0、前言
这两周总有些奇奇怪怪的事情发生,原定上周就应该结束的InfluxDB-python客户端使用被多次打断,上周最后还发生了令人发指的数据丢失现象,这周刚解决完就被更多的奇奇怪怪的事情给绕晕了头。好在写数据部分的代码调试好了;取数据的代码在python中就是一组字符串,跟MySQL的python查询类似,具体的flux语言可以根据具体需求查询官网文档;可视化部分再说吧。
那开始今天的内容,首先会简单介绍一下InfluxDB的客户端,以python客户端为例;然后会提供一个官网案例进行解析;最后会根据我在实践中的经验提出几个问题和解决方法。
一、InfluxDB-python客户端
这里主要参考的网址为:
https://docs.influxdata.com/influxdb/v2.0/api-guide/client-libraries/#
https://github.com/influxdata/influxdb-client-python
InfluxDB的客户端有多种语言选项,这里因为python更熟一点,所以使用了python客户端。

为了避免时间拖长以后没有热情把核心内容呈现出来,这里对于基础部分只做简单描述。
首先是基础的库安装和加载:
pip install 'influxdb-client[ciso]'
import influxdb_client
然后是使用简介。客户端大致可以分为客户端配置,写入API、查询API等所需API。其中,客户端配置可以通过直接赋值的方式,也可以通过配置文件的方式:
self.client = InfluxDBClient.from_config_file("config.ini")
配置文件内容:
[influx2]url=http://localhost:8086org=my-orgtoken=my-tokentimeout=6000verify_ssl=False
这里根据需求,可以通过配置文件配置其他变量,我就是这么做的,为了避免使用者直接在代码中输入变量。python中的配置文件使用方法可以参考:
from configparser import ConfigParser#……conf = ConfigParser()conf.read("config.ini")bucket_= conf.get('influx2','bucket')#……
需要注意的是,从配置文件中get到的是字符串,数值可以考虑使用类型转换成数值,列表之类的可以考虑使用eval()。
关于写入,需要注意一下write_options,分为异步(ASYNCHRONOUS )、同步(SYNCHRONOUS)、批处理(write_options=WriteOptions (……))三种方式。根据大神解释,在并行处理中,异步表现为一个进程中的处理流程结束,就会马上抢用计算资源;同步则表现为一批处理流程都要完成以后才会开启下一轮计算资源配置使用;批处理的话是由自己指定写入格式,具体参数如下:
| Property | Description | Default Value |
| batch_size | the number of data pointx to collect in a batch | 1000 |
| flush_interval | the number of milliseconds before the batch is written | 1000 |
| jitter_interval | the number of milliseconds to increase the batch flush interval by a random amount | 0 |
| retry_interval | the number of milliseconds to retry first unsuccessful write. The next retry delay is computed using exponential random backoff. The retry interval is used when the InfluxDB server does not specify "Retry-After" header. | 5000 |
| max_retry_time | maximum total retry timeout in milliseconds. | 180_000 |
| max_retries | the number of max retries when write fails | 5 |
| max_retry_delay | the maximum delay between each retry attempt in milliseconds | 125_000 |
| exponential_base | the base for the exponential retry delay, the next delay is computed using random exponential backoff as a random value within the intervalretry_interval * exponential_base^(attempts-1) and retry_interval * exponential_base^(attempts). Example for retry_interval=5_000, exponential_base=2, max_retry_delay=125_000, total=5 Retry delays are random distributed values within the ranges of [5_000-10_000, 10_000-20_000, 20_000-40_000, 40_000-80_000, 80_000-125_000] | 2 |
查询方式有多种,有一个例子中全部包含了,根据我自身的需求,我使用了DataFrame的方式:
query_api.query_data_frame(……)
二、一个并行计算的例子
这里有个官网的并行写入例子分享一下:
"""Import public NYC taxi and for-hire vehicle (Uber, Lyft, etc.) trip data into InfluxDB 2.0https://github.com/toddwschneider/nyc-taxi-data"""import concurrent.futuresimport ioimport multiprocessingfrom collections import OrderedDictfrom csv import DictReaderfrom datetime import datetimefrom multiprocessing import Valuefrom urllib.request import urlopenimport rxfrom rx import operators as opsfrom influxdb_client import Point, InfluxDBClient, WriteOptionsfrom influxdb_client.client.write_api import WriteTypeclass ProgressTextIOWrapper(io.TextIOWrapper):"""TextIOWrapper that store progress of read."""def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):io.TextIOWrapper.