作者
digoal
日期
2017-11-07
标签
PostgreSQL , HTAP , OLTP , OLAP , 场景与性能测试
背景
PostgreSQL是一个历史悠久的数据库,历史可以追溯到1973年,最早由2014计算机图灵奖得主,关系数据库的鼻祖Michael_Stonebraker 操刀设计,PostgreSQL具备与Oracle类似的功能、性能、架构以及稳定性。

PostgreSQL社区的贡献者众多,来自全球各个行业,历经数年,PostgreSQL 每年发布一个大版本,以持久的生命力和稳定性著称。
2017年10月,PostgreSQL 推出10 版本,携带诸多惊天特性,目标是胜任OLAP和OLTP的HTAP混合场景的需求:
《最受开发者欢迎的HTAP数据库PostgreSQL 10特性》
1、多核并行增强
2、fdw 聚合下推
3、逻辑订阅
4、分区
5、金融级多副本
6、json、jsonb全文检索
7、还有插件化形式存在的特性,如 向量计算、JIT、SQL图计算、SQL流计算、分布式并行计算、时序处理、基因测序、化学分析、图像分析 等。
在各种应用场景中都可以看到PostgreSQL的应用:

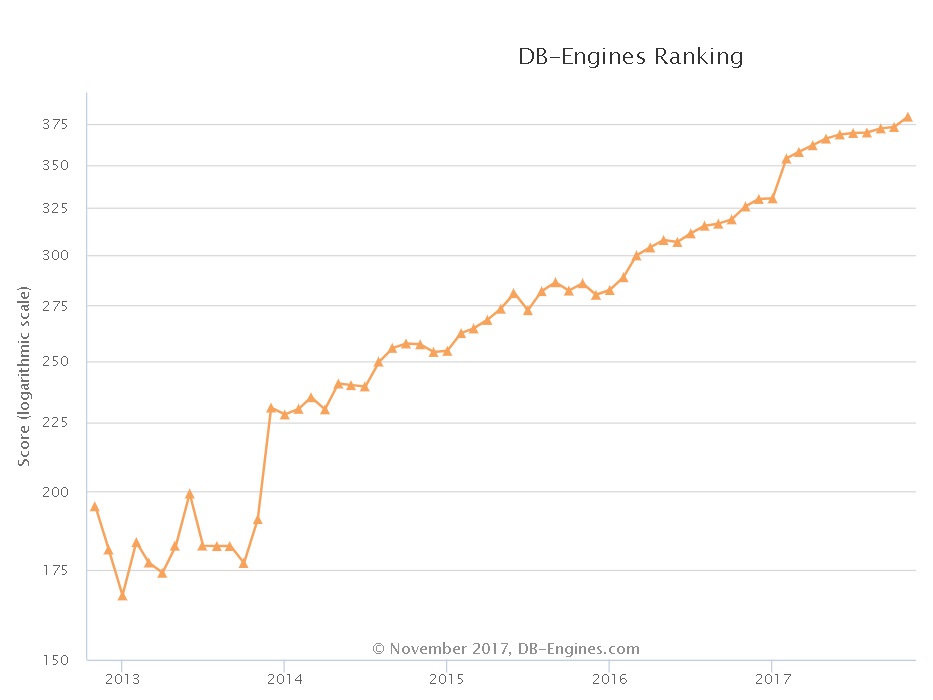
PostgreSQL近年来的发展非常迅猛,从知名数据库评测网站dbranking的数据库评分趋势,可以看到PostgreSQL向上发展的趋势:
从每年PostgreSQL中国召开的社区会议,也能看到同样的趋势,参与的公司越来越多,分享的公司越来越多,分享的主题越来越丰富,横跨了 传统企业、互联网、医疗、金融、国企、物流、电商、社交、车联网、共享XX、云、游戏、公共交通、航空、铁路、军工、培训、咨询服务等 行业。
接下来的一系列文章,将给大家介绍PostgreSQL的各种应用场景以及对应的性能指标。
环境
环境部署方法参考:
《PostgreSQL 10 + PostGIS + Sharding(pg_pathman) + MySQL(fdw外部表) on ECS 部署指南(适合新用户)》
阿里云 ECS:56核,224G,1.5TB*2 SSD云盘。
操作系统:CentOS 7.4 x64
数据库版本:PostgreSQL 10
PS:ECS的CPU和IO性能相比物理机会打一定的折扣,可以按下降1倍性能来估算。跑物理主机可以按这里测试的性能乘以2来估算。
场景 - IN , EXISTS 查询 (OLTP)
1、背景
in 查询,多用在多个输入值的匹配场景。
实际上PostgreSQL支持很多种多个输入值匹配的语法。
1、in (...)
