简介
用磁盘上的文件实现,替换共享内存固定大小的空闲空间映射(FSM)。
看到这个定义,当时就想起了main、VM、FSM这三种磁盘上的文件,按照上面的定义来说难道还有某个版本的PG中FSM文件不是存储在磁盘上的?赶紧上官网查了一下,恍然大悟ing... ...
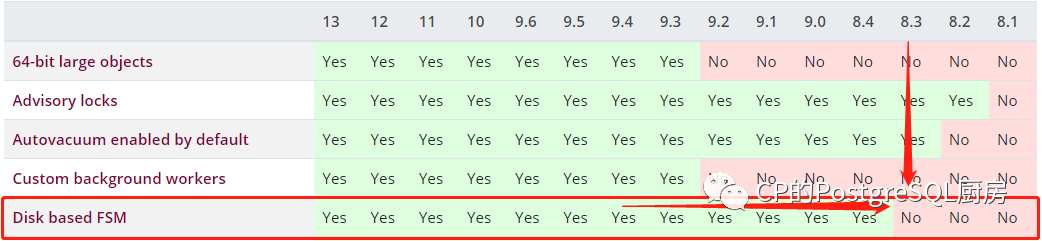
原来8.3之前FSM可见空间映射文件是不存储在物理磁盘上的呀~
定义说明
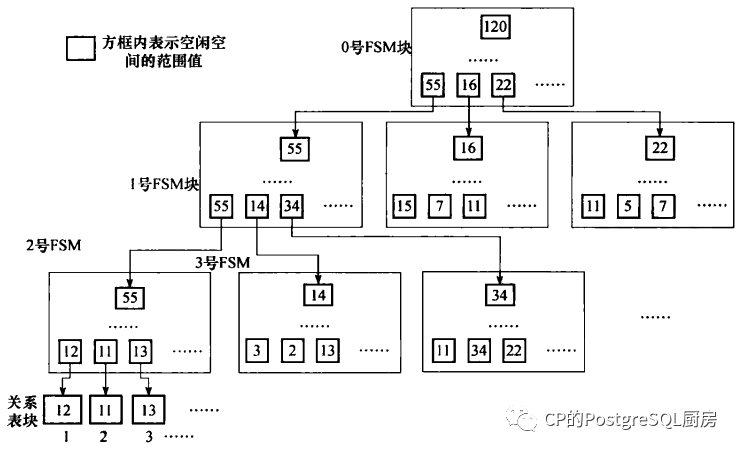
FSM,指的是Free Space Map,空闲空间映射表。一个relation有多个8KB大小的block,这些block存储在磁盘上。一个relation最大只能有4G个block,每个block大小为8KB,也就是说一个relation的磁盘大小最大为32TB。
relation的不断的插入删除记录,会造成很多的block其实是有空闲空间的,Page的空闲空间管理的只是8KB空间内有多少剩余空间,而FSM管理的则是relation对应的所有的Block(或者说page,whatever,反正都是这8KB的空间)分别有多少剩余空间。
-rw-------. 1 postgres postgres 8.0K Nov 16 2020 3600-rw-------. 1 postgres postgres 24K Nov 16 2020 3600_fsm-rw-------. 1 postgres postgres 8.0K Nov 16 2020 3600_vm
在数据库系统内部,这些文件(main、FSM、VM等)也被成为相应关系的分支(fork);空闲空间映射是表/索引数据文件的第一个分支(分支编号为1),可见性映射文件是数据文件的第二个分支(分支编号为2),数据文件的分支编号为0。
每个关系可能有4种分支,分支编号分别为0、1、2、3,0号分支main为关系数据文件的文件主体。1号分支fsm保存了main分支中空闲空间的信息,2号分支vm保存了main分支中可见性的信息,3号分支init是很少见的特殊分支,通常表示不背日志记录的表与索引。
源码导读
创建FSMsrc/include/storage/fsm_internals.h/** Structure of a FSM page. See src/backend/storage/freespace/README for* details.*/typedef struct{/** fsm_search_avail() tries to spread the load of multiple backends by* returning different pages to different backends in a round-robin* fashion. fp_next_slot points to the next slot to be returned (assuming* there's enough space on it for the request). It's defined as an int,* because it's updated without an exclusive lock. uint16 would be more* appropriate, but int is more likely to be atomically* fetchable/storable.*/int fp_next_slot;/** fp_nodes contains the binary tree, stored in array. The first* NonLeafNodesPerPage elements are upper nodes, and the following* LeafNodesPerPage elements are leaf nodes. Unused nodes are zero.*/uint8 fp_nodes[FLEXIBLE_ARRAY_MEMBER];} FSMPageData;
查找FSMsrc/backend/storage/freespace/freespace.c/** The internal FSM routines work on a logical addressing scheme. Each* level of the tree can be thought of as a separately addressable file.*/typedef struct{int level; /* level */int logpageno; /* page number within the level */} FSMAddress;src/backend/storage/freespace/freespace.c/** Search the tree for a heap page with at least min_cat of free space*/static BlockNumberfsm_search(Relation rel, uint8 min_cat){int restarts = 0;FSMAddress addr = FSM_ROOT_ADDRESS;for (;;){int slot;Buffer buf;uint8 max_avail = 0;/* Read the FSM page. */buf = fsm_readbuf(rel, addr, false);/* Search within the page */if (BufferIsValid(buf)){LockBuffer(buf, BUFFER_LOCK_SHARE);slot = fsm_search_avail(buf, min_cat,(addr.level == FSM_BOTTOM_LEVEL),false);if (slot == -1)max_avail = fsm_get_max_avail(BufferGetPage(buf));UnlockReleaseBuffer(buf);}elseslot = -1;if (slot != -1){/** Descend the tree, or return the found block if we're at the* bottom.