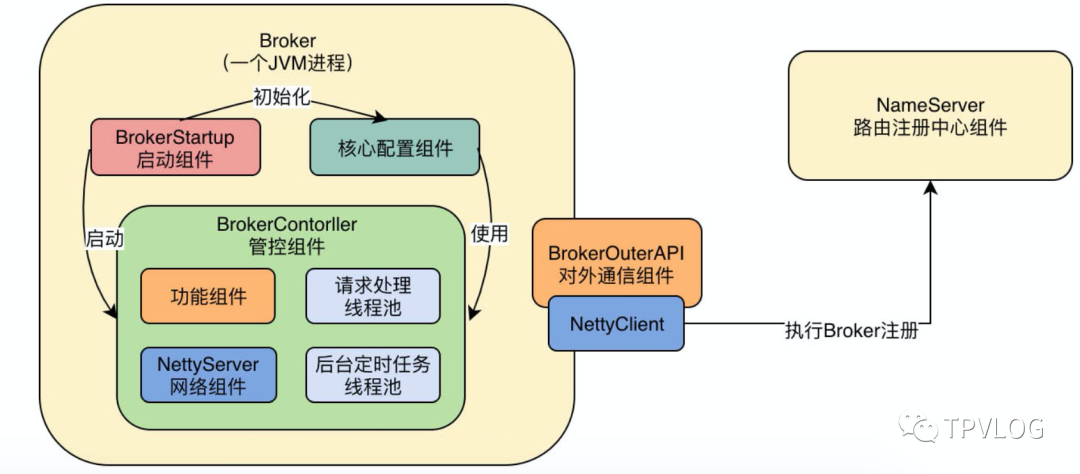
本章,我们就来看下BrokerController是如何将当前的Broker实例注册到NameServer中的:
1BrokerController.this.registerBrokerAll(true, false, brokerConfig.isForceRegister());
一、发送注册请求
我们进入BrokerController的registerBrokerAll()
方法中,一探究竟:
1public synchronized void registerBrokerAll(final boolean checkOrderConfig, boolean oneway, boolean forceRegister) {
2 // Topic配置相关操作,暂时忽略
3 TopicConfigSerializeWrapper topicConfigWrapper = this.getTopicConfigManager().buildTopicConfigSerializeWrapper();
4
5 // TopicConfig相关操作,暂时忽略
6 if (!PermName.isWriteable(this.getBrokerConfig().getBrokerPermission())
7 || !PermName.isReadable(this.getBrokerConfig().getBrokerPermission())) {
8 ConcurrentHashMap<String, TopicConfig> topicConfigTable = new ConcurrentHashMap<String, TopicConfig>();
9 for (TopicConfig topicConfig : topicConfigWrapper.getTopicConfigTable().values()) {
10 TopicConfig tmp =
11 new TopicConfig(topicConfig.getTopicName(), topicConfig.getReadQueueNums(), topicConfig.getWriteQueueNums(),
12 this.brokerConfig.getBrokerPermission());
13 topicConfigTable.put(topicConfig.getTopicName(), tmp);
14 }
15 topicConfigWrapper.setTopicConfigTable(topicConfigTable);
16 }
17
18 // 这里比较关键,注册Broker
19 if (forceRegister || needRegister(this.brokerConfig.getBrokerClusterName(),
20 this.getBrokerAddr(),
21 this.brokerConfig.getBrokerName(),
22 this.brokerConfig.getBrokerId(),
23 this.brokerConfig.getRegisterBrokerTimeoutMills())) {
24 doRegisterBrokerAll(checkOrderConfig, oneway, topicConfigWrapper);
25 }
26}
上述代码一开始都是对TopicConfig这个对象的相关操作,可以忽略,我们的目的是了解Broker的核心注册流程,最后一段代码才是关键:先判断是否要进行注册,如果需求则调用doRegisterBrokerAll
进行注册:
1private void doRegisterBrokerAll(boolean checkOrderConfig, boolean oneway,
2 TopicConfigSerializeWrapper topicConfigWrapper) {
3
4 // 调用brokerOuterAPI.registerBrokerAll发送请求到NameServer进行注册,返回注册结果
5 List<RegisterBrokerResult> registerBrokerResultList = this.brokerOuterAPI.registerBrokerAll(
6 this.brokerConfig.getBrokerClusterName(),
7 this.getBrokerAddr(),
8 this.brokerConfig.getBrokerName(),
9 this.brokerConfig.getBrokerId(),
10 this.getHAServerAddr(),
11 topicConfigWrapper,
12 this.filterServerManager.buildNewFilterServerList(),
13 oneway,
14 this.brokerConfig.getRegisterBrokerTimeoutMills(),
15 this.brokerConfig.isCompressedRegister());
16
17 // 对注册结果进行处理
18 if (registerBrokerResultList.size() > 0) {
19 RegisterBrokerResult registerBrokerResult = registerBrokerResultList.get(0);
20 if (registerBrokerResult != null) {
21 // 涉及Master/Slave的一些机制,暂时忽略
22 if (this.updateMasterHAServerAddrPeriodically && registerBrokerResult.getHaServerAddr() != null) {
23 this.messageStore.updateHaMasterAddress(registerBrokerResult.getHaServerAddr());
24 }
25
26 this.slaveSynchronize.setMasterAddr(registerBrokerResult.getMasterAddr());
27
28 if (checkOrderConfig) {
29 this.getTopicConfigManager().updateOrderTopicConfig(registerBrokerResult.getKvTable());
30 }
31 }
32 }
33}
doRegisterBrokerAll方法最核心的地方,其实就是调用了brokerOuterAPI.registerBrokerAll()
发送请求给NameServer进行注册。
1.1 BrokerOuterAPI
