作者
digoal
日期
2016-06-17
标签
PostgreSQL , 绑定变量 , 执行计划 , 倾斜
背景
早上写了一篇文章《为什么用 PostgreSQL 绑定变量 没有 Oracle pin S 等待问题》,可以看到PostgreSQL为开发人员着想的,设计得非常人性化。
https://yq.aliyun.com/articles/55698
同时也收到了一些朋友发来的问题,有朋友问我PostgreSQL plan cache有没有计划倾斜的问题。
本文将针对这个问题展开和大家聊一聊。
什么是执行计划缓存倾斜
我先解释一下什么是执行计划缓存倾斜。
例如一张表数据本来就有倾斜,在使用绑定变量后,如果所有的条件都走同一个执行计划,那就可能是倾斜了?
例子
```
create table tbl (id int , info text);
insert into tbl select 1 from generate_series(1,20000000);
insert into tbl select generate_series(1,200);
2000万行 id = 1
另外 id = 1~200 每个一行
create index idx_tbl_id on tbl(id);
vacuum analyze tbl;
prepare p(int) as select * from tbl where id=$1;
execute p(2); -- 正常情况下它应该走索引扫描
execute p(1); -- 它应该走全表扫描
```
如果plan cache是index scan, 假设出现倾斜,那么execute p(1)也会走索引(但实际上走索引的COST更高,不应该走索引。)
PostgreSQL 不会出现这样的问题。
看实际的例子
生成一个服务端绑定SQL
postgres=# prepare p(int) as select * from tbl where id=$1;
PREPARE
查看参数是2和1的执行计划的COST
```
postgres=# explain execute p(2);
QUERY PLAN
Index Scan using idx_tbl_id on tbl (cost=0.44..4.46 rows=1 width=36)
Index Cond: (id = 2)
(2 rows)
```
参数为1时,成本最低的是全表扫描 cost = 338500.00
```
postgres=# explain execute p(1);
QUERY PLAN
Seq Scan on tbl (cost=0.00..338500.00 rows=20000240 width=36)
Filter: (id = 1)
(2 rows)
```
参数为1时,index scan cost = 657868.64
```
postgres=# set enable_seqscan=off;
postgres=# explain execute p(1);
QUERY PLAN
Index Scan using idx_tbl_id on tbl (cost=0.44..657868.64 rows=20000240 width=36)
Index Cond: (id = 1)
(2 rows)
```
参数为1时,index scan cost = 712866.30
```
postgres=# set enable_indexscan=off;
postgres=# explain execute p(1);
QUERY PLAN
Bitmap Heap Scan on tbl (cost=374366.30..712866.30 rows=20000240 width=36)
Recheck Cond: (id = 1)
-> Bitmap Index Scan on idx_tbl_id (cost=0.00..369366.24 rows=20000240 width=0)
Index Cond: (id = 1)
(4 rows)
postgres=# \q
```
好了,接下来看看实际是不是这样呢?
```
postgres=# prepare p(int) as select * from tbl where id=$1;
postgres=# explain analyze execute p(2);
QUERY PLAN
Index Scan using idx_tbl_id on tbl (cost=0.44..4.46 rows=1 width=36) (actual time=0.013..0.013 rows=1 loops=1)
Index Cond: (id = 2)
Execution time: 0.030 ms
(3 rows)
```
执行5次会生成generic plan cache。
然后换参数1,PostgreSQL很聪敏,没有走索引,而是选择了对于1这个参数最优的全表扫描
```
postgres=# explain analyze execute p(1);
QUERY PLAN
Seq Scan on tbl (cost=0.00..338500.00 rows=20000240 width=36) (actual time=0.014..2480.369 rows=20000001 loops=1)
Filter: (id = 1)
Rows Removed by Filter: 199
Execution time: 3395.182 ms
(4 rows)
```
后面大家可以继续演示,选择的执行计划都是正确的。
那么为什么PostgreSQL这么智能呢?它是通过什么方法避免的执行计划缓存倾斜?
