分布式调度Elastic-job
1.概述
1.1什么是任务调度
我们可以思考一下下面业务场景的解决方案:
某电商平台需要每天上午10点,下午3点,晚上8点发放一批优惠券
某银行系统需要在信用卡到期还款日的前三天进行短信提醒
某财务系统需要在每天凌晨0:10分结算前一天的财务数据,统计汇总
以上场景就是任务调度所需要解决的问题
任务调度是为了自动完成特定任务,在约定的特定时刻去执行任务的过程;可以就理解成定时任务(以前做Redis的持久化)。
我们在之前骡窝窝项目的学习中,使用过Spring中提供的定时任务注解@Scheduled
在业务类中方法中贴上这个注解
@Scheduled(cron = "0/20 * * * * ? ")public void doWork(){//doSomething}
然后在启动类上贴上@EnableScheduling
注解,但是它仅仅能够适应单体应用的任务调度。
1.2 为什么需要分布式调度
感觉Spring给我们提供的这个注解可以完成任务调度的功能,好像已经完美解决问题了,为什么还需要分布式呢?
主要有如下这几点原因:
1.单机处理极限:原本1分钟内需要处理1万个订单,但是现在需要1分钟内处理10万个订单;原来一个统计需要1小时,现在业务方需要10分钟就统计出来。你也许会说,你也可以多线程、单机多进程处理。的确,多线程并行处理可以提高单位时间的处理效率,但是单机能力毕竟有限(主要是CPU、内存和磁盘),始终会有单机处理不过来的情况。
2.高可用:单机版的定式任务调度只能在一台机器上运行,如果程序或者系统出现异常就会导致功能不可用。虽然可以在单机程序实现的足够稳定,但始终有机会遇到非程序引起的故障,而这个对于一个系统的核心功能来说是不可接受的。
3.防止重复执行: 在单机模式下,定时任务是没什么问题的。但当我们部署了多台服务,同时又每台服务又有定时任务时,若不进行合理的控制在同一时间,只有一个定时任务启动执行,这时,定时执行的结果就可能存在混乱和错误了
这个时候就需要分布式的任务调度来实现了。
1.3 Elastic-Job介绍
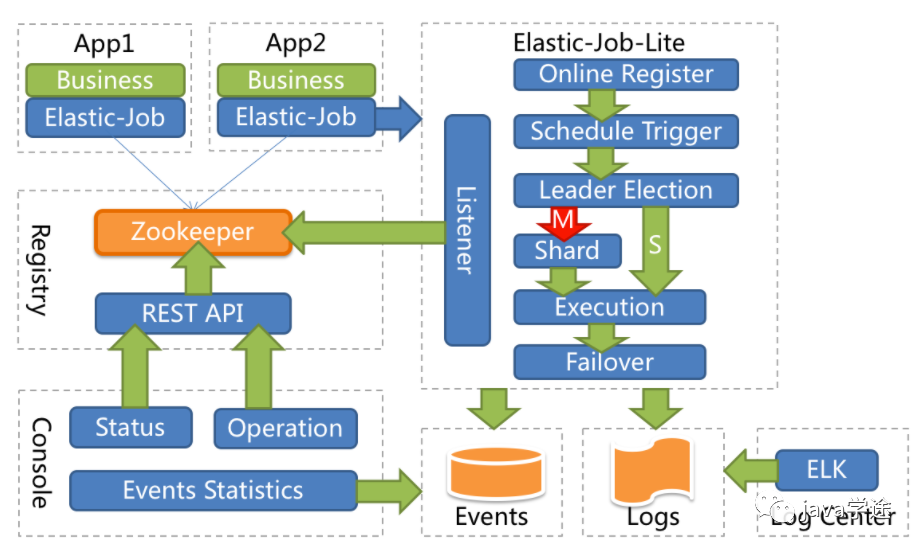
Elastic-Job是一个分布式调度的解决方案,由当当网开源,它由两个相互独立的子项目Elastic-job-Lite和Elastic-Job-Cloud组成,使用Elastic-Job可以快速实现分布式任务调度。
Elastic-Job的github地址:https://github.com/elasticjob
功能列表:
分布式调度协调
在分布式环境中,任务能够按照指定的调度策略执行,并且能够避免同一任务多实例重复执行。
丰富的调度策略:
基于成熟的定时任务作业框架Quartz cron表达式执行定时任务。
弹性拓容缩容
当集群中增加一个实例,它应当能够被选举被执行任务;当集群减少一个实例时,他所执行的任务能被转移到别的示例中执行。
失效转移
某示例在任务执行失败后,会被转移到其他实例执行。
错过执行任务重触发
若因某种原因导致作业错过执行,自动记录错误执行的作业,并在下次次作业完成后自动触发。
支持并行调度
支持任务分片,任务分片是指将一个任务分成多个小任务在多个实例同时执行。
作业分片一致性
当任务被分片后,保证同一分片在分布式环境中仅一个执行实例。
支持作业生命周期操作
可以动态对任务进行开启及停止操作。
丰富的作业类型
支持Simple、DataFlow、Script三种作业类型
系统架构图
2.Elastic-Job快速入门
2.1 环境搭建
2.1.1 版本要求
JDK 要求1.7以上版本
Maven 要求3.0.4及以上版本
Zookeeper 要求采取3.4.6以上版本
2.1.2 Zookeeper安装&运行
2.1.3 创建Maven项目
添加如下依赖
<dependency><groupId>com.dangdang</groupId><artifactId>elastic-job-lite-core</artifactId><version>2.1.5</version></dependency>
2.2 代码实现
2.2.1 任务类
/*** 自己的任务类*/public class MyElasticJob implements SimpleJob {//会根据 cron 表达式定义的时间来执行这个方法;shardingContext分片才会用到public void execute(ShardingContext shardingContext) {System.out.println("定时任务开始执行————>" + new Date());}}
2.2.2 配置类
public class JobDemo {public static void main(String[] args) {//创建 JobScheduler ,然后 init 方法初始化//参数1:注册中心zookeeper配置;参数2:任务相关的配置new JobScheduler(createRegistryCenter(), createJobConfiguration()).init();}//启动作业配置private static CoordinatorRegistryCenter createRegistryCenter() {//参数1:配置zookeeper的地址,调度任务的组名;参数2:项目名即可ZookeeperConfiguration zookeeperConfiguration = new ZookeeperConfiguration("localhost:2181", "elastic-job-demo");//设置超时时间(一定要配置)zookeeperConfiguration.setSessionTimeoutMilliseconds(100);//创建注册中心配置CoordinatorRegistryCenter regCenter = new ZookeeperRegistryCenter(zookeeperConfiguration);//初始化regCenter.init();return regCenter;}//作业配置private static LiteJobConfiguration createJobConfiguration() {// 