registerBrokerAll
注册请求实际是委托给BrokerOuterAPI去操作的,BrokerOuterAPI我们在上一章提到过,其实就是个Netty客户端,我们看下这个对象的registerBrokerAll
方法内部到底做了些什么:
1public List<RegisterBrokerResult> registerBrokerAll(
2 final String clusterName,
3 final String brokerAddr,
4 final String brokerName,
5 final long brokerId,
6 final String haServerAddr,
7 final TopicConfigSerializeWrapper topicConfigWrapper,
8 final List<String> filterServerList,
9 final boolean oneway,
10 final int timeoutMills,
11 final boolean compressed) {
12
13 // 存放注册结果
14 final List<RegisterBrokerResult> registerBrokerResultList = Lists.newArrayList();
15
16 // 获取NameServer集群地址
17 List<String> nameServerAddressList = this.remotingClient.getNameServerAddressList();
18 if (nameServerAddressList != null && nameServerAddressList.size() > 0) {
19
20 // 创建一个请求头,里面放当前Broker的各种信息
21 final RegisterBrokerRequestHeader requestHeader = new RegisterBrokerRequestHeader();
22 requestHeader.setBrokerAddr(brokerAddr);
23 requestHeader.setBrokerId(brokerId);
24 requestHeader.setBrokerName(brokerName);
25 requestHeader.setClusterName(clusterName);
26 requestHeader.setHaServerAddr(haServerAddr);
27 requestHeader.setCompressed(compressed);
28
29 // 创建一个请求体,里面放些Topic、Filter的配置
30 RegisterBrokerBody requestBody = new RegisterBrokerBody();
31 requestBody.setTopicConfigSerializeWrapper(topicConfigWrapper);
32 requestBody.setFilterServerList(filterServerList);
33 final byte[] body = requestBody.encode(compressed);
34 final int bodyCrc32 = UtilAll.crc32(body);
35 requestHeader.setBodyCrc32(bodyCrc32);
36
37 // 弄个CountDownLatch,目的是等主线程注册完所有NameServer后才往下走
38 final CountDownLatch countDownLatch = new CountDownLatch(nameServerAddressList.size());
39
40 // 遍历NameServer地址列表,每一个都去发送注册请求
41 for (final String namesrvAddr : nameServerAddressList) {
42 brokerOuterExecutor.execute(new Runnable() {
43 @Override
44 public void run() {
45 try {
46 // 真正执行注册的地方在这里
47 RegisterBrokerResult result = registerBroker(namesrvAddr,oneway, timeoutMills,requestHeader,body);
48 if (result != null) {
49 // 保存注册结果
50 registerBrokerResultList.add(result);
51 }
52
53 log.info("register broker[{}]to name server {} OK", brokerId, namesrvAddr);
54 } catch (Exception e) {
55 log.warn("registerBroker Exception, {}", namesrvAddr, e);
56 } finally {
57 countDownLatch.countDown();
58 }
59 }
60 });
61 }
62
63 try {
64 countDownLatch.await(timeoutMills, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
65 } catch (InterruptedException e) {
66 }
67 }
68
69 return registerBrokerResultList;
70}
上述整个逻辑还是很清晰的:
创建请求头、请求体,里面保存了待会儿要发送注册请求的信息;
遍历NameServer地址列表,发送请求;
返回注册结果。
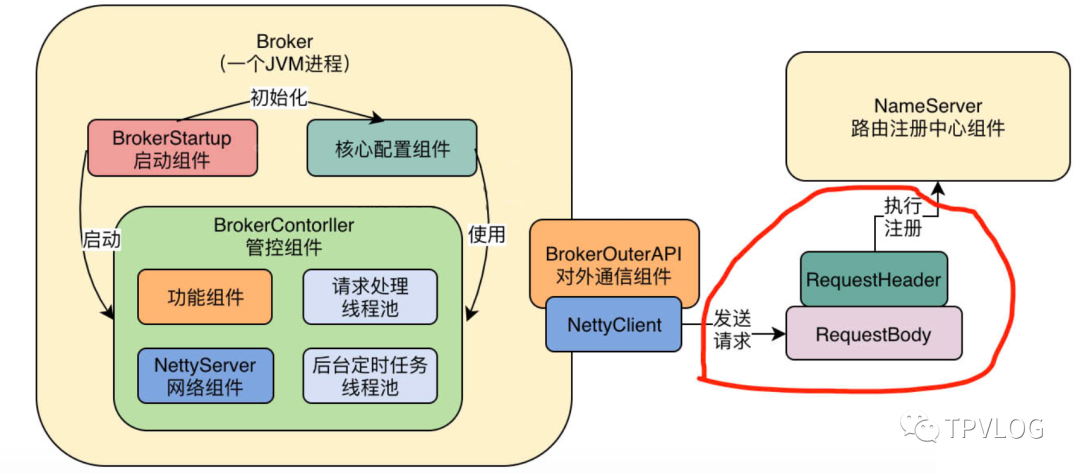
CountDownLatch是J.U.C包提供的一个同步器工具类,可以看成是一个倒数计时器,用来控制线程的行为,不了解的童鞋建议好好看看我写的透彻理解Java并发编程系列。
registerBroker
真正执行注册逻辑的是下面这一行,我们来看下registerBroker方法:
1RegisterBrokerResult result = registerBroker(namesrvAddr,oneway, timeoutMills,requestHeader,body);
registerBroker方法会通过底层的NettyClient
,把这个请求发送到NameServer进行注册:
1private RegisterBrokerResult registerBroker(
2 final String namesrvAddr,
3 final boolean oneway,
