作者
digoal
日期
2016-06-12
标签
PostgreSQL , freeze , 大表 , 冻结 , io风暴 , 预测
背景
还记得我写的这篇文档吗? 《PostgreSQL 大表自动 freeze 优化思路》
https://yq.aliyun.com/articles/50411
文章主要针对如何优化大表的freeze调度来减少IO风暴的问题,请注意只是减少,不是避免。
作为一名有追求的PGer,要时刻保持警惕,生于忧患、死于安乐;
本文要给大家讲的是预测风暴,掌握了预测能力,才能未雨绸缪,淡定的面对暴风雨。

预测 IO 风暴
如何预测此类(prevent wrapped vacuum freeze) IO 风暴的来临呢?
首先需要测量几个维度的值。
1. 表的大小以及距离它需要被强制vacuum freeze prevent wrap的年龄
2. 每隔一段时间的XID值的采样(例如每分钟一次),采样越多越好,因为需要用于预测下一个时间窗口的XID。(其实就是每分钟消耗多少个事务号的数据)
3. 通过第二步得到的结果,预测下一个时间窗口的每分钟的pXID(可以使用线性回归来进行预测)
预测方法这里不在细说,也可以参考我以前写的一些预测类的文章。
预测的结论包括 未来一段时间的总Freeze IO量,以及分时的Freeze IO量。
预测结果范例
Freeze IO 时段总量

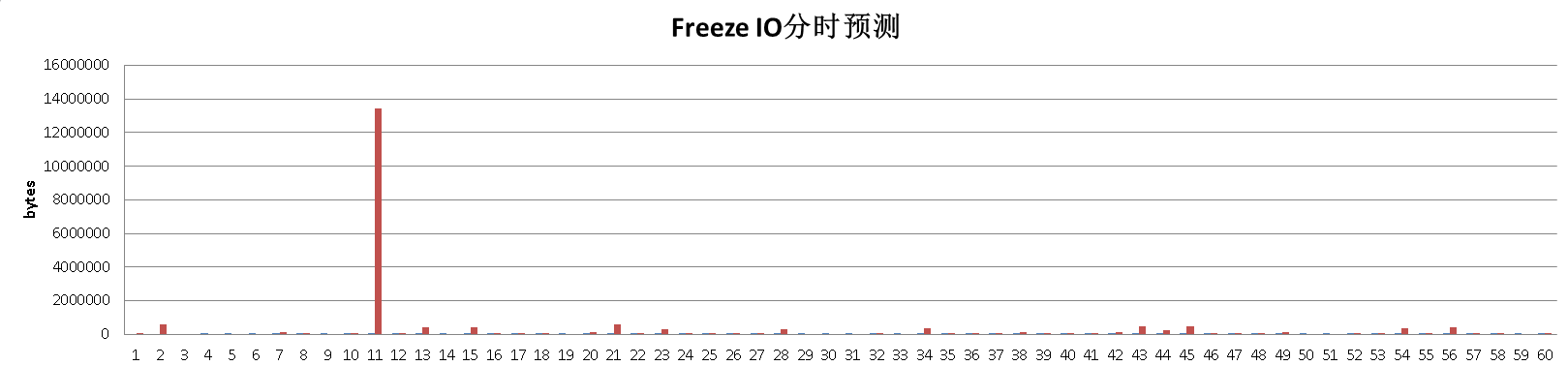
Freeze IO 分时走势
详细的预测过程
1.
每隔一段时间的XID值的采样(例如每分钟一次),采样越多越好,因为需要用于预测下一个时间窗口的XID。(其实就是每分钟消耗多少个事务号的数据)
```
vi xids.sh
!/bin/bash
export PATH=/home/digoal/pgsql9.5/bin:$PATH
export PGHOST=127.0.0.1
export PGPORT=1921
export PGDATABASE=postgres
export PGUSER=postgres
export PGPASSWORD=postgres
psql -c "create table xids(crt_time timestamp, xids int8)"
for ((i=1;i>0;))
do
保留1个月的数据
psql -c "with a as (select ctid from xids order by crt_time desc limit 100 offset 43200) delete from xids where ctid in (select ctid from a);"
psql -c "insert into xids values (now(), txid_current());"
sleep 60
done
chmod 500 xids.sh
nohup ./xids.sh >/dev/null 2>&1 &
```
采集1天的数据可能是这样的
postgres=# select * from xids ;
crt_time | xids
----------------------------+------
2016-06-12 12:36:13.201315 | 2020
2016-06-12 12:37:13.216002 | 9021
2016-06-12 12:38:13.240739 | 21022
2016-06-12 12:39:13.259203 | 32023
2016-06-12 12:40:13.300604 | 42024
2016-06-12 12:41:13.325874 | 52025
2016-06-12 12:42:13.361152 | 62026
2016-06-12 12:43:15.481609 | 72027
...
2.