定义作业核心配置//参数1:作业名称;参数2:corn 表达式;参数3:分片数JobCoreConfiguration simpleCoreConfig = JobCoreConfiguration.newBuilder("demoSimpleJob", "0/3 * * * * ?", 1).build();// 定义SIMPLE类型配置//参数1:作业配置;参数2:任务类的全限定名;SimpleJobConfiguration simpleJobConfig = new SimpleJobConfiguration(simpleCoreConfig, MyElasticJob.class.getCanonicalName());// 定义Lite作业根配置LiteJobConfiguration simpleJobRootConfig = LiteJobConfiguration.newBuilder(simpleJobConfig).build();return simpleJobRootConfig;}}
需要运行zookeeper服务:
解压文件:
zookeeper-3.4.11.tar.gz进入conf目录下,拷贝
zoo_sample.cfg
文件,并将文件名改成zoo.cfg
,用于加载自定义配置的,这里不需要做任何修改;bin目录下双击
zkServer.cmd
文件启动zookeeper服务;双击
zkCli.cmd
启动窗口界面;ls 可以看到节点;不方便,选择使用图形化界面;
图形化界面:
解压文件
ZooInspector.zip
;进入builder中运行jar包:
zookeeper-dev-ZooInspector.jar启动后点击连接,不做修改,OK即可。
2.2.3 测试
运行单个程序,查看是否按照cron表达式的内容进行任务的调度
运行多个程序(集群),查看是否只会有一个实例进行任务调度
运行多个程序后,把正在进行任务调度的进程关掉,查看其它进程是否能继续进行任务调度
这样就表示了elastic-job的高可用;
3.SpringBoot集成Elastic-Job
3.1 添加Maven依赖
<groupId>cn.wolfcode</groupId><artifactId>elastic-job-springboot</artifactId><version>1.0.0</version><parent><groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId><artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId><version>2.1.3.RELEASE</version></parent><properties><project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding><project.reporting.outputEncoding>UTF-8</project.reporting.outputEncoding><java.version>1.8</java.version></properties><dependencies><dependency><groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId><artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId></dependency><dependency><groupId>com.dangdang</groupId><artifactId>elastic-job-lite-spring</artifactId><version>2.1.5</version></dependency><dependency><groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId><artifactId>lombok</artifactId></dependency></dependencies>
elastic-job-lite-spring
和SpringBoot整合需要导如的依赖;在elastic-job
中没有提供想starter之类的依赖,所以需要我们自己把bean通过注解的方式创建出来;可以自定义stater,自己封装也比较简单??(我没有思路)
3.2 相关配置
因为配置中心的地址并不是固定的,所以我们应该把这个地址信息配置在配置文件中,所以在配置文件application.yml中添加配置如下:
#配置中心的地址和命名空间按,在配置文件管理,方法中获取elastic-job:zookeeper-url: localhost:2181group-name: elastic-job-group
zk注册中心配置类:
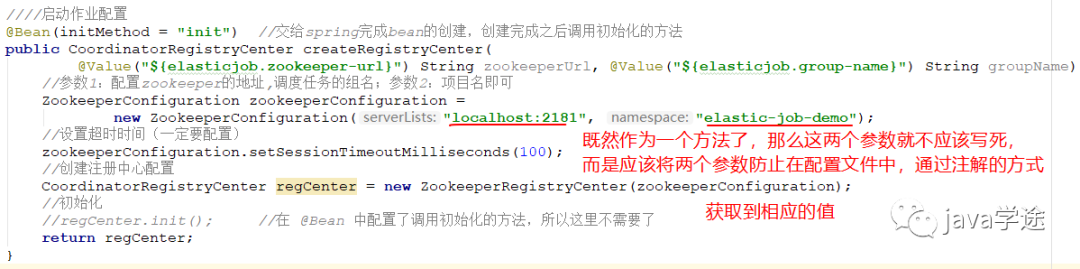
/*** zookeeper 注册中心配置类*/@Configurationpublic class RegistryCenterConfig {////启动作业配置@Bean(initMethod = "init") //交给spring完成bean的创建,创建完成之后调用初始化的方法public CoordinatorRegistryCenter createRegistryCenter(@Value("${elastic-job.zookeeper-url}") String zookeeperUrl, @Value("${elastic-job.group-name}") String groupName) {//参数1:配置zookeeper的地址,调度任务的组名;参数2:项目名即可ZookeeperConfiguration zookeeperConfiguration =new ZookeeperConfiguration(zookeeperUrl, groupName);//设置超时时间(一定要配置)zookeeperConfiguration.setSessionTimeoutMilliseconds(100);//其实这个100也可以配到配置文件中//创建注册中心配置CoordinatorRegistryCenter regCenter = new ZookeeperRegistryCenter(zookeeperConfiguration);//初始化//regCenter.init(); 在 @Bean 中配置了调用初始化的方法,所以这里不需要了return regCenter;}}