4 final int timeoutMills,
5 final RegisterBrokerRequestHeader requestHeader,
6 final byte[] body
7) throws RemotingCommandException, MQBrokerException, RemotingConnectException, RemotingSendRequestException, RemotingTimeoutException,
8 InterruptedException {
9
10 // 将请求头和请求体封装成一个完整请求——RemotingCommand
11 RemotingCommand request = RemotingCommand.createRequestCommand(RequestCode.REGISTER_BROKER, requestHeader);
12 request.setBody(body);
13
14 // oneway表示不同等待注册结果
15 if (oneway) {
16 try {
17 this.remotingClient.invokeOneway(namesrvAddr, request, timeoutMills);
18 } catch (RemotingTooMuchRequestException e) {
19 // Ignore
20 }
21 return null;
22 }
23
24 // 利用RemotingClient发送注册请求,这个RemotingClient其实就是个Netty客户端
25 RemotingCommand response = this.remotingClient.invokeSync(namesrvAddr, request, timeoutMills);
26
27 // 下面是处理返回结果,封装成一个RegisterBrokerResult,暂时忽略
28 assert response != null;
29 switch (response.getCode()) {
30 case ResponseCode.SUCCESS: {
31 RegisterBrokerResponseHeader responseHeader =
32 (RegisterBrokerResponseHeader) response.decodeCommandCustomHeader(RegisterBrokerResponseHeader.class);
33 RegisterBrokerResult result = new RegisterBrokerResult();
34 result.setMasterAddr(responseHeader.getMasterAddr());
35 result.setHaServerAddr(responseHeader.getHaServerAddr());
36 if (response.getBody() != null) {
37 result.setKvTable(KVTable.decode(response.getBody(), KVTable.class));
38 }
39 return result;
40 }
41 default:
42 break;
43 }
44
45 throw new MQBrokerException(response.getCode(), response.getRemark());
46}
上述代码最核心的就是下面这行:
1RemotingCommand response = this.remotingClient.invokeSync(namesrvAddr, request, timeoutMills);
1.2 NettyRemotingClient
remotingClient其实就是一个Netty客户端,它的实现类是NettyRemotingClient
,底层封装了Netty的API调用。
invokeSync
我们看下NettyRemotingClient
的invokeSync
方法:
1public RemotingCommand invokeSync(String addr, final RemotingCommand request, long timeoutMillis)
2 throws InterruptedException, RemotingConnectException, RemotingSendRequestException, RemotingTimeoutException {
3 long beginStartTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
4
5 // 创建一个Channel,这个Channel可以理解成跟NameServer之间建立的一个连接
6 final Channel channel = this.getAndCreateChannel(addr);
7 if (channel != null && channel.isActive()) {
8 try {
9 // 计算时间开销,忽略
10 doBeforeRpcHooks(addr, request);
11 long costTime = System.currentTimeMillis() - beginStartTime;
12 if (timeoutMillis < costTime) {
13 throw new RemotingTimeoutException("invokeSync call timeout");
14 }
15
16 // 这里是真正发送请求
17 RemotingCommand response = this.invokeSyncImpl(channel, request, timeoutMillis - costTime);
18
19 // 忽略
20 doAfterRpcHooks(RemotingHelper.parseChannelRemoteAddr(channel), request, response);
21 return response;
22 } catch (RemotingSendRequestException e) {
23 log.warn("invokeSync: send request exception, so close the channel[{}]", addr);
24 this.closeChannel(addr, channel);
25 throw e;
26 } catch (RemotingTimeoutException e) {
27 if (nettyClientConfig.isClientCloseSocketIfTimeout()) {
28 this.closeChannel(addr, channel);