表的大小以及距离它需要被强制vacuum freeze prevent wrap的年龄
(因为freeze是全集群的,所以需要把所有库得到的数据汇总到一起)
```
vi pred_io.sh
!/bin/bash
export PATH=/home/digoal/pgsql9.5/bin:$PATH
export PGHOST=127.0.0.1
export PGPORT=1921
export PGDATABASE=postgres
export PGUSER=postgres
export PGPASSWORD=postgres
psql -c "drop table pred_io; create table pred_io(crt_time timestamp, bytes int8, left_live int8);"
for db in psql -A -t -q -c "select datname from pg_database where datname <> 'template0'"
do
psql -d $db -c " copy (
select now(), bytes, case when max_age>age then max_age-age else 0 end as xids from
(select block_size*relpages bytes,
case when d_max_age is not null and d_max_age<max_age then d_max_age else max_age end as max_age,
age from
(select
(select setting from pg_settings where name='block_size')::int8 as block_size,
(select setting from pg_settings where name='autovacuum_freeze_max_age')::int8 as max_age,
relpages,
substring(reloptions::text,'autovacuum_freeze_max_age=(\d+)')::int8 as d_max_age,
age(relfrozenxid) age
from pg_class where relkind in ('r', 't')) t) t
) to stdout;" | psql -d $PGDATABASE -c "copy pred_io from stdin"
done
. ./pred_io.sh
```
得到的数据可能是这样的
postgres=# select * from pred_io limit 10;
crt_time | bytes | left_live
----------------------------+--------+-----------
2016-06-12 13:24:08.666995 | 131072 | 199999672
2016-06-12 13:24:08.666995 | 65536 | 199999672
2016-06-12 13:24:08.666995 | 0 | 199999672
2016-06-12 13:24:08.666995 | 0 | 199999672
2016-06-12 13:24:08.666995 | 0 | 199999672
2016-06-12 13:24:08.666995 | 0 | 199999672
...
3.
预测XIDs走势(略),本文直接取昨天的同一时间点开始后的数据。
create view v_pred_xids as
with b as (select min(crt_time) tbase from pred_io),
a as (select crt_time + interval '1 day' as crt_time, xids from xids,b where crt_time >= b.tbase - interval '1 day')
select crt_time, xids - (select min(xids) from a) as xids from a ;
数据可能是这样的,预测未来分时的相对XIDs消耗量
crt_time | xids
----------------------------+------
2016-06-13 12:36:13.201315 | 0
2016-06-13 12:37:13.216002 | 100
2016-06-13 12:38:13.240739 | 200
2016-06-13 12:39:13.259203 | 300
2016-06-13 12:40:13.300604 | 400
4.
结合pred_io与v_pred_xids 进行 io风暴预测
基准视图,后面的数据通过这个基准视图得到
create view pred_tbased_io as
with a as (select crt_time, xids as s_xids, lead(xids) over(order by crt_time) as e_xids from v_pred_xids)
select a.crt_time, sum(b.bytes) bytes from a, pred_io b where b.left_live >=a.s_xids and b.left_live < a.e_xids group by a.crt_time order by a.crt_time;
未来一天的总freeze io bytes预测
postgres=# select min(crt_time),max(crt_time),sum(bytes) from pred_tbased_io ;
min | max | sum
----------------------------+----------------------------+----------
2016-06-13 12:36:13.201315 | 2016-06-14 12:35:26.104025 | 19685376
(1 row)
未来一天的freeze io bytes分时走势
得到的结果可能是这样的
postgres=# select * from pred_tbased_io ;
crt_time | bytes
----------------------------+----------
2016-06-13 12:36:13.201315 | 65536
2016-06-13 12:37:13.216002 | 581632
2016-06-13 12:38:13.240739 | 0
2016-06-13 12:39:13.259203 | 0
2016-06-13 12:40:13.300604 | 0
2016-06-13 12:41:13.325874 | 0
2016-06-13 12:43:15.481609 | 106496
2016-06-13 12:43:24.133055 | 8192
2016-06-13 12:45:24.193318 | 0
2016-06-13 12:46:24.225559 | 16384
2016-06-13 12:48:24.296223 | 13434880
2016-06-13 12:49:24.325652 | 24576
2016-06-13 12:50:24.367232 | 401408
2016-06-13 12:51:24.426199 | 0
2016-06-13 12:52:24.457375 | 393216
......
小结
主要用到什么?
1. 线性回归
2. with语法
3. 窗口函数
4. xid分时消耗统计
5. 强制prevent wrap freeze vacuum的剩余XIDs统计
6. 《PostgreSQL Freeze 风暴预测续 - 珍藏级SQL》
PostgreSQL 许愿链接
您的愿望将传达给PG kernel hacker、数据库厂商等, 帮助提高数据库产品质量和功能, 说不定下一个PG版本就有您提出的功能点. 针对非常好的提议,奖励限量版PG文化衫、纪念品、贴纸、PG热门书籍等,奖品丰富,快来许愿。开不开森.
9.9元购买3个月阿里云RDS PostgreSQL实例
PostgreSQL 解决方案集合
德哥 / digoal's github - 公益是一辈子的事.