自己的任务类:交给spring管理
/*** 自己的任务类*/@Component //需要交给spring来进行管理public class MyElasticJob implements SimpleJob {//会根据 cron 表达式定义的时间来执行这个方法;shardingContext分片才会用到public void execute(ShardingContext shardingContext) {System.out.println("定时任务开始执行————>" + new Date());}}
任务调度配置类:
/*** 任务调度配置类*/@Configurationpublic class ElasticJobConfig {@Autowired //注入下文参数2private CoordinatorRegistryCenter registryCenter;//返回作业配置的方法 参数3 需要//同样的 newBuilder的参数不能写死,用方法来传递参数来解决,所以定义了四个形参private LiteJobConfiguration createJobConfig(Class<? extends ElasticJob> clazz, //任务类的字节码String cron, //cron表达式int shrdingTotalCount, //分片个数String shardingParamter //分片参数) {JobCoreConfiguration.Builder builder = JobCoreConfiguration.newBuilder(clazz.getSimpleName(), cron, shrdingTotalCount);if (!StringUtils.isEmpty(shardingParamter)) {//如果传了分片参数,我们需要设置进去builder.shardingItemParameters(shardingParamter);}// 定义作业核心配置//参数1:作业名称;参数2:corn 表达式;参数3:分片数//JobCoreConfiguration simpleCoreConfig = JobCoreConfiguration.newBuilder("demoSimpleJob", "0/3 * * * * ?", 1).build(); 不写死JobCoreConfiguration simpleCoreConfig = builder.build(); //把builder提起前的原因是要设置分片的次数// 定义SIMPLE类型配置//参数1:作业配置;参数2:任务类的全限定名;SimpleJobConfiguration simpleJobConfig = new SimpleJobConfiguration(simpleCoreConfig, clazz.getCanonicalName());// 定义Lite作业根配置//overwrite(true):如果没有这个配置,分片参数的值将始终是第一次设置的值,不会被覆盖,代码修改没有效果,只能删除配置重新设置;加上即可覆盖LiteJobConfiguration simpleJobRootConfig = LiteJobConfiguration.newBuilder(simpleJobConfig).overwrite(true).build();return simpleJobRootConfig;}@Bean(initMethod = "init") // 需要将MyElasticJob对象给注入进来,这里给MyElasticJob创建对象并做初始化public SpringJobScheduler initMyElasticJobBean(MyElasticJob myElasticJob) {//需要的参数:// 参数1ElasticJob类型的参数:myElasticJob是间接继承自ElasticJob的,// 参数2:需要注入RegistryCenterConfig的对象// 参数3LiteJobConfiguration:内容比较多,封装成一个方法createJobConfig,return new SpringJobScheduler(myElasticJob, registryCenter,createJobConfig(myElasticJob.getClass(),"0/3 * * * * ?", 1, null));}}
测试:
如何开启多个服务呢?
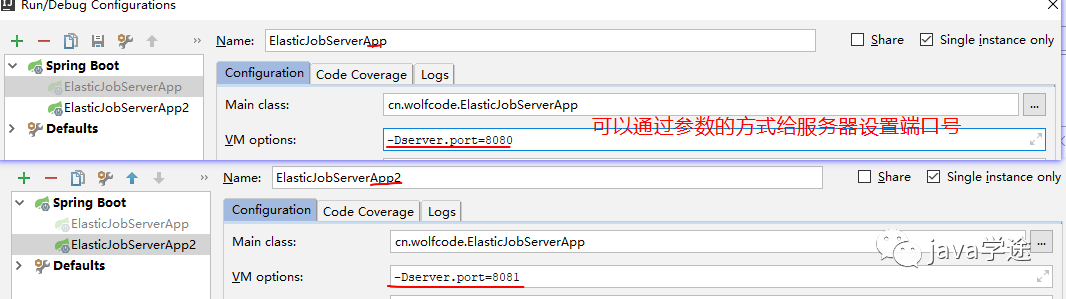
效果和快速入门是一样的,两个服务器只有一个在执行分时任务,当执行的服务器挂掉之后,会选举出新的服务器做分时任务。
4.案例需求
需求:数据库中有一些列的数据,需要对这些数据进行备份操作,备份完之后,修改数据的状态,标记已经备份了。
4.1 初始化数据
在数据库中导入elastic-job-demo.sql
数据;
4.2 集成Druid&MyBatis
4.2.1 添加依赖
<dependency><groupId>com.alibaba</groupId><artifactId>druid</artifactId><version>1.1.10</version></dependency><dependency><groupId>org.mybatis.spring.boot</groupId><artifactId>mybatis-spring-boot-starter</artifactId><version>1.2.0</version></dependency><!--mysql驱动--><dependency><groupId>mysql</groupId><artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId></dependency>
4.2.2 添加配置