29 log.warn("invokeSync: close socket because of timeout, {}ms, {}", timeoutMillis, addr);
30 }
31 log.warn("invokeSync: wait response timeout exception, the channel[{}]", addr);
32 throw e;
33 }
34 } else {
35 this.closeChannel(addr, channel);
36 throw new RemotingConnectException(addr);
37 }
38}
通过上面代码的分析,我们其实可以知道,Broker和NameServer之间通过Channel建立了一个网络连接,然后基于这个Channel就可以发送实际的网络请求了:
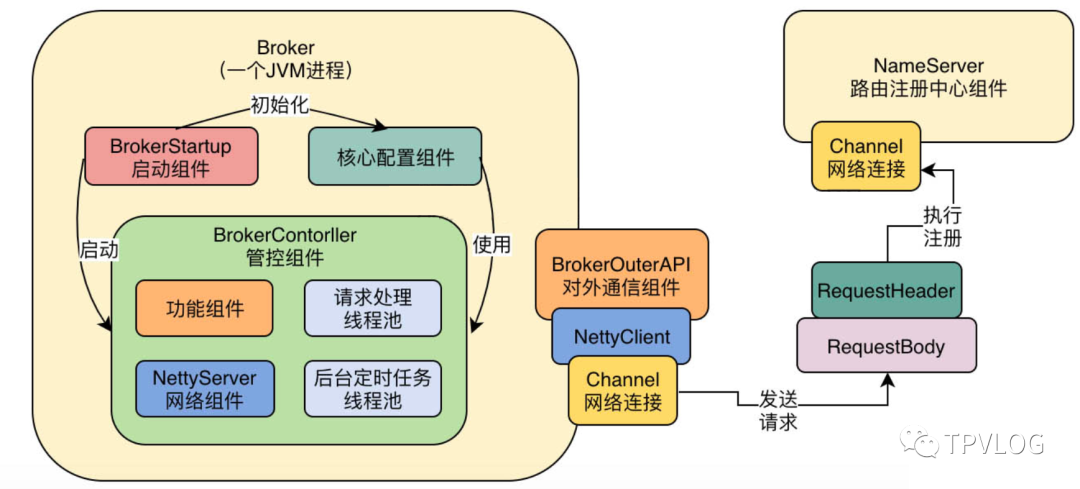
getAndCreateChannel
接着我们进入上面的this.getAndCreateChannel(addr)
这行代码看看,他是如何跟NameServer之间建立实际的网络连接的?
1private Channel getAndCreateChannel(final String addr) throws RemotingConnectException, InterruptedException {
2 // 先尝试从缓存中获取连接
3 if (null == addr) {
4 return getAndCreateNameserverChannel();
5 }
6
7 ChannelWrapper cw = this.channelTables.get(addr);
8 if (cw != null && cw.isOK()) {
9 return cw.getChannel();
10 }
11
12 // 没有就创建一个
13 return this.createChannel(addr);
14}
1/**
2 * 通过一个NameServer的地址创建出一个网络连接
3 */
4private Channel createChannel(final String addr) throws InterruptedException {
5 // 先尝试从缓存获取连接
6 ChannelWrapper cw = this.channelTables.get(addr);
7 if (cw != null && cw.isOK()) {
8 return cw.getChannel();
9 }
10
11 if (this.lockChannelTables.tryLock(LOCK_TIMEOUT_MILLIS, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS)) {
12 try {
13 // 下面一堆代码都是尝试从缓存获取连接
14 boolean createNewConnection;
15 cw = this.channelTables.get(addr);
16 if (cw != null) {
17
18 if (cw.isOK()) {
19 return cw.getChannel();
20 } else if (!cw.getChannelFuture().isDone()) {
21 createNewConnection = false;
22 } else {
23 this.channelTables.remove(addr);
24 createNewConnection = true;
25 }
26 } else {
27 createNewConnection = true;
28 }
29
30 // 这里是真正创建连接的地方
31 if (createNewConnection) {
32 // 本质是基于Netty的Bootstrap类的connnect方法,创建一个连接
33 ChannelFuture channelFuture = this.bootstrap.connect(RemotingHelper.string2SocketAddress(addr));
34 log.info("createChannel: begin to connect remote host[{}] asynchronously", addr);
35 cw = new ChannelWrapper(channelFuture);
36 this.channelTables.put(addr, cw);
37 }
38 } catch (Exception e) {
39 log.error("createChannel: create channel exception", e);
40 } finally {
41 this.lockChannelTables.unlock();
42 }
43 } else {
44 log.warn("createChannel: try to lock channel table, but timeout, {}ms", LOCK_TIMEOUT_MILLIS);
45 }
46
47 // 返回连接的代码,忽略
48 if (cw != null) {
49 ChannelFuture channelFuture = cw.getChannelFuture();
50 if (channelFuture.awaitUninterruptibly(this.nettyClientConfig.getConnectTimeoutMillis())) {
51 if (cw.isOK()) {
52 log.info("createChannel: connect remote host[{}] success, {}", addr, channelFuture.toString());
53 return cw.getChannel();
54 } else {
55 log.warn("createChannel: connect remote host[" + addr + "] failed, " + channelFuture.toString(), channelFuture.cause());
56 }
57 } else {
58 log.warn("createChannel: connect remote host[{}] timeout {}ms, {}", addr, this.nettyClientConfig.getConnectTimeoutMillis(),
59 channelFuture.toString());
60 }
61 }
62
63 return null;
64}
真相大白了,核心就是基于Netty的Bootstrap
类的connnect
方法,创建了一个连接。那么连接建立完成后,如何发送请求呢?
