
读写Excel三种常用技术
1.POI:
Apache POI是Apache软件基金会的开放源码函数库,POI提供API给Java程序对Microsoft Office格式档案读和写的功能。
HSSF是Horrible SpreadSheet Format的缩写,也即“讨厌的电子表格格式”
,通过HSSF,你可以用纯Java代码来读取,写入,修改,Excel文件。
HSSF-读写Microsoft Excel格式档案的功能
XSSF-读写micorsoft Excel OOXML格式档案的功能
HWPF-读写micorsoft Word格式档案的功能
HSLF-读写microsoft PowerPoint格式档案
HDGF-读写Microsoft Visio格式档案的功能
iText:通过itext不仅可以生成PDF或者rtf的文档,而且可以将xml,Html文件转化为PDF文件
下载iText.jar文件后,只需要在系统的ClassPath中加入iText.jar的路径,在程序中就可以使用iText类库了。
2.JXL
Java Excel是一种开放的源码项目,可以读取Excel文件的内容,创建新的Excel文件,更新已经存在的Excel文件
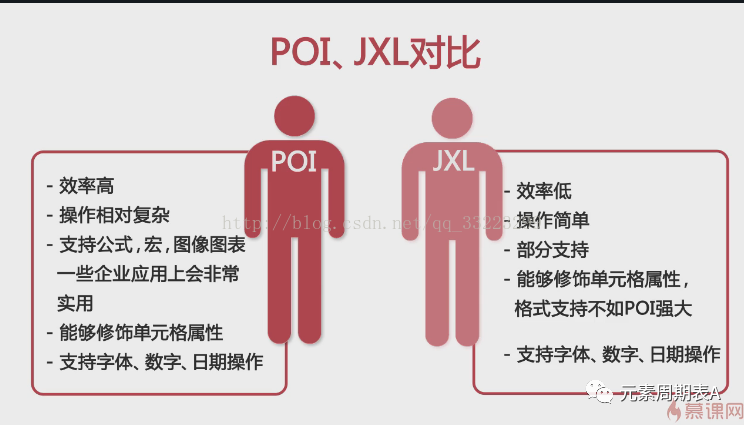
POI和JXL对比
POI:效率高,操作复杂,支持公式,宏,图表图像一些企业应用上会非常实用,能够修饰单元格属性,支持字体,数字,日期操作。
JXL:效率低,操作简单,部分支持,能够修饰单元格属性,格式支持不如POI强大,支持字体,数字,日期操作
3.FSATEXCEL
是一个采用纯Java开发的excel文件读写组件,支持Excel97-2003文件格式。只能读取单元格的字符信息,而其他属性如颜色,字体就不支持了。因此只需很小的内存。
代码实现:
1.导入pom,版本号要一致
<!--读取excel文件--><dependency><groupId>org.apache.poi</groupId><artifactId>poi</artifactId><version>3.17</version></dependency><!--导出excel文件--><dependency><groupId>org.apache.poi</groupId><artifactId>poi-ooxml</artifactId><version>3.17</version></dependency>
导出功能:
public static void main(String[] args) {String title[]= {"名字","课程","分数"};//1.创建Excel工作簿HSSFWorkbook workbook=new HSSFWorkbook();//2.创建一个工作表HSSFSheet sheet=workbook.createSheet("sheet2");//3.创建第一行HSSFRow row=sheet.createRow(0);HSSFCell cell=null;//4.插入第一行数据for (int i = 0; i < title.length; i++) {cell=row.createCell(i);cell.setCellValue(title[i]);}//5.追加数据// Data data=new Data();// ResultSet rs=data.getString();// while(rs.next()) {// HSSFRow row2=sheet.createRow(rs.getRow());// HSSFCell cell2=row2.createCell(0);// cell2.setCellValue(rs.getString(1));// cell2=row2.createCell(1);// cell2.setCellValue(rs.getString(2));// cell2=row2.createCell(2);// cell2.setCellValue(rs.getString(3));// }//创建一个文件,将Excel内容存盘File file=new File("e:/sheet2.xls");try {file.createNewFile();FileOutputStream stream=FileUtils.openOutputStream(file);workbook.write(stream);stream.close();} catch (IOException e) {// TODO Auto-generated catch blocke.printStackTrace();}}
导入功能:
public static void readExcel(String fileName) throws Exception {fileName = "E:/firefox_download/2021-05-18.xlsx";//fileName = "E:/firefox_download/llll.xlsx";InputStream is = new FileInputStream(new File(fileName));Workbook hssfWorkbook = null;if (fileName.endsWith("xlsx")) {// Excel 2007hssfWorkbook = new XSSFWorkbook(is);} else if (fileName.endsWith("xls")) {// Excel 2003hssfWorkbook = new HSSFWorkbook(is);}int SheetNum = hssfWorkbook.getNumberOfSheets();System.out.println("sheet表格数:"+SheetNum);SysUserVO tbClass = null;List<SysUserVO> list = new ArrayList<SysUserVO>();// 循环工作表Sheetfor (int i = 0; i < SheetNum; i++) {// HSSFSheet hssfSheet = hssfWorkbook.getSheetAt(i);Sheet hssfSheet = hssfWorkbook.getSheetAt(i);if (hssfSheet == null) {continue;}// 循环行Rowfor (Row row:hssfSheet) {//第一行标题可不读if (row.getRowNum() ==0){continue;}if (row != null) {tbClass = new SysUserVO();Cell cId = row.getCell(0);Cell cName = row.getCell(1);// 处理具体的业务数据,把业务数据装到List中//tbClass.setUsername(Integer.parseInt(getStringValueFromCell(cId)));tbClass.setUsername(cId.toString());list.add(tbClass);}}}// List中的数据就是在Excel中读取的内容for (SysUserVO tbClass2 : list) {// 在这里可以进行业务操作}}
2021.05.20公司业务开发,需导入大量数据
解决内存问题的关键就是使用流式处理,读取一批数据解析完后就释放,再进行下一批,Streaming-Reader就是使用这种方式.