spring:datasource:url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/elastic-job-demo?serverTimezone=GMT%2B8driverClassName: com.mysql.jdbc.Drivertype: com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSourceusername: rootpassword: root
4.2.3 添加实体类
@Datapublic class FileCustom {//唯一标识private Long id;//文件名private String name;//文件类型private String type;//文件内容private String content;//是否已备份private Boolean backedUp = false;public FileCustom(){}public FileCustom(Long id, String name, String type, String content){this.id = id;this.name = name;this.type = type;this.content = content;}}
4.2.4 添加Mapper处理类
使用注解的方式操作MyBatis执行SQL语句:
/*** 连接MySQL数据库的mapper接口*/@Mapperpublic interface FileCustomMapper {//执行SQL的方式有两种:mapper.xml 和注解的方式,这里使用注解的方式执行SQL语句@Select("SELECT * FROM t_file_custom WHERE backedUp = 0")List<FileCustom> selectAll();@Update("UPDATE t_file_custom SET backedUp = #{state} WHERE id = #{id}")int changeState(@Param("id") Long id,@Param("state") int state);}
4.3 业务功能实现
4.3.1 添加任务类
/*** 任务类:数据库中有一些列的数据,需要对这些数据进行备份操作,备份完之后,修改数据的状态,标记已经备份了。*/@Componentpublic class FileCustomJob implements SimpleJob{@Autowiredprivate FileCustomMapper fileCustomMapper;@Overridepublic void execute(ShardingContext shardingContext) {doWork();}private void doWork(){List<FileCustom> fileList = fileCustomMapper.selectAll();System.out.println("此次需要备份文件个数:"+fileList.size());for(FileCustom fileCustom:fileList){backUpFile(fileCustom);}}private void backUpFile(FileCustom fileCustom){try {//模拟备份动作,假设一堆操作花一秒钟TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}System.out.println("执行文件备份====> id:"+fileCustom.getId()+" 类型:"+fileCustom.getType());fileCustomMapper.changeState(fileCustom.getId(),1);}}
4.3.2 添加任务调度配置
在配置类中新增这个Bean,将任务类加入配置当中生效。
@Bean(initMethod = "init")public SpringJobScheduler initFileCustomElasticJob(FileCustomElasticJob fileCustomElasticJob){SpringJobScheduler springJobScheduler = new SpringJobScheduler(fileCustomElasticJob,registryCenter,createJobConfiguration(FileCustomElasticJob.class,"0 0/1 * * * ?",1,null));return springJobScheduler;}
4.4 测试&问题
为了高可用,我们会对这个项目做集群的操作,可以保证其中一台挂了,另外一台可以继续工作.但是在集群的情况下,调度任务只在一台机器上运行,如果单个任务调度比较耗时,耗资源的情况下,对这台机器的消耗还是比较大的,
但是这个时候,其他机器却是空闲着的。如何合理的利用集群的其他机器且如何让任务执行得更快些呢?这时候Elastic-Job提供了任务调度分片的功能。
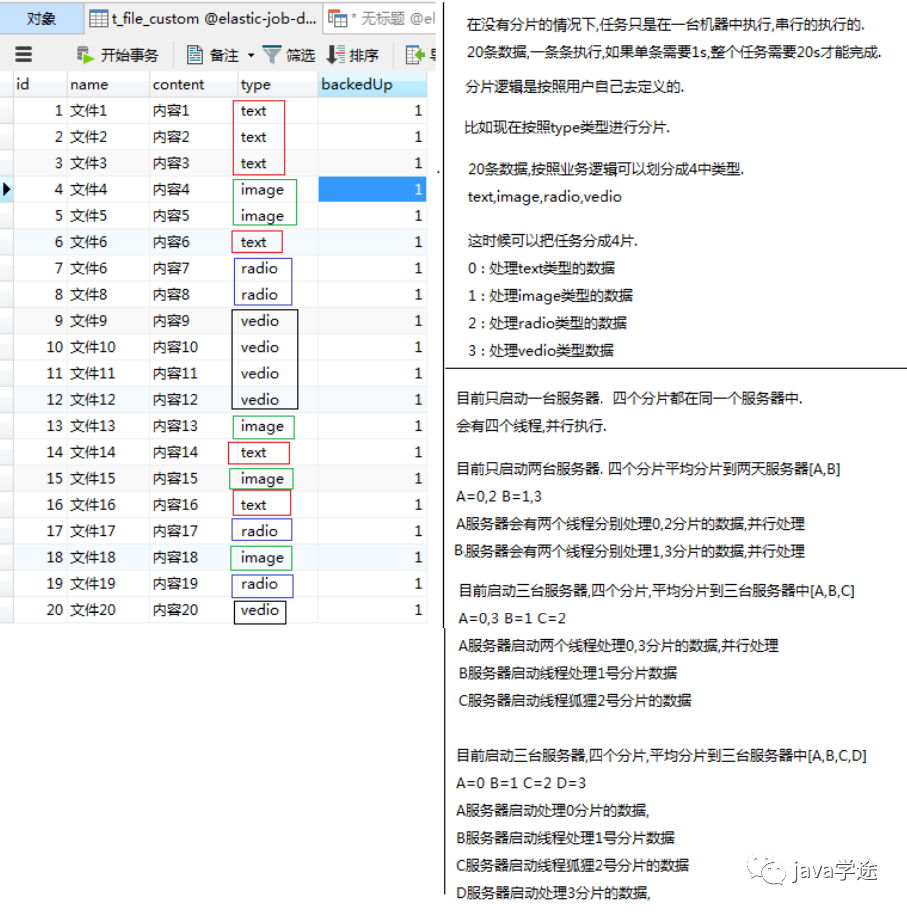
5.分片概念
作业分片是指任务的分布式执行,需要将一个任务拆分为多个独立的任务项,然后由分布式的应用实例分别执行某一个或者几个分布项。
例如:Elastic-Job快速入门中文件备份的案例,现有两台服务器,每台服务器分别跑一个应用实例。为了快速执行作业,那么可以讲任务分成4片,每个应用实例都执行两片。作业遍历数据逻辑应为:实例1查找text和image类型文件执行备份,实例2查找radio和vedio类型文件执行备份。如果由于服务器拓容应用实例数量增加为4,则作业遍历数据的逻辑应为: 4个实例分别处理text,image,radio,video类型的文件。
可以看到,通过对任务的合理分片化,从而达到任务并行处理的效果.
分片项与业务处理解耦
Elastic-Job并不直接提供数据处理的功能,框架只会将分片项分配至各个运行中的作业服务器,开发者需要自行处理分片项与真实数据的对应关系
最大限度利用资源
将分片项设置大于服务器的数据,最好是大于服务器倍数的数量,作业将会合理利用分布式资源,动态的分配分片项.