我们回到NettyRemotingClient
的invokeSync
方法,看下面这行调用:
1RemotingCommand response = this.invokeSyncImpl(channel, request, timeoutMillis - costTime);
invokeSyncImpl
invokeSyncImpl方法,重点要知道的就是:NettyRemotingClient
底层是基于Netty的Channel API,把注册的请求给发送到了NameServer就可以了。
1public RemotingCommand invokeSyncImpl(final Channel channel, final RemotingCommand request,
2 final long timeoutMillis)
3 throws InterruptedException, RemotingSendRequestException, RemotingTimeoutException {
4 final int opaque = request.getOpaque();
5
6 try {
7 final ResponseFuture responseFuture = new ResponseFuture(channel, opaque, timeoutMillis, null, null);
8 this.responseTable.put(opaque, responseFuture);
9 final SocketAddress addr = channel.remoteAddress();
10
11 // 基于Netty的Channel组件,将请求发送出去
12 channel.writeAndFlush(request).addListener(new ChannelFutureListener() {
13 @Override
14 public void operationComplete(ChannelFuture f) throws Exception {
15 if (f.isSuccess()) {
16 responseFuture.setSendRequestOK(true);
17 return;
18 } else {
19 responseFuture.setSendRequestOK(false);
20 }
21
22 responseTable.remove(opaque);
23 responseFuture.setCause(f.cause());
24 responseFuture.putResponse(null);
25 log.warn("send a request command to channel <" + addr + "> failed.");
26 }
27 });
28
29 // 这里比较重要,等待请求响应结果
30 RemotingCommand responseCommand = responseFuture.waitResponse(timeoutMillis);
31 if (null == responseCommand) {
32 if (responseFuture.isSendRequestOK()) {
33 throw new RemotingTimeoutException(RemotingHelper.parseSocketAddressAddr(addr), timeoutMillis,
34 responseFuture.getCause());
35 } else {
36 throw new RemotingSendRequestException(RemotingHelper.parseSocketAddressAddr(addr), responseFuture.getCause());
37 }
38 }
39
40 return responseCommand;
41 } finally {
42 this.responseTable.remove(opaque);
43 }
44}
二、处理注册请求
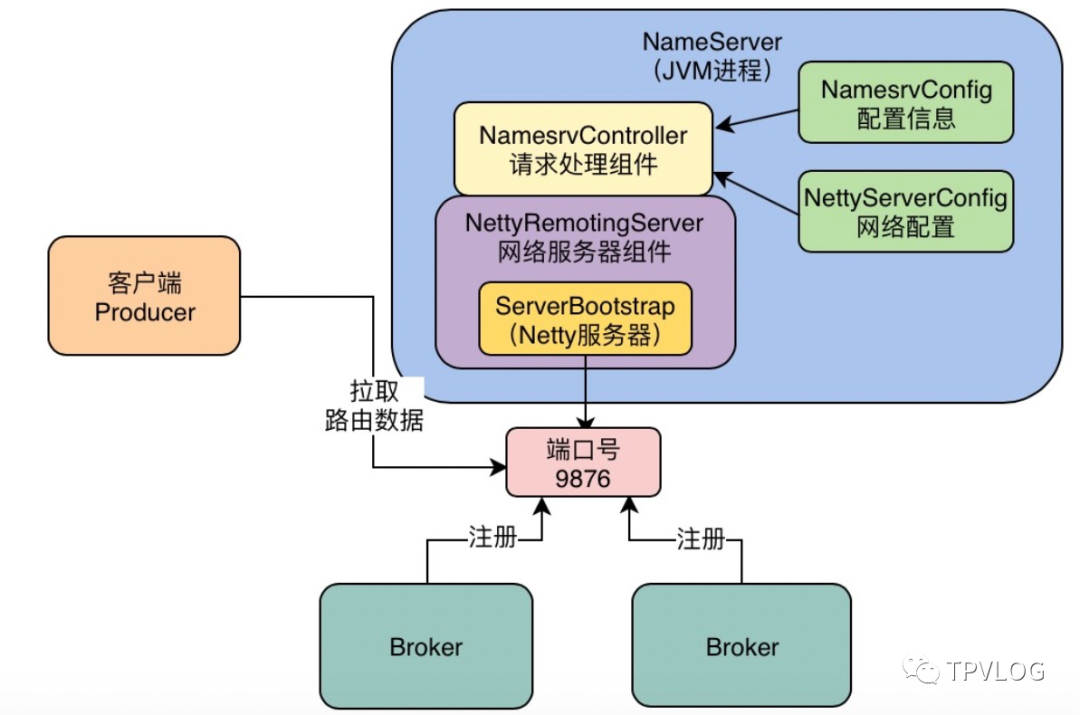
了解了Broker是如何发送注册请求的之后,我们需要来看下NameServer是如何处理注册请求的。我在《NameServer启动流程》讲过,NameServer启动后,其实内部有个Netty服务器,监听着9876端口:
2.1 NamesrvController
我们回到NamesrvController.initialize()
,里面有个很关键的方法调用——registerProcessor:
1public boolean initialize() {
2
3 this.kvConfigManager.load();
4
5 // 创建一个内部的Netty服务器
6 this.remotingServer = new NettyRemotingServer(this.nettyServerConfig, this.brokerHousekeepingService);
7
8 this.remotingExecutor =
9 Executors.newFixedThreadPool(nettyServerConfig.getServerWorkerThreads(), new ThreadFactoryImpl("RemotingExecutorThread_"));