从代码角度解释为什么PostgreSQL不会出现plan cache倾斜
其实原理也很简单,PG在生成执行计划缓存前,会先走若干次(目前代码写死了5次)custom plan。
同时会记录总的custom plan 的cost, 以及custom plan的次数。
然后会生成generic plan。
以后,每次bind时,会根据缓存的执行计划以及给定的参数值计算一个COST,如果这个COST 小于前面存储的custom plan cost的平均值,则使用当前缓存的执行计划。
如果这个COST大于前面存储的custom plan cost的平均值,则使用custom plan(即重新生成执行计划),同时custom plan的次数加1,custom plan总成本也会累加进去。
循环往复。
如图
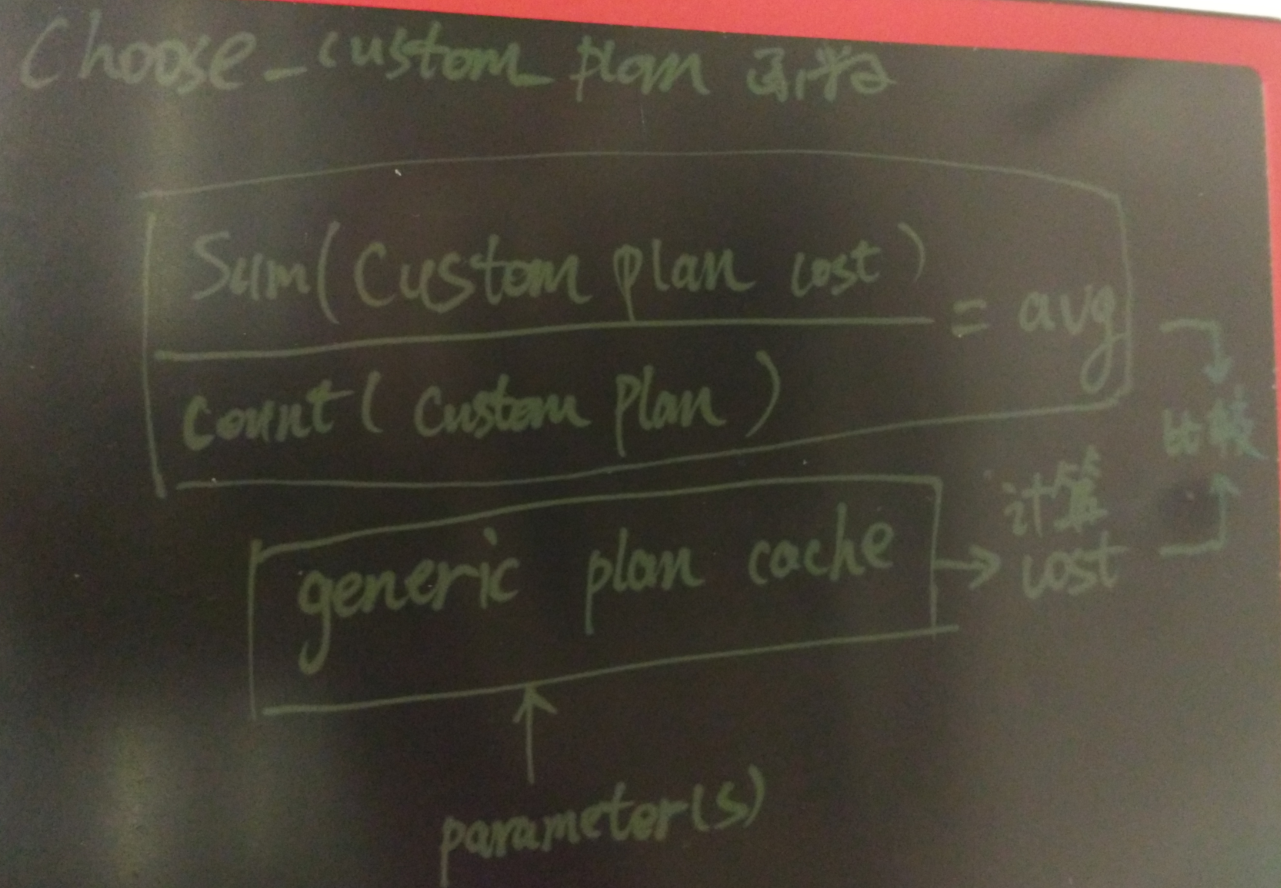
因此在上面的例子中,是怎么影响执行计划的呢?