例如: 3台服务器,分成10片,则分片项结果为服务器A=0,1,2;服务器B=3,4,5;服务器C=6,7,8,9.如果 服务器C奔溃,则分片项分配结果为服务器A=0,1,2,3,4;服务器B=5,6,7,8,9.在不丢失分片项的情况下,最大限度利用现有的资源提高吞吐量。
在没有分片的情况下,任务仅仅在一台服务器上执行的,并且是串行执行,所有数据逐条执行,完成整个任务还是很耗时,对执行的服务器压力还是很大。我们可以将数据按照业务逻辑(type)进行分片;
分成四片:0:text、1:image、2:radio、3:video 每种序号的分片分别处理四种类型的数据;
6.案例改造成任务分片
6.1 配置类修改
在任务配置类中增加分片个数以及分片参数.
@Bean(initMethod = "init")public SpringJobScheduler initFileCustomElasticJob(FileCustomElasticJob fileCustomElasticJob){SpringJobScheduler springJobScheduler = new SpringJobScheduler(fileCustomElasticJob,registryCenter,createJobConfiguration(FileCustomElasticJob.class,"0 0/1 * * * ?",4,"0=text,1=image,2=radio,3=vedio"));return springJobScheduler;}
6.2 新增作业分片逻辑
@Componentpublic class FileCustomJob implements SimpleJob {@Autowiredprivate FileCustomMapper fileCustomMapper;@Overridepublic void execute(ShardingContext shardingContext) {System.out.println("ShardingParameter:" + shardingContext.getShardingParameter());System.out.println("ShardingItem:" + shardingContext.getShardingItem());doWork(shardingContext.getShardingParameter());}private void doWork(String shardingParameter) {List<FileCustom> fileList = fileCustomMapper.selecByType(shardingParameter);System.out.println("线程id :" + Thread.currentThread().getId());System.out.println("分片的类型为:" + shardingParameter + "此次需要备份文件个数:" + fileList.size());for (FileCustom fileCustom : fileList) {backUpFile(fileCustom);}}private void backUpFile(FileCustom fileCustom) {try {//模拟备份动作,假设一堆操作花一秒钟TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}System.out.println("执行文件备份====> id:" + fileCustom.getId() + " 类型:" + fileCustom.getType());fileCustomMapper.changeState(fileCustom.getId(), 1);}}
6.3 Mapper类修改
@Mapperpublic interface FileCustomMapper {@Select("select * from t_file_custom where backedUp = 0")List<FileCustom> selectAll();@Select("select * from t_file_custom where backedUp = 0 and type=#{fileType}")List<FileCustom> selecByType(String fileType);@Update("update t_file_custom set backedUp = #{state} where id = #{id}")int changeState(@Param("id") Long id, @Param("state")int state);}
6.4 测试
只有一台机器的情况下,任务分片是如何执行的:4个线程并行执行;
有多台机器的情况下,任务分片是如何执行的:两台服务器,每个服务器两条线程并行执行;
7.Dataflow类型调度任务
Dataflow类型的定时任务需要实现Dataflowjob接口,该接口提供2个方法供覆盖,分别用于抓取(fetchData)和处理(processData)数据,我们继续对例子进行改造。
Dataflow类型用于处理数据流,他和SimpleJob不同,它以数据流的方式执行,调用fetchData抓取数据,知道抓取不到数据才停止作业。
SimpleJob类型是一次性的取出,然后执行;
Dataflow每次取,直到取不到为止;
应用场景:
现在定时任务需要处理100w数据;单条数据对象比较大,一次性查询出来的话,到时内存溢出。所以选择Dataflow类型的定时任务;Dataflow一次取10w,10w做完之后再去下一个10w的数据。
7.1 任务类
@Componentpublic class FileDataflowJob implements DataflowJob<FileCustom> {@Autowiredprivate FileCustomMapper fileCustomMapper;@Overridepublic List<FileCustom> fetchData(ShardingContext shardingContext) {List<FileCustom> fileCustoms = fileCustomMapper.fetchData(2);System.out.println("抓取时间:"+new Date()+",个数"+fileCustoms.size());return fileCustoms;}@Overridepublic void processData(ShardingContext shardingContext, List<FileCustom> data) {for(FileCustom fileCustom:data){backUpFile(fileCustom);}}private void backUpFile(FileCustom fileCustom){try {//模拟备份动作TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}System.out.println("执行文件备份====>"+fileCustom);fileCustomMapper.changeState(fileCustom.getId(),1);}}
Mapper中的fetchData方法:
@Select("SELECT * FROM t_file_custom WHERE backedUp = 0 limit 0,#{size}")List<FileCustom> fetchData(int size);
7.2 配置类
