pandas 可以分析结构化数据,DataFrame是pandas中的一个表格型的数据结构,包含有一组有序的列,每列可以是不同的值类型(数值,字符串,布尔型等), DataFrame既有行索引也有列索引,可以被看作是有series组成的字典
因为要写入excel的列宽不同,所以采用concat连接函数,axis=1 为横向(columns)合并
多次写入excel不同的sheet,通过ExcelWriter方法中加参数mode避免写入被覆盖的问题
def to_excel(list1, list2, name):"""数据写入到excel,写入到不同的sheet"""diff = pd.concat([pd.DataFrame({u'业务表有单据表无': list1}), pd.DataFrame({u'单据表有业务表无': list2})],axis=1)if not os.path.exists(r'diff.xlsx'):writer = pd.ExcelWriter('diff.xlsx')diff.to_excel(writer, sheet_name=name, encoding='UTF-8', index=False)else:# mode=a append已有excelwriter = pd.ExcelWriter('diff.xlsx', mode='a')diff.to_excel(writer, sheet_name=name, encoding='UTF-8', index=False)writer.save()writer.close()
创建DataFrame的几种方法
利用字典创建,为每一列赋值,字典key值为列索引
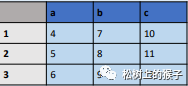
df = pd.DataFrame({"a" : [4 ,5, 6],"b" : [7, 8, 9],"c" : [10, 11, 12]},index = [1, 2, 3])
利用数组创建,为每一行赋值,不需要index时置为false即可
df2 = pd.DataFrame(np.array([[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6], [7, 8, 9]]), index=Falsecolumns=['a', 'b', 'c'])df2a b c1 2 34 5 67 8 9
多个索引创建
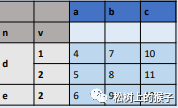
df = pd.DataFrame({"a" : [4 ,5, 6],"b" : [7, 8, 9],"c" : [10, 11, 12]},index = pd.MultiIndex.from_tuples([('d',1),('d',2),('e',2)],names=['n','v']))
参照文档:
https://www.pypandas.cn/docs/
https://pandas.pydata.org/
文章转载自松树上的猴子,如果涉嫌侵权,请发送邮件至:contact@modb.pro进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,墨天轮将立刻删除相关内容。