10
11 // 关键就在这里,这个Processor其实就是一个请求处理器,是NameServer处理网络请求的组件
12 this.registerProcessor();
13
14 //...省略无关代码
15
16 return true;
17}
registerProcessor
1private void registerProcessor() {
2 // 测试集群的代码,忽略
3 if (namesrvConfig.isClusterTest()) {
4 this.remotingServer.registerDefaultProcessor(new ClusterTestRequestProcessor(this, namesrvConfig.getProductEnvName()),
5 this.remotingExecutor);
6 } else {
7 // 核心是这里:在内部Netty服务器中注册了一个请求处理组件——DefaultRequestProcessor
8 this.remotingServer.registerDefaultProcessor(new DefaultRequestProcessor(this), this.remotingExecutor);
9 }
10}
我们可以看到,上述代码将DefaultRequestProcessor
这个请求处理组件注册到了NameServer内部的Netty服务器中,也就是说Netty服务器会把接收到的网络请求交给DefaultRequestProcessor
去处理。也就是下面这个样子:
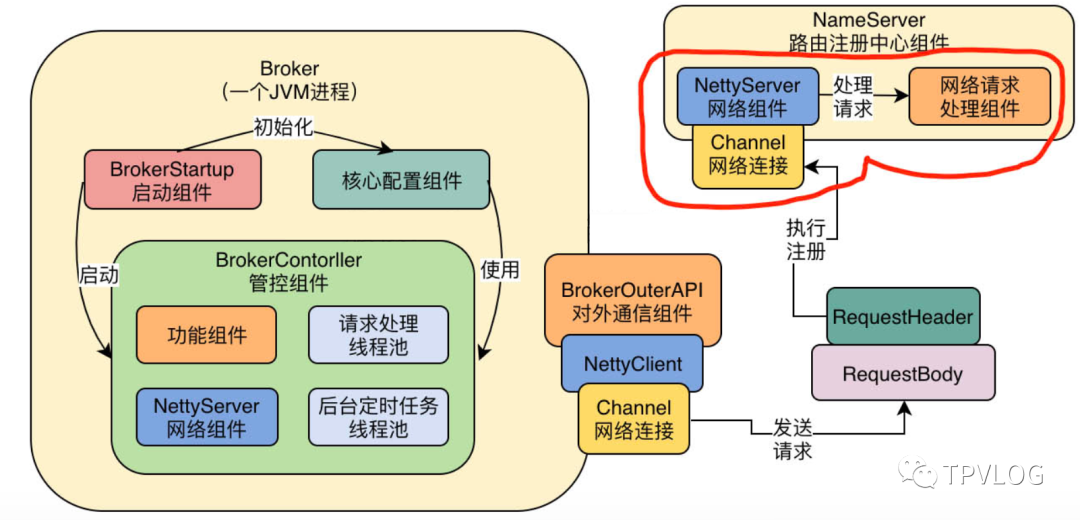
2.2 DefaultRequestProcessor
我们进入DefaultRequestProcessor类,看下它到底是怎么处理网络请求的。
processRequest
processRequest方法用于处理各类请求,它的主体逻辑就是根据请求报文里面的请求码判断如何处理,我们关心的是Broker的注册请求,所以直接看registerBroker
方法即可。
1public RemotingCommand processRequest(ChannelHandlerContext ctx,
2 RemotingCommand request) throws RemotingCommandException {
3
4 // 打印日志,忽略
5 if (ctx != null) {
6 log.debug("receive request, {} {} {}",
7 request.getCode(),
8 RemotingHelper.parseChannelRemoteAddr(ctx.channel()),
9 request);
10 }
11
12 // 这里是核心逻辑,根据不同的请求类型分别处理
13 switch (request.getCode()) {
14 case RequestCode.PUT_KV_CONFIG:
15 return this.putKVConfig(ctx, request);
16 case RequestCode.GET_KV_CONFIG:
17 return this.getKVConfig(ctx, request);
18 case RequestCode.DELETE_KV_CONFIG:
19 return this.deleteKVConfig(ctx, request);
20 case RequestCode.QUERY_DATA_VERSION:
21 return queryBrokerTopicConfig(ctx, request);
22 // 我们关键看这里,这就是注册Broker的请求
23 case RequestCode.REGISTER_BROKER:
24 Version brokerVersion = MQVersion.value2Version(request.getVersion());
25 if (brokerVersion.ordinal() >= MQVersion.Version.V3_0_11.ordinal()) {
26 return this.registerBrokerWithFilterServer(ctx, request);
27 } else {
28 // 核心的处理Broker注册请求的逻辑
29 return this.registerBroker(ctx, request);
30 }
31
32 //...省略
33 default:
34 break;
35 }
36 return null;
37}
registerBroker
registerBroker方法主要就是:解析请求,然后调用RouteInfoManager这个核心组件去注册Broker,RouteInfoManager是NameServer中的路由信息管理器:
1public RemotingCommand registerBroker(ChannelHandlerContext ctx,
2 RemotingCommand request) throws RemotingCommandException {