/*** 任务调度配置类*/@Configurationpublic class ElasticJobConfig {@Autowired //注入下文参数2private CoordinatorRegistryCenter registryCenter;//返回作业配置的方法 参数3 需要//同样的 newBuilder的参数不能写死,用方法来传递参数来解决,所以定义了四个形参private LiteJobConfiguration createJobConfig(Class<? extends ElasticJob> clazz, //任务类的字节码String cron, //cron表达式int shrdingTotalCount, //分片个数String shardingParamter, //分片参数Boolean isDataFlowType //是否是数据流DataflowJob类型的任务) {JobCoreConfiguration.Builder builder = JobCoreConfiguration.newBuilder(clazz.getSimpleName(), cron, shrdingTotalCount);if (!StringUtils.isEmpty(shardingParamter)) {//如果传了分片参数,我们需要设置进去builder.shardingItemParameters(shardingParamter);}//数据流DataflowJob类型的任务需要用到 JobTypeConfiguration 做配置定义JobTypeConfiguration jobTypeConfiguration = null;//根据不同的;任务累心设置不同的配置对象if (isDataFlowType){//是DataflowJob数据流类型的任务// 定义DataflowJob类型配置jobTypeConfiguration = new DataflowJobConfiguration(builder.build(), clazz.getCanonicalName(),true);}else {//不是DataflowJob数据流类型的任务// 定义SIMPLE类型配置jobTypeConfiguration = new SimpleJobConfiguration(builder.build(), clazz.getCanonicalName());}// 定义Lite作业根配置//overwrite(true):如果没有这个配置,分片参数的值将始终是第一次设置的值,不会被覆盖,代码修改没有效果,只能删除配置重新设置;加上即可覆盖LiteJobConfiguration simpleJobRootConfig = LiteJobConfiguration.newBuilder(jobTypeConfiguration).overwrite(true).build();return simpleJobRootConfig;}/*返回作业配置的方法 参数3 需要同样的 newBuilder的参数不能写死,用方法来传递参数来解决,所以定义了四个形参private LiteJobConfiguration createJobConfig(Class<? extends ElasticJob> clazz, 任务类的字节码String cron, cron表达式int shrdingTotalCount, 分片个数String shardingParamter 分片参数) {JobCoreConfiguration.Builder builder = JobCoreConfiguration.newBuilder(clazz.getSimpleName(), cron, shrdingTotalCount);if (!StringUtils.isEmpty(shardingParamter)) {//如果传了分片参数,我们需要设置进去builder.shardingItemParameters(shardingParamter);}// 定义作业核心配置//参数1:作业名称;参数2:corn 表达式;参数3:分片数//JobCoreConfiguration simpleCoreConfig = JobCoreConfiguration.newBuilder("demoSimpleJob", "0/3 * * * * ?", 1).build(); //不写死JobCoreConfiguration simpleCoreConfig = builder.build(); //把builder提起前的原因是要设置分片的次数// 定义SIMPLE类型配置//参数1:作业配置;参数2:任务类的全限定名;SimpleJobConfiguration simpleJobConfig = new SimpleJobConfiguration(simpleCoreConfig, clazz.getCanonicalName());// 定义Lite作业根配置//overwrite(true):如果没有这个配置,分片参数的值将始终是第一次设置的值,不会被覆盖,代码修改没有效果,只能删除配置重新设置;加上即可覆盖LiteJobConfiguration simpleJobRootConfig = LiteJobConfiguration.newBuilder(simpleJobConfig).overwrite(true).build();return simpleJobRootConfig;}*//*@Bean(initMethod = "init") // 需要将MyElasticJob对象给注入进来,这里给MyElasticJob创建对象并做初始化public SpringJobScheduler initMyElasticJobBean(MyElasticJob myElasticJob) {//需要的参数:// 参数1ElasticJob类型的参数:myElasticJob是间接继承自ElasticJob的,// 参数2:需要注入RegistryCenterConfig的对象// 参数3LiteJobConfiguration:内容比较多,封装成一个方法createJobConfig,return new SpringJobScheduler(myElasticJob, registryCenter,createJobConfig(myElasticJob.getClass(),"0/3 * * * * ?", 1, null));}*//*@Bean(initMethod = "init") //一分钟去执行public SpringJobScheduler initMyElasticJobBean(FileCustomJob fileCustomJob) {return new SpringJobScheduler(fileCustomJob, registryCenter,//createJobConfig(fileCustomJob.getClass(),"0 0/1 * * * ?", 1, null)); //不分片的情况createJobConfig(fileCustomJob.getClass(),"0 0/1 * * * ?", 4, "0=text,1=image,2=radio,3=vedio"));}*/@Bean(initMethod = "init") //一分钟去执行一次public SpringJobScheduler initFileDataflowJobBean(FileDataflowJob fileDataflowJob) {return new SpringJobScheduler(fileDataflowJob, registryCenter,createJobConfig(fileDataflowJob.getClass(),"0 0/1 * * * ?", 1, null,true)); //不分片的情况}}
7.3 测试
8.运维管理
8.1 事件追踪
Elastic-Job-Lite在配置中提供了JobEventConfiguration,支持数据库方式配置,会在数据库中自动创建JOB_EXECUTION_LOG和JOB_STATUS_TRACE_LOG两张表以及若干索引来近路作业的相关信息。
8.1.1 修改Elastic-Job配置类
在ElasticJobConfig配置类中注入DataSource
@Configurationpublic class ElasticJobConfig {@Autowired //注入DataSourceprivate DataSource dataSource;......}
在任务配置中增加事件追踪配置
@Bean(initMethod = "init")public SpringJobScheduler initFileCustomElasticJob(FileCustomElasticJob fileCustomElasticJob){//增加任务事件追踪配置,即可做事件追踪JobEventConfiguration jobEventConfiguration = new JobEventRdbConfiguration(dataSource);SpringJobScheduler springJobScheduler = new SpringJobScheduler(fileCustomElasticJob,registryCenter,createJobConfiguration(FileCustomElasticJob.class,"0 0/1 * * * ?",4,"0=text,1=image,2=radio,3=vedio",false),jobEventConfiguration);return springJobScheduler;}
8.1.2 日志信息表
启动后会发现在elastic-job-demo数据库中新增以下两张表
job_execution_log
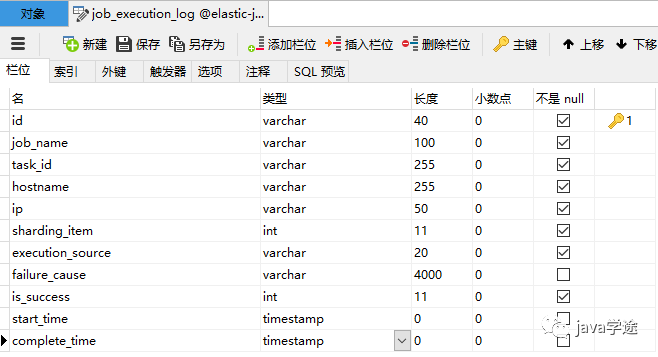
记录每次作业的执行历史,分为两个步骤:
1.作业开始执行时间想数据库插入数据.