2、in (table or subquery or srf)
3、= any (array)
4、exists (select 1 from (values (),(),...) as t(id) where x.?=t.id)
5、=? or =? or =? or .....
他们的执行计划分别如下,(in (values....) or = any (array)最佳) :
```
postgres=# explain select * from a where id in (1,2,3,4,5);
QUERY PLAN
Index Scan using a_pkey on a (cost=0.43..9.46 rows=5 width=45)
Index Cond: (id = ANY ('{1,2,3,4,5}'::integer[]))
(2 rows)
postgres=# explain select * from a where id = any (array[1,2,3,4,5]);
QUERY PLAN
Index Scan using a_pkey on a (cost=0.43..9.46 rows=5 width=45)
Index Cond: (id = ANY ('{1,2,3,4,5}'::integer[]))
(2 rows)
postgres=# explain select * from a where id = any (array(select generate_series(1,10)));
QUERY PLAN
Index Scan using a_pkey on a (cost=5.45..22.74 rows=10 width=45)
Index Cond: (id = ANY ($0))
InitPlan 1 (returns $0)
-> ProjectSet (cost=0.00..5.02 rows=1000 width=4)
-> Result (cost=0.00..0.01 rows=1 width=0)
(5 rows)
postgres=# explain select * from a where id = any (array(select id from (values (1),(2),(3),(4),(5)) t (id)));
QUERY PLAN
Index Scan using a_pkey on a (cost=0.50..17.79 rows=10 width=45)
Index Cond: (id = ANY ($0))
InitPlan 1 (returns $0)
-> Values Scan on "VALUES" (cost=0.00..0.06 rows=5 width=4)
(4 rows)
postgres=# explain select * from a where id in (select id from (values (1),(2),(3),(4),(5)) t (id));
QUERY PLAN
Nested Loop (cost=0.51..14.39 rows=5 width=45)
-> HashAggregate (cost=0.07..0.12 rows=5 width=4)
Group Key: "VALUES".column1
-> Values Scan on "VALUES" (cost=0.00..0.06 rows=5 width=4)
-> Index Scan using a_pkey on a (cost=0.43..2.85 rows=1 width=45)
Index Cond: (id = "VALUES".column1)
(6 rows)
postgres=# explain select * from a where exists (select 1 from (values (1),(2),(3),(4),(5)) t (id) where t.id=a.id);
QUERY PLAN
Nested Loop (cost=0.51..14.39 rows=5 width=45)
-> HashAggregate (cost=0.07..0.12 rows=5 width=4)
Group Key: "VALUES".column1
-> Values Scan on "VALUES" (cost=0.00..0.06 rows=5 width=4)
-> Index Scan using a_pkey on a (cost=0.43..2.85 rows=1 width=45)
Index Cond: (id = "VALUES".column1)
(6 rows)
postgres=# explain select * from a where id=1 or id=2 or id=3 or id=4 or id =5;
QUERY PLAN
Bitmap Heap Scan on a (cost=8.22..14.32 rows=5 width=45)
Recheck Cond: ((id = 1) OR (id = 2) OR (id = 3) OR (id = 4) OR (id = 5))
-> BitmapOr (cost=8.22..8.22 rows=5 width=0)
-> Bitmap Index Scan on a_pkey (cost=0.00..1.64 rows=1 width=0)
Index Cond: (id = 1)
-> Bitmap Index Scan on a_pkey (cost=0.00..1.64 rows=1 width=0)
Index Cond: (id = 2)
-> Bitmap Index Scan on a_pkey (cost=0.00..1.64 rows=1 width=0)
Index Cond: (id = 3)
-> Bitmap Index Scan on a_pkey (cost=0.00..1.64 rows=1 width=0)
Index Cond: (id = 4)
-> Bitmap Index Scan on a_pkey (cost=0.00..1.64 rows=1 width=0)
Index Cond: (id = 5)
(13 rows)
```
2、设计
1亿记录,查询匹配多个输入值的性能。分别输入1,10,100,1000,10000,100000,1000000个值作为匹配条件。
1、in (...)
2、in (table or subquery or srf)
3、= any (array)
4、exists (select 1 from (values (),(),...) as t(id) where x.?=t.id)
5、=? or =? or =? or .....