<dependency><groupId>com.monitorjbl</groupId><artifactId>xlsx-streamer</artifactId><version>2.0.0</version></dependency>
/*** service层读取操作*/public HashMap<String, String> importExcel(MultipartFile file, String targetDate) throws Exception {HashMap<String,String> map = new HashMap<>();InputStream in = file.getInputStream();Workbook wk = StreamingReader.builder()//缓存到内存中的行数,默认是10.rowCacheSize(100)//读取资源时,缓存到内存的字节大小,默认是1024.bufferSize(4096)//打开资源,必须,可以是InputStream或者是File,注意:只能打开XLSX格式的文件.open(in);Sheet sheet = wk.getSheetAt(0);CurveBean curveBean = null;List<CurveBean> list = new ArrayList<>();SimpleDateFormat df = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");System.out.println("导入开始:"+df.format(new Date()));//遍历所有的行for (Row row:sheet){//第一行标题不读if (row.getRowNum() == 0) {continue;}//logger.info("开始遍历第" + row.getRowNum() + "行数据:");//获取列的值Cell time = row.getCell(0);Cell param1 = row.getCell(1);Cell param2 = row.getCell(2);Cell param3 = row.getCell(3);Cell param4 = row.getCell(4);Cell param5 = row.getCell(5);curveBean = new CurveBean();curveBean.setTargetDate(targetDate);if (time != null && time.getCellTypeEnum() !=CellType.BLANK ){String excelTime = time.getStringCellValue();SimpleDateFormat format = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy/MM/dd HH:mm:ss");Date parse = format.parse(excelTime);SimpleDateFormat format2 = new SimpleDateFormat("HHmmss");String realTime = format2.format(parse);curveBean.setTargetTime(realTime);}if (param1 != null && param1.getCellTypeEnum() !=CellType.BLANK ){curveBean.setParam1(Float.parseFloat(param1.getStringCellValue()));}if (param2 != null && param2.getCellTypeEnum() !=CellType.BLANK){curveBean.setParam2(Float.parseFloat(param2.getStringCellValue()));}if (param3 != null && param3.getCellTypeEnum() !=CellType.BLANK ){curveBean.setParam3(Float.parseFloat(param3.getStringCellValue()));}if (param4 != null && param4.getCellTypeEnum() !=CellType.BLANK ){curveBean.setParam4(Float.parseFloat(param4.getStringCellValue()));}if (param5 != null && param5.getCellTypeEnum() !=CellType.BLANK ){curveBean.setParam5(Float.parseFloat(param5.getStringCellValue()));}list.add(curveBean);}System.out.println("导入结束:"+df.format(new Date()));// new Date()为获取当前系统时间// 处理具体的业务数据,写入实时表与历史表System.out.println("读取到数据量:"+ list.size());// 单行插入效率慢// for (CurveBean bean : list) {// curveDao.saveCurveBean(bean);// curveHisDao.saveCurveBean(bean);// }System.out.println("数据插入开始:"+df.format(new Date()));//批量插入int batchNum = 2000;//循环次数int num = list.size()/batchNum + 1;int listSize=list.size();int toIndex=2000;//int keyToken = 0;for(int i = 0;i<list.size();i+=2000){//作用为toIndex最后没有5000条数据则剩余几条newList中就装几条if(i+2000>listSize){toIndex=listSize-i;}List newList = list.subList(i,i+toIndex);//System.out.println("插入数据条数:"+newList.size());curveDao.saveBatchCurveBean(newList);curveHisDao.saveBatchCurveBean(newList);//keyToken++;}System.out.println("数据插入结束:"+df.format(new Date()));map.put("code","200");map.put("msg","模板导入成功!");return map;}
注意解释:判断表格是否为空 与 表格中字符串是否为空的方法
网上大部分都是4.0以下的判断单元格是否为空如下:cell != null || cell.getCellType() != Cell.CELL_TYPE_BLANK(这个方法在4.0以后已经被废弃了)最新的应该是cell.getCellType() !=CellType.BLANK
读取完成,数据入库阶段:
数据批量插入:
<insert id="saveBatchCurveBean" parameterType="java.util.List">INSERT INTO ${TH_DB_PEFIX}T_UNIT_TARGETVAL_REAL(TARGETDATE, TARGETTIME, T1, T2,T3,T4,T5)VALUES<foreach collection="list" item="item" separator=",">(#{item.targetDate},#{item.targetTime},#{item.param1},#{item.param2},#{item.param3},#{item.param4},#{item.param5})</foreach></insert>
//dao层接口void saveBatchCurveBean(List<CurveBean> list);
对list数据循环截取插入的操作demo:
List<String> list = new ArrayList<>();list.add("a,"); list.add("a,");list.add("a,");list.add("a,");list.add("a,");list.add("b1");list.add("b2");int listSize=list.size();int toIndex=10;int keyToken = 0;for(int i = 0;i<list.size();i+=10){//作用为toIndex最后没有10条数据则剩余几条newList中就装几条if(i+10>listSize){toIndex=listSize-i;}List newList = list.subList(i,i+toIndex);System.out.println(newList);keyToken++;}