2.作业完成执行时向数据库更新数据,更新is_success,complete_time和failure_cause(如果任务执行失败)
job_status_trace_log
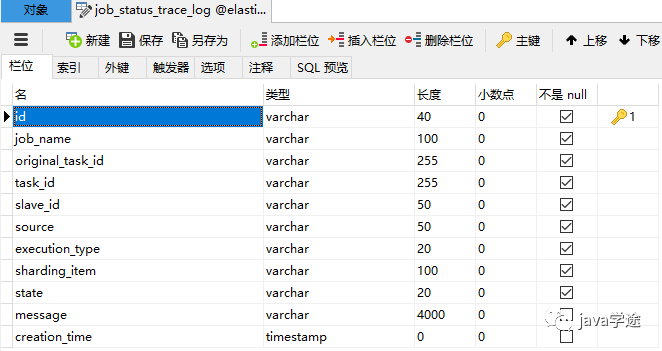
记录作业状态变更痕迹表,可通过每次作业运行的task_id查询作业状态变化的生命轨迹和运行轨迹.
8.2 运维控制台
elastic-job中提供了一个elastic-job-lite-console控制台
设计理念
1.本 控制台和Elastic-Job并无直接关系,是通过读取Elastic-Job的注册中心数据展示作业状态,或更新注册中心数据修改全局配置。
2.控制台只能控制任务本身是否运行,但不能控制作业进程的启停,因为控制台和作业本身服务器是完全分布式的,控制台并不能控制作业服务器。
主要功能:
1.查看作业以及服务器状态
2.快捷的修改以及删除作业配置
3.启用和禁用作业
4.跨注册中心查看作业
5.查看作业运行轨迹和运行状态
不支持项
1.添加作业,因为作业都是在首次运行时自动添加,使用控制台添加作业并无必要.直接在作业服务器启动包含Elasitc-Job的作业进程即可。
8.2.1 搭建步骤
解压缩
elastic-job-lite-console-2.1.5.tar进入bin目录,并执行:
bin\start.bat打开浏览器访问
http://localhost:8899用户名: root 密码: root,进入之后界面如下:
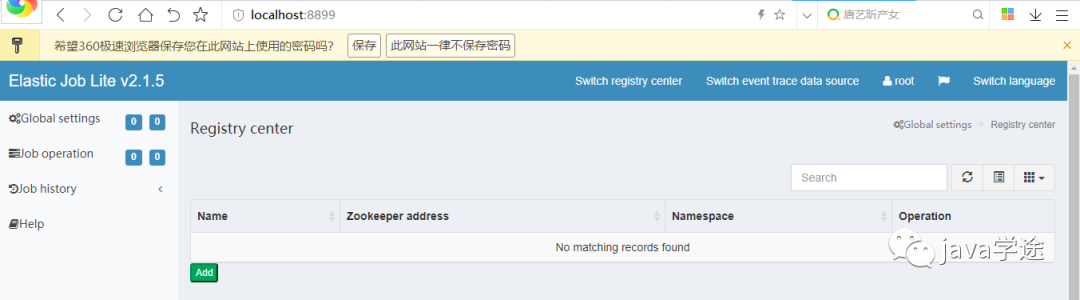
提供两种用户:管理员和访客,管理员拥有全部操作权限,访客仅拥有查看权限。默认管理员账号和面膜是root/root,访客用户名和密码是guest/guest,通过conf\auth.properties可以修改管理员以及访客用户名及密码
8.2.2 配置及使用
配置注册中心地址
先启动zookeeper然后再注册中心配置界面,点添加
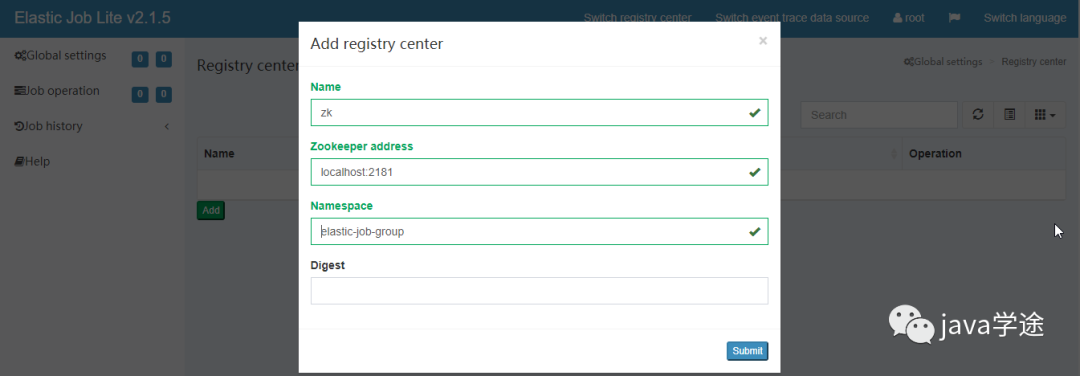
点击提交后,然后点连接(zookeeper必须处于启动状态)
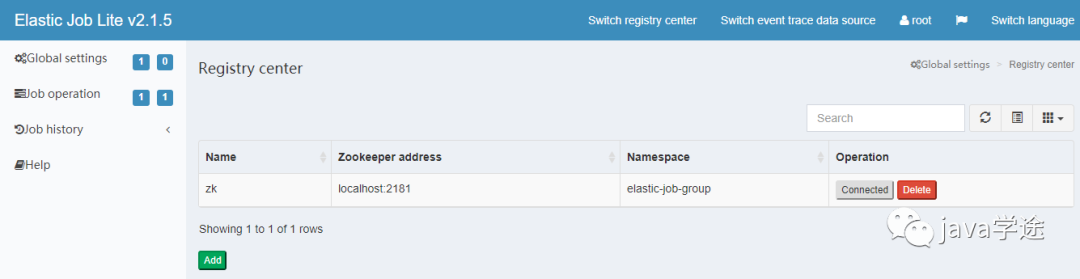
连接成功后,在作业纬度下可以显示该命名空间作业名称,分片数量及该作业的cron表达式等信息
在服务器纬度可以查看到服务器ip,当前运行的是实例数,作业总数等信息。
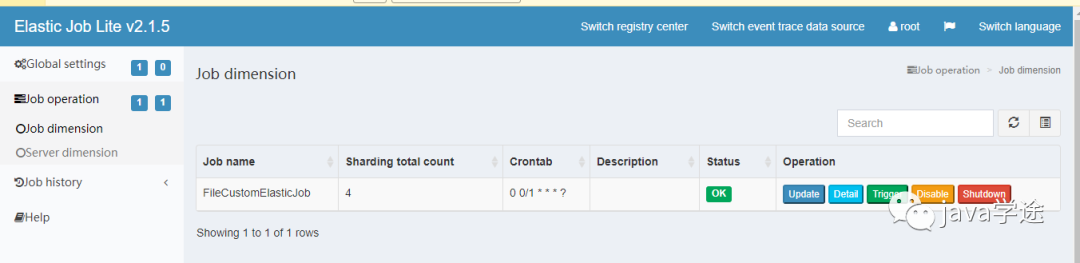
添加数据库连接之后可以查看任务的执行结果
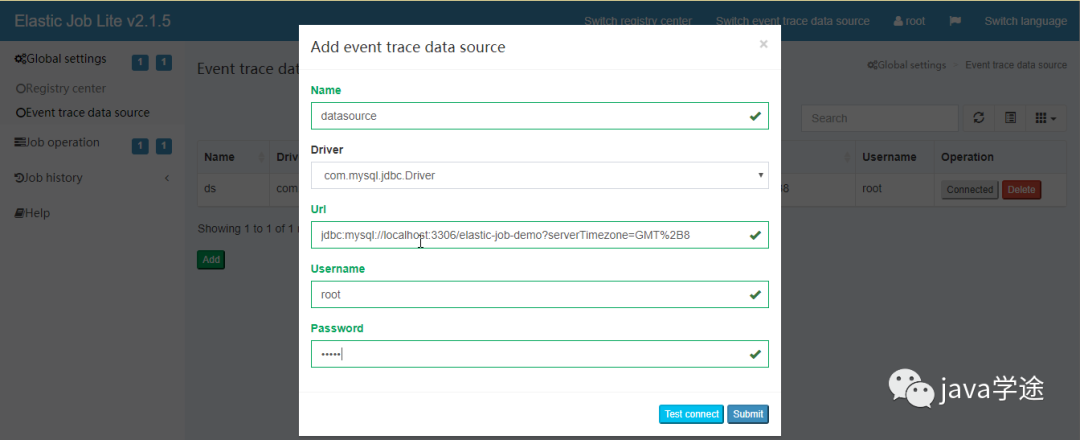
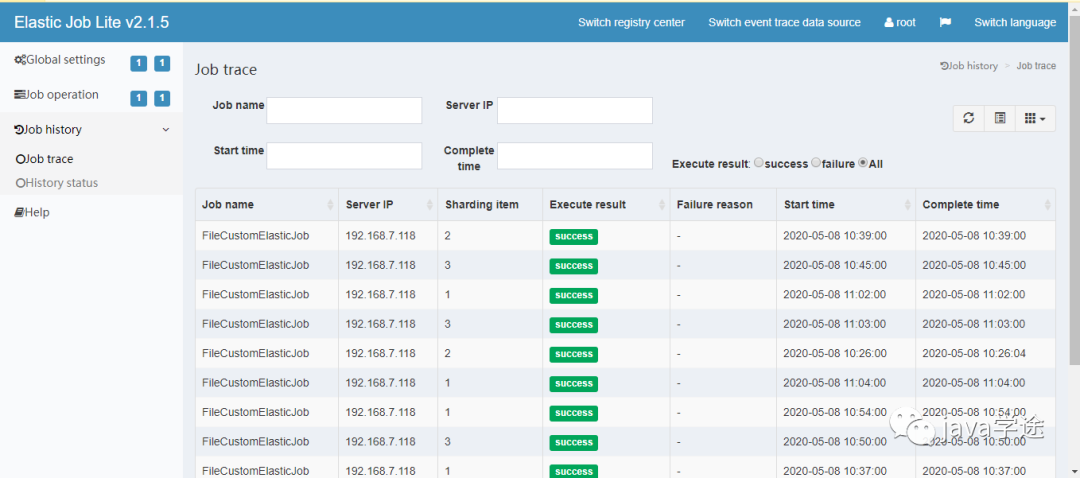
然后在作业历史中就可以看到任务执行历史了。
补充
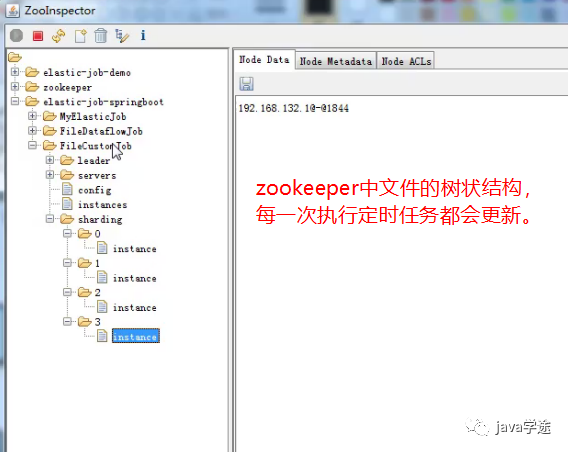
管控台的数据其实都是从zookeeper
和数据库获取出来的。
小伙砸,欢迎再看分享给其他小伙伴!共同进步!