前面5次产生的是custom plan
count (custom plan) = 5
sum (custom plan cost) = 4.46*5
avg (custom plan cost) = 4.46
第六次调用时, 参数=1 会使用generic plan 计算cost, 算出来是generic plan (index scan)对应的657868.64
明显大于avg (custom plan cost),所以会选择custom plan,优化器选择了seq scan.
对custom plan进行累加得到
count (custom plan) = 6
sum (custom plan cost) = 4.46*5 + 338500.00
avg (custom plan cost) = (4.46*5 + 338500.00) / 6 = 56420.3833
第七次调用,参数如果=2,会走plan cache, 如果参数=1则继续走custom plan,选择 全表扫描、。
源码如下
接收客户端请求
PostgresMain @ src/backend/tcop/postgres.c
prepare消息略,我们看bind的消息。
exec_bind_message @ src/backend/tcop/postgres.c
在bind里会调用获取执行计划缓存, 获取执行计划缓存是会根据bind的参数以及plansource(即缓存的计划)计算是否需要使用customplan
GetCachedPlan @ src/backend/utils/cache/plancache.c
...
customplan = choose_custom_plan(plansource, boundParams);
...
if (customplan)
{
/* Build a custom plan */
plan = BuildCachedPlan(plansource, qlist, boundParams);
/* Accumulate total costs of custom plans, but 'ware overflow */
if (plansource->num_custom_plans < INT_MAX)
{
plansource->total_custom_cost += cached_plan_cost(plan, true);
plansource->num_custom_plans++;
}
}
..
计算是否需要custom plan的算法如下
choose_custom_plan @ src/backend/utils/cache/plancache.c
```
/
* choose_custom_plan: choose whether to use custom or generic plan
* This defines the policy followed by GetCachedPlan.
/
static bool
choose_custom_plan(CachedPlanSource plansource, ParamListInfo boundParams)
{
double avg_custom_cost;
/* One-shot plans will always be considered custom */
if (plansource->is_oneshot)
return true;
/* Otherwise, never any point in a custom plan if there's no parameters */
if (boundParams == NULL)
return false;
/* ... nor for transaction control statements */
if (IsTransactionStmtPlan(plansource))
return false;
/* See if caller wants to force the decision */
if (plansource->cursor_options & CURSOR_OPT_GENERIC_PLAN)
return false;
if (plansource->cursor_options & CURSOR_OPT_CUSTOM_PLAN)
return true;
/* Generate custom plans until we have done at least 5 (arbitrary) */
if (plansource->num_custom_plans < 5)
return true;
avg_custom_cost = plansource->total_custom_cost / plansource->num_custom_plans;
/*
* Prefer generic plan if it's less expensive than the average custom
* plan. (Because we include a charge for cost of planning in the
* custom-plan costs, this means the generic plan only has to be less
* expensive than the execution cost plus replan cost of the custom
* plans.)
*
* Note that if generic_cost is -1 (indicating we've not yet determined
* the generic plan cost), we'll always prefer generic at this point.
*/
if (plansource->generic_cost < avg_custom_cost)
return false;
return true;
}
```
小结
1. PostgreSQL的bind使用choose_custom_plan巧妙的解决了执行计划缓存倾斜的问题。
用户再也不用担心一个执行计划会导致某些数据倾斜是不适用某些VALUE。
2. 需要注意一点,generic plan的选择,是和前面几次调用有关,如果前面几次调用的都是p(1),seq scan将会变成generic plan,然后avg custom plan的值会很高,达到338500.00 . 接下来的p(2),全表扫描算出来的成本也会低于avg custom plan, 会继续走seq scan。 这个算法对于这种情况还没辙。 所以算法还有优化的空间,但是还要注意算法太复杂的话,会影响高并发下的性能。所以PG还提供了一种选择,那就是plan hint,这个和Oracle用法一样。先安装pg hint插件就好了。
阿里云RDS PG已经打包了这个插件。
PostgreSQL 许愿链接
您的愿望将传达给PG kernel hacker、数据库厂商等, 帮助提高数据库产品质量和功能, 说不定下一个PG版本就有您提出的功能点. 针对非常好的提议,奖励限量版PG文化衫、纪念品、贴纸、PG热门书籍等,奖品丰富,快来许愿。开不开森.
9.9元购买3个月阿里云RDS PostgreSQL实例
PostgreSQL 解决方案集合
德哥 / digoal's github - 公益是一辈子的事.