3、准备测试表
create table t_in_test (id int primary key, info text, crt_time timestamp);
4、准备测试函数(可选)
5、准备测试数据
insert into t_in_test select generate_series(1,100000000), md5(random()::text), clock_timestamp();
6、准备测试脚本
1、in (...)
1,10,100,1000,10000,100000,1000000 个输入值的测试性能
do language plpgsql $$
declare
arr text;
ts timestamp := clock_timestamp();
mx int8;
begin
for i in 0..6 loop
mx := (1*(10^i))::int8;
select string_agg((random()*100000)::int::text, ',') into arr from generate_series(1, mx);
ts := clock_timestamp();
execute 'select * from t_in_test where id in ('||arr||')';
raise notice '%: %', mx, clock_timestamp()-ts;
end loop;
end;
$$ ;
2、in (table or subquery or srf)
1,10,100,1000,10000,100000,1000000 个输入值的测试性能
do language plpgsql $$
declare
arr text;
ts timestamp := clock_timestamp();
mx int8;
begin
for i in 0..6 loop
mx := (1*(10^i))::int8;
ts := clock_timestamp();
perform * from t_in_test where id in ( select (random()*100000)::int from generate_series(1, mx) );
raise notice '%: %', mx, clock_timestamp()-ts;
end loop;
end;
$$ ;
3、= any (array)
1,10,100,1000,10000,100000,1000000 个输入值的测试性能
do language plpgsql $$
declare
arr int[];
ts timestamp := clock_timestamp();
mx int8;
begin
for i in 0..6 loop
mx := (1*(10^i))::int8;
select array_agg((random()*100000)::int) into arr from generate_series(1, mx);
ts := clock_timestamp();
perform * from t_in_test where id = any ( arr );
raise notice '%: %', mx, clock_timestamp()-ts;
end loop;
end;
$$ ;
4、exists (select 1 from (values (),(),...) as t(id) where x.?=t.id)
1,10,100,1000,10000,100000,1000000 个输入值的测试性能
do language plpgsql $$
declare
ts timestamp := clock_timestamp();
mx int8;
begin
for i in 0..6 loop
mx := (1*(10^i))::int8;
ts := clock_timestamp();
perform * from t_in_test where exists ( select 1 from ( select (random()*100000)::int id from generate_series(1,mx) ) t where t_in_test.id=t.id );
raise notice '%: %', mx, clock_timestamp()-ts;
end loop;
end;
$$ ;
5、压测
匹配1 ~ 100个输入值,求聚合。高并发。
```
vi test.sql
\set x random(1,100)
select count() from t_in_test where id = any(array(select (random()100000000)::int from generate_series(1,:x)));
```
压测
```
CONNECTS=56
TIMES=300
export PGHOST=$PGDATA
export PGPORT=1999
export PGUSER=postgres
export PGPASSWORD=postgres
export PGDATABASE=postgres
pgbench -M prepared -n -r -f ./test.sql -P 5 -c $CONNECTS -j $CONNECTS -T $TIMES
```
7、测试
1、in (...)