__init__(self, *args, **kwargs)self.progress = Nonepassdef readline(self, *args, **kwarg) -> str:readline = super().readline(*args, **kwarg)self.progress.value += len(readline)return readlineclass InfluxDBWriter(multiprocessing.Process):"""Writer that writes data in batches with 50_000 items."""def __init__(self, queue):multiprocessing.Process.__init__(self)self.queue = queueself.client = InfluxDBClient(url="http://localhost:8086", token="my-token", org="my-org", debug=False)self.write_api = self.client.write_api(write_options=WriteOptions(write_type=WriteType.batching, batch_size=50_000, flush_interval=10_000))def run(self):while True:next_task = self.queue.get()if next_task is None:# Poison pill means terminateself.terminate()self.queue.task_done()breakself.write_api.write(bucket="my-bucket", record=next_task)self.queue.task_done()def terminate(self) -> None:proc_name = self.nameprint()print('Writer: flushing data...')self.write_api.close()self.client.close()print('Writer: closed'.format(proc_name))def parse_row(row: OrderedDict):"""Parse row of CSV file into Point with structure:taxi-trip-data,DOLocationID=152,PULocationID=79,dispatching_base_num=B02510 dropoff_datetime="2019-01-01 01:27:24" 1546304267000000000CSV format:dispatching_base_num,pickup_datetime,dropoff_datetime,PULocationID,DOLocationID,SR_FlagB00001,2019-01-01 00:30:00,2019-01-01 02:51:55,,,B00001,2019-01-01 00:45:00,2019-01-01 00:54:49,,,B00001,2019-01-01 00:15:00,2019-01-01 00:54:52,,,B00008,2019-01-01 00:19:00,2019-01-01 00:39:00,,,B00008,2019-01-01 00:27:00,2019-01-01 00:37:00,,,B00008,2019-01-01 00:48:00,2019-01-01 01:02:00,,,B00008,2019-01-01 00:50:00,2019-01-01 00:59:00,,,B00008,2019-01-01 00:51:00,2019-01-01 00:56:00,,,B00009,2019-01-01 00:44:00,2019-01-01 00:58:00,,,B00009,2019-01-01 00:19:00,2019-01-01 00:36:00,,,B00009,2019-01-01 00:36:00,2019-01-01 00:49:00,,,B00009,2019-01-01 00:26:00,2019-01-01 00:32:00,,,...:param row: the row of CSV file:return: Parsed csv row to [Point]"""return Point("taxi-trip-data") \.tag("dispatching_base_num", row['dispatching_base_num']) \.tag("PULocationID", row['PULocationID']) \.tag("DOLocationID", row['DOLocationID']) \.tag("SR_Flag", row['SR_Flag']) \.field("dropoff_datetime", row['dropoff_datetime']) \.time(row['pickup_datetime']) \.to_line_protocol()def parse_rows(rows, total_size):"""Parse bunch of CSV rows into LineProtocol:param total_size: Total size of file:param rows: CSV rows:return: List of line protocols"""_parsed_rows = list(map(parse_row, rows))counter_.value += len(_parsed_rows)if counter_.value % 10_000 == 0:print('{0:8}{1}'.format(counter_.value, ' - {0:.2f} %'.format(100 * float(progress_.value) float(int(total_size))) if total_size else ""))passqueue_.put(_parsed_rows)return Nonedef init_counter(counter, progress, queue):"""Initialize shared counter for display progress"""global counter_counter_ = counterglobal progress_progress_ = progressglobal queue_queue_ = queueif __name__ == "__main__":"""Create multiprocess shared environment"""queue_ = multiprocessing.Manager().Queue()counter_ = Value('i', 0)progress_ = Value('i', 0)startTime = datetime.now()url = "https://s3.amazonaws.com/nyc-tlc/trip+data/fhv_tripdata_2019-01.csv"# url = "file:///Users/bednar/Developer/influxdata/influxdb-client-python/examples/fhv_tripdata_2019-01.csv""""Open URL and for stream data"""response = urlopen(url)if response.headers:content_length = response.headers['Content-length']io_wrapper = ProgressTextIOWrapper(response)io_wrapper.progress = progress_"""Start writer as a new process"""writer = InfluxDBWriter(queue_)writer.start()"""Create process pool for parallel encoding into LineProtocol"""cpu_count = multiprocessing.cpu_count()with concurrent.futures.ProcessPoolExecutor(cpu_count, initializer=init_counter,initargs=(counter_, progress_, queue_)) as executor:"""Converts incoming HTTP stream into sequence of LineProtocol"""data = rx \.from_iterable(DictReader(io_wrapper)) \.pipe(ops.buffer_with_count(10_000),# Parse 10_000 rows into LineProtocol on subprocessops.flat_map(lambda rows: executor.submit(parse_rows, rows, content_length)))"""Write data into InfluxDB"""data.subscribe(on_next=lambda x: None, on_error=lambda ex: print(f'Unexpected error: {ex}'))"""Terminate Writer"""queue_.put(None)queue_.join()print()print(f'Import finished in: {datetime.now() - startTime}')print()"""Querying 10 pickups from dispatching 'B00008'"""query = 'from(bucket:"my-bucket")' \'|> range(start: 2019-01-01T00:00:00Z, stop: now()) ' \'|> filter(fn: (r) => r._measurement == "taxi-trip-data")' \'|> filter(fn: (r) => r.dispatching_base_num == "B00008")' \'|> pivot(rowKey:["_time"], columnKey: ["_field"], valueColumn: "_value")' \'|> rename(columns: {_time: "pickup_datetime"})' \'|> drop(columns: ["_start", "_stop"])|> limit(n:10, offset: 0)'client = InfluxDBClient(url="http://localhost:8086", token="my-token", org="my-org", debug=False)result = client.query_api().query(query=query)"""Processing results"""print()print("=== Querying 10 pickups from dispatching 'B00008' ===")print()for table in result:for record in table.records:print(f'Dispatching: {record["dispatching_base_num"]} pickup: {record["pickup_datetime"]} dropoff: {record["dropoff_datetime"]}')"""Close client"""client.close()
分解一下的话,大致有以下内容:
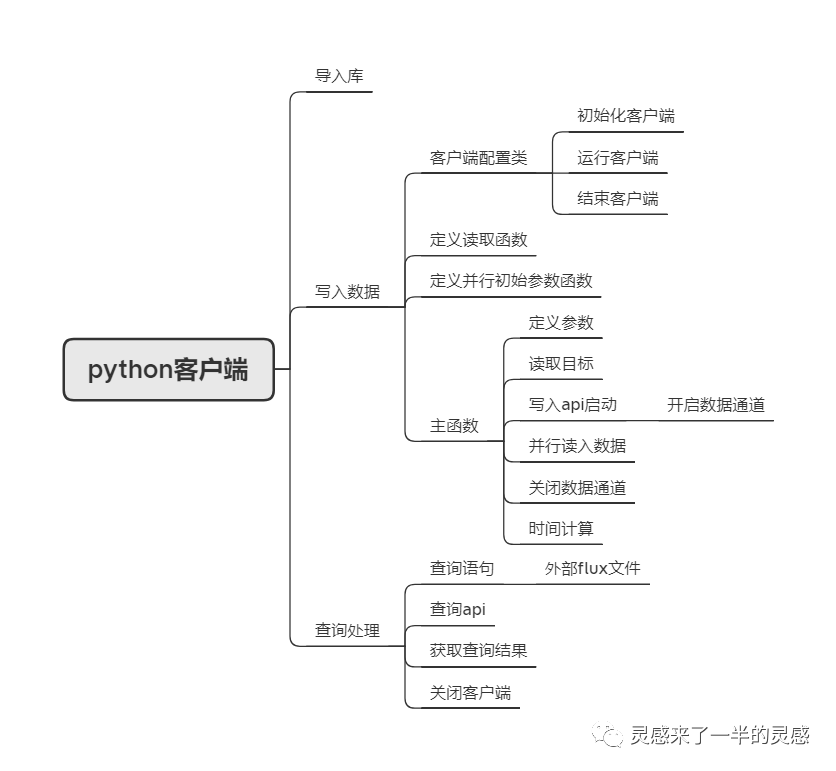
当然了,参考这个例子可以根据自己的需求进行改造。
三、一些问题与处理方法
并行处理很慢,调试过程中发现部分代码重复调用
写主程序代码前需要注意加上:if __name__ == "__main__":写入环节耗时严重,I/O并非制约写入效率的环节,写入API才是
a.将写入API放进并行程序中,具体的可以放在类似于案例中的parse_rows函数定义当中;
b.为了解决DataFrame自身的资源释放问题,可以考虑使用python的原始类:
@dataclass(repr=False,eq=False,order=False)class DataFrameContainer:df:pd.DataFrame=Nonec.客户端和写入API的配置可以放在并行的初始化函数当中,并用Finalize()函数关闭客户端和写入API:
def init_writer(que):global f_queuef_queue=queglobal clientclient = InfluxDBClient.from_config_file(ini_file,debug=False,enable_gzip=True)global write_apiwrite_api = client.write_api(write_options=SYNCHRONOUS)print(f"writer started:{os.getpid()}")Finalize(write_api,write_api.close)Finalize(client,client.close)写入过程中数据丢失问题
测试过转py文件运行、调timeout参数、将异步写入调为同步写入、在batching方式下调参、查看读取的文件等方式。
最终发现,问题主要出现在read_csv()为DataFrame时,部分列格式不一致导致数据丢失,而写入方式为异步时不会提示该错误,所以将DataFrame所有的非时间列都转换为了float格式,字符串列drop掉。这样,解决了大部分的问题。不过还是有部分数据丢失,当写入方式为同步而非异步时,对于测试的数据,这部分问题解决,数据不再丢失。
四、尾声
按照原计划,查询和可视化工作也需要一起撰写,但由于这部分工作没有完成,而且查询语法可以在官网找到,可视化也可以通过python进行,所以这一篇主讲了并行写入的内容,毕竟,这一部分是最耗时的。
下周的内容可能与InfluxDB-python客户端的查询、可视化有关,也可能复盘一下以前的内容。
同时,根据最近一时手痒的操作,8月的专业复盘工作可能会比较紧张,尽量完成。