3
4 // 下面这堆代码用于解析请求,创建一个响应对象
5 final RemotingCommand response = RemotingCommand.createResponseCommand(RegisterBrokerResponseHeader.class);
6 final RegisterBrokerResponseHeader responseHeader = (RegisterBrokerResponseHeader) response.readCustomHeader();
7 final RegisterBrokerRequestHeader requestHeader =
8 (RegisterBrokerRequestHeader) request.decodeCommandCustomHeader(RegisterBrokerRequestHeader.class);
9
10 if (!checksum(ctx, request, requestHeader)) {
11 response.setCode(ResponseCode.SYSTEM_ERROR);
12 response.setRemark("crc32 not match");
13 return response;
14 }
15
16 // 忽略
17 TopicConfigSerializeWrapper topicConfigWrapper;
18 if (request.getBody() != null) {
19 topicConfigWrapper = TopicConfigSerializeWrapper.decode(request.getBody(), TopicConfigSerializeWrapper.class);
20 } else {
21 topicConfigWrapper = new TopicConfigSerializeWrapper();
22 topicConfigWrapper.getDataVersion().setCounter(new AtomicLong(0));
23 topicConfigWrapper.getDataVersion().setTimestamp(0);
24 }
25
26 // 关键是这里,利用RouteInfoManager这个核心组件来注册Broker
27 RegisterBrokerResult result = this.namesrvController.getRouteInfoManager().registerBroker(
28 requestHeader.getClusterName(),
29 requestHeader.getBrokerAddr(),
30 requestHeader.getBrokerName(),
31 requestHeader.getBrokerId(),
32 requestHeader.getHaServerAddr(),
33 topicConfigWrapper,
34 null,
35 ctx.channel()
36 );
37
38 // 下面的一堆都是构造响应信息,忽略
39 responseHeader.setHaServerAddr(result.getHaServerAddr());
40 responseHeader.setMasterAddr(result.getMasterAddr());
41
42 byte[] jsonValue = this.namesrvController.getKvConfigManager().getKVListByNamespace(NamesrvUtil.NAMESPACE_ORDER_TOPIC_CONFIG);
43 response.setBody(jsonValue);
44 response.setCode(ResponseCode.SUCCESS);
45 response.setRemark(null);
46 return response;
47}
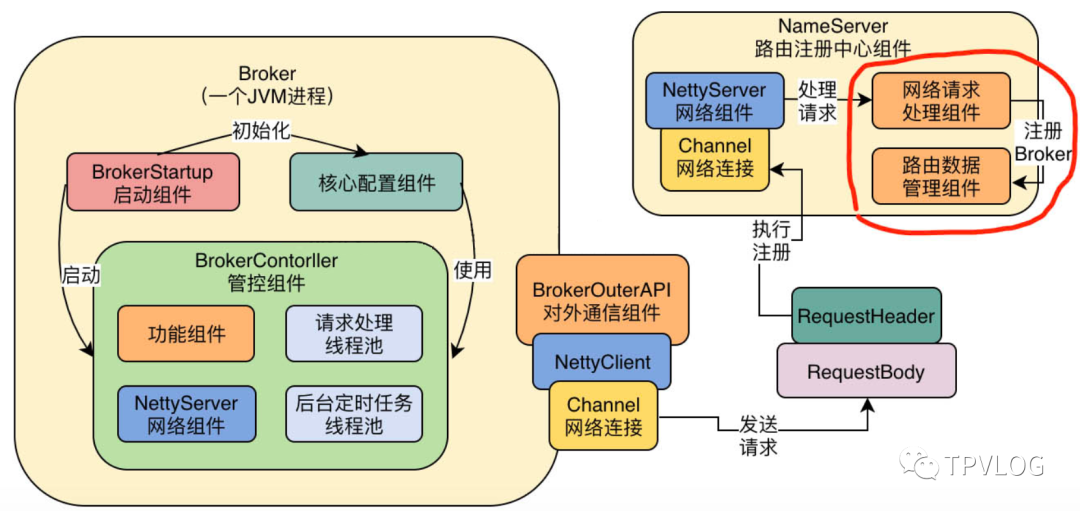
2.3 RouteInfoManager
我们最后来看下RouteInfoManager这个路由信息管理组件,从构造函数就可以看出,它其实内部就是用了Map,去存放Broker的一些相关信息:
1public RouteInfoManager() {
2 this.topicQueueTable = new HashMap<String, List<QueueData>>(1024);
3 // Broker地址信息
4 this.brokerAddrTable = new HashMap<String, BrokerData>(128);
5 this.clusterAddrTable = new HashMap<String, Set<String>>(32);
6 // Broker存活信息
7 this.brokerLiveTable = new HashMap<String, BrokerLiveInfo>(256);
8 this.filterServerTable = new HashMap<String, List<String>>(256);
9}
registerBroker