*/if (addr.level == FSM_BOTTOM_LEVEL)return fsm_get_heap_blk(addr, slot);addr = fsm_get_child(addr, slot);}else if (addr.level == FSM_ROOT_LEVEL){/** At the root, failure means there's no page with enough free* space in the FSM. Give up.*/return InvalidBlockNumber;}else{uint16 parentslot;FSMAddress parent;/** At lower level, failure can happen if the value in the upper-* level node didn't reflect the value on the lower page. Update* the upper node, to avoid falling into the same trap again, and* start over.** There's a race condition here, if another backend updates this* page right after we release it, and gets the lock on the parent* page before us. We'll then update the parent page with the now* stale information we had. It's OK, because it should happen* rarely, and will be fixed by the next vacuum.*/parent = fsm_get_parent(addr, &parentslot);fsm_set_and_search(rel, parent, parentslot, max_avail, 0);/** If the upper pages are badly out of date, we might need to loop* quite a few times, updating them as we go. Any inconsistencies* should eventually be corrected and the loop should end. Looping* indefinitely is nevertheless scary, so provide an emergency* valve.*/if (restarts++ > 10000)return InvalidBlockNumber;/* Start search all over from the root */addr = FSM_ROOT_ADDRESS;}}}
调整FSMsrc/backend/storage/freespace/freespace.c/** RecordPageWithFreeSpace - update info about a page.** Note that if the new spaceAvail value is higher than the old value stored* in the FSM, the space might not become visible to searchers until the next* FreeSpaceMapVacuum call, which updates the upper level pages.*/voidRecordPageWithFreeSpace(Relation rel, BlockNumber heapBlk, Size spaceAvail){int new_cat = fsm_space_avail_to_cat(spaceAvail);FSMAddress addr;uint16 slot;/* Get the location of the FSM byte representing the heap block */addr = fsm_get_location(heapBlk, &slot);fsm_set_and_search(rel, addr, slot, new_cat, 0);}
参考
https://www.postgresql.org/about/featurematrix/detail/140/
“PostgreSQL指南-内幕探索”
“PostgreSQL数据库内核分析”