1,10,100,1000,10000,100000,1000000 个输入值的测试性能
do language plpgsql $$
declare
arr text;
ts timestamp := clock_timestamp();
mx int8;
begin
for i in 0..6 loop
mx := (1*(10^i))::int8;
select string_agg((random()*100000)::int::text, ',') into arr from generate_series(1, mx);
ts := clock_timestamp();
execute 'select * from t_in_test where id in ('||arr||')';
raise notice '%: %', mx, clock_timestamp()-ts;
end loop;
end;
$$ ;
NOTICE: 1: 00:00:00.000256
NOTICE: 10: 00:00:00.000173
NOTICE: 100: 00:00:00.000772
NOTICE: 1000: 00:00:00.004445
NOTICE: 10000: 00:00:00.024073
NOTICE: 100000: 00:00:00.195439
NOTICE: 1000000: 00:00:01.638982
DO
2、in (table or subquery or srf)
1,10,100,1000,10000,100000,1000000 个输入值的测试性能
do language plpgsql $$
declare
arr text;
ts timestamp := clock_timestamp();
mx int8;
begin
for i in 0..6 loop
mx := (1*(10^i))::int8;
ts := clock_timestamp();
perform * from t_in_test where id in ( select (random()*100000)::int from generate_series(1, mx) );
raise notice '%: %', mx, clock_timestamp()-ts;
end loop;
end;
$$ ;
NOTICE: 1: 00:00:00.00044
NOTICE: 10: 00:00:00.000244
NOTICE: 100: 00:00:00.000788
NOTICE: 1000: 00:00:00.004455
NOTICE: 10000: 00:00:00.028793
NOTICE: 100000: 00:00:00.187841
NOTICE: 1000000: 00:00:00.583744
DO
3、= any (array)
1,10,100,1000,10000,100000,1000000 个输入值的测试性能
do language plpgsql $$
declare
arr int[];
ts timestamp := clock_timestamp();
mx int8;
begin
for i in 0..6 loop
mx := (1*(10^i))::int8;
select array_agg((random()*100000)::int) into arr from generate_series(1, mx);
ts := clock_timestamp();
perform * from t_in_test where id = any ( arr );
raise notice '%: %', mx, clock_timestamp()-ts;
end loop;
end;
$$ ;
NOTICE: 1: 00:00:00.000216
NOTICE: 10: 00:00:00.000151
NOTICE: 100: 00:00:00.000654
NOTICE: 1000: 00:00:00.00399
NOTICE: 10000: 00:00:00.021216
NOTICE: 100000: 00:00:00.106335
NOTICE: 1000000: 00:00:00.386113
DO
4、exists (select 1 from (values (),(),...) as t(id) where x.?=t.id)
1,10,100,1000,10000,100000,1000000 个输入值的测试性能
do language plpgsql $$
declare
ts timestamp := clock_timestamp();
mx int8;
begin
for i in 0..6 loop
mx := (1*(10^i))::int8;
ts := clock_timestamp();
perform * from t_in_test where exists ( select 1 from ( select (random()*100000)::int id from generate_series(1,mx) ) t where t_in_test.id=t.id );
raise notice '%: %', mx, clock_timestamp()-ts;
end loop;
end;
$$ ;
NOTICE: 1: 00:00:00.000458
NOTICE: 10: 00:00:00.000224
NOTICE: 100: 00:00:00.000687
NOTICE: 1000: 00:00:00.003916
NOTICE: 10000: 00:00:00.02734
NOTICE: 100000: 00:00:00.187671
NOTICE: 1000000: 00:00:00.570389
DO
5、匹配1 ~ 100个输入值,求聚合。高并发。
transaction type: ./test.sql
scaling factor: 1
query mode: prepared
number of clients: 56
number of threads: 56
duration: 300 s
number of transactions actually processed: 13913566
latency average = 1.207 ms
latency stddev = 0.840 ms
tps = 46378.142149 (including connections establishing)
tps = 46384.723274 (excluding connections establishing)
script statistics:
- statement latencies in milliseconds:
0.002 \set x random(1,100)
1.207 select count(*) from t_in_test where id = any(array(select (random()*100000000)::int from generate_series(1,:x)));
TPS: 46384
5、匹配1 ~ 100个输入值,求聚合。高并发。
平均响应时间: 1.207 毫秒
5、匹配1 ~ 100个输入值,求聚合。高并发。
1到100万个输入值的响应时间
1亿条记录,匹配100万个输入值( = any (array) ),只需要386毫秒。
NOTICE: 1: 00:00:00.000216
NOTICE: 10: 00:00:00.000151
NOTICE: 100: 00:00:00.000654
NOTICE: 1000: 00:00:00.00399
NOTICE: 10000: 00:00:00.021216
NOTICE: 100000: 00:00:00.106335
NOTICE: 1000000: 00:00:00.386113
参考
《PostgreSQL、Greenplum 应用案例宝典《如来神掌》 - 目录》
《PostgreSQL 使用 pgbench 测试 sysbench 相关case》
https://www.postgresql.org/docs/10/static/pgbench.html
《PostgreSQL 与关系代数 (Equi-Join , Semi-Join , Anti-Join , Division)》
PostgreSQL 许愿链接
您的愿望将传达给PG kernel hacker、数据库厂商等, 帮助提高数据库产品质量和功能, 说不定下一个PG版本就有您提出的功能点. 针对非常好的提议,奖励限量版PG文化衫、纪念品、贴纸、PG热门书籍等,奖品丰富,快来许愿。开不开森.
9.9元购买3个月阿里云RDS PostgreSQL实例
PostgreSQL 解决方案集合
德哥 / digoal's github - 公益是一辈子的事.