从registerBroker方法内容,我们可以看到,待注册的Broker的相关信息,其实被拆解到了RouteInfoManager内部的各个Map中:
1public RegisterBrokerResult registerBroker(
2 final String clusterName,
3 final String brokerAddr,
4 final String brokerName,
5 final long brokerId,
6 final String haServerAddr,
7 final TopicConfigSerializeWrapper topicConfigWrapper,
8 final List<String> filterServerList,
9 final Channel channel) {
10 RegisterBrokerResult result = new RegisterBrokerResult();
11 try {
12 try {
13 this.lock.writeLock().lockInterruptibly();
14
15 // 设置这个待注册的Broker的集群信息
16 Set<String> brokerNames = this.clusterAddrTable.get(clusterName);
17 if (null == brokerNames) {
18 brokerNames = new HashSet<String>();
19 this.clusterAddrTable.put(clusterName, brokerNames);
20 }
21 brokerNames.add(brokerName);
22
23 boolean registerFirst = false;
24
25 // Broker相关数据放在brokerAddrTable这个Map里
26 BrokerData brokerData = this.brokerAddrTable.get(brokerName);
27 if (null == brokerData) {
28 registerFirst = true;
29 brokerData = new BrokerData(clusterName, brokerName, new HashMap<Long, String>());
30 this.brokerAddrTable.put(brokerName, brokerData);
31 }
32
33 // 下面是主从相关的一些代码,暂时忽略
34 Map<Long, String> brokerAddrsMap = brokerData.getBrokerAddrs();
35 //Switch slave to master: first remove <1, IP:PORT> in namesrv, then add <0, IP:PORT>
36 //The same IP:PORT must only have one record in brokerAddrTable
37 Iterator<Entry<Long, String>> it = brokerAddrsMap.entrySet().iterator();
38 while (it.hasNext()) {
39 Entry<Long, String> item = it.next();
40 if (null != brokerAddr && brokerAddr.equals(item.getValue()) && brokerId != item.getKey()) {
41 it.remove();
42 }
43 }
44
45 String oldAddr = brokerData.getBrokerAddrs().put(brokerId, brokerAddr);
46 registerFirst = registerFirst || (null == oldAddr);
47
48 //...忽略无关代码
49 } finally {
50 this.lock.writeLock().unlock();
51 }
52 } catch (Exception e) {
53 log.error("registerBroker Exception", e);
54 }
55
56 return result;
57}
上面代码还有一点比较关键,为了提升注册Broker时的性能,用了一个读写锁——ReadWriteLock,这样的更新操作只能有一个线程执行,保证了数据的一致性。关于读写锁,童鞋们可以参考我写的《透彻理解Java并发编程系列》,里面有对整个J.U.C包的详细讲解。
三、总结
本章,我讲解了Broker的注册原理,以及NameServer是如何处理Broker的注册请求的。
对于Broker来说,注册流程的核心点就是基于底层的Netty API与NameServer建立Channel,然后发送注册请求;
对于NameServer来说,也是基于内部的NettyServer服务器先接受请求,然后将请求转交给请求处理器组件处理,而请求处理器组件则是根据不同的请求类型,将请求转交给NameServer内部的其它组件处理。比如本章的注册请求,最终就是由RouteInfoManager这个组件来处理的。






