




Lift3D.pdf
100墨值下载
Lift3D: Synthesize 3D Training Data
by Lifting 2D GAN to 3D Generative Radiance Field
Leheng Li
1
*
Qing Lian
2
Luozhou Wang
1
Ningning Ma
3
Ying-Cong Chen
1,2†
1
HKUST(GZ)
2
HKUST
3
NIO Autonomous Driving
Abstract
This work explores the use of 3D generative models to
synthesize training data for 3D vision tasks. The key require-
ments of the generative models are that the generated data
should be photorealistic to match the real-world scenar-
ios, and the corresponding 3D attributes should be aligned
with given sampling labels. However, we find that the recent
NeRF-based 3D GANs hardly meet the above requirements
due to their designed generation pipeline and the lack of
explicit 3D supervision. In this work, we propose Lift3D, an
inverted 2D-to-3D generation framework to achieve the data
generation objectives. Lift3D has several merits compared to
prior methods: (1) Unlike previous 3D GANs that the output
resolution is fixed after training, Lift3D can generalize to any
camera intrinsic with higher resolution and photorealistic
output. (2) By lifting well-disentangled 2D GAN to 3D object
NeRF, Lift3D provides explicit 3D information of generated
objects, thus offering accurate 3D annotations for down-
stream tasks. We evaluate the effectiveness of our framework
by augmenting autonomous driving datasets. Experimental
results demonstrate that our data generation framework can
effectively improve the performance of 3D object detectors.
Project page: len-li.github.io/lift3d-web.
1. Introduction
It is well known that the training of current deep learning
models requires a large amount of labeled data. However, col-
lecting and labeling the training data is often expensive and
time-consuming. This problem is especially critical when
the data is hard to annotate. For example, it is difficult for
humans to annotate 3D bounding boxes using a 2D image
due to the inherent ill-posed 3D-2D projection (3D bounding
boxes are usually annotated using LiDAR point clouds).
To alleviate this problem, a promising direction is to use
synthetic data to train our models. For example, data genera-
tion that can be conveniently performed using 3D graphics
*
Work done during an internship at NIO Autonomous Driving.
†
Corresponding author.
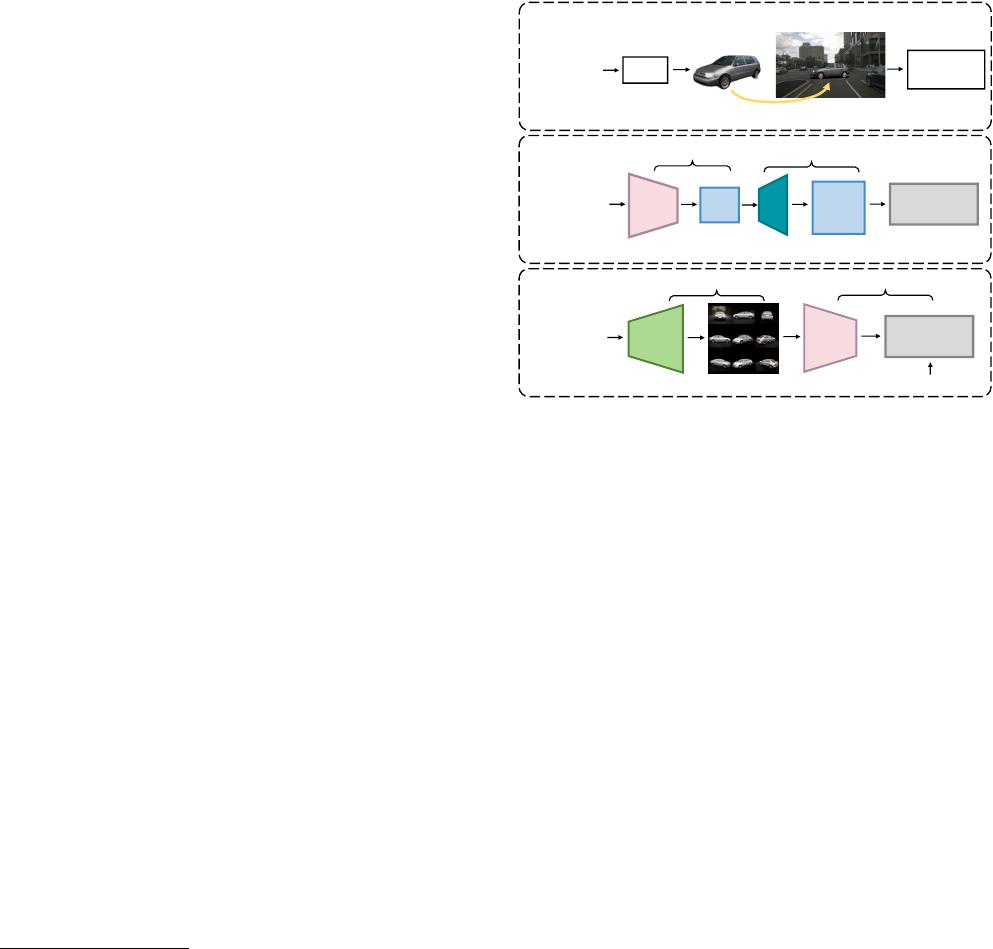
Noise z ∈
Pose p ∈
Low
Reso.
High
Reso.
Image
2D Upsample
Pose p ∈
2D
3D
3D
2D
a: Previous 3D GANs
b: Our approach
2D GAN
Noise z ∈
NeRF
NeRF
Downstream
Tasks (3D)
Add novel objects
Goal: Synthesize downstream task dataset
Noise z ∈
Pose p ∈
Train 3D
Detectors
GAN
Downstream
Tasks (3D)
Figure 1. Our goal is to generate novel objects and use them to
augment existing datasets.
(a)
Previous 3D GANs (e.g., [28, 45])
rely on a 2D upsampler to ease the training of 3D generative ra-
diance field, while struggle a trade-off between high-resolution
synthesis and 3D consistency.
(b)
Our 2D-to-3D lifting process
disentangles the 3D generation from generative image synthesis,
leading to arbitrary rendering resolution and object pose sampling
for downstream tasks.
engines offers incredible convenience for visual perception
tasks. Several such simulated datasets have been created
in recent years [3, 14, 30, 31, 42]. These datasets have been
used successfully to train networks for perception tasks such
as semantic segmentation and object detection. However,
these datasets are expensive to generate, requiring specialists
to model specific objects and environments in detail. Such
datasets also tend to have a large domain gap from real-world
ones.
With the development of Generative Adversarial Net-
works (GAN) [18], researchers have paid increasing atten-
tion to utilize GANs to replace graphics engines for syn-
thesizing training data. For example, BigDatasetGAN [23]
utilizes condition GAN to generate classification datasets via
1
arXiv:2304.03526v1 [cs.CV] 7 Apr 2023

conditioning the generation process on the category labels.
SSOD [27] designs a GAN-based generator to synthesize
images with 2D bounding boxes annotation for the object
detection task. In this paper, we explore the use of 3D GANs
to synthesize datasets with 3D-related annotations, which is
valuable but rarely explored.
Neural radiance field (NeRF) [26] based 3D GANs [6,28],
which display photorealistic synthesis and 3D controllable
property, is a natural choice to synthesize 3D-related train-
ing data. However, our experimental results show that they
struggle to keep high-resolution outputs and geometry-
consistency results by relying on a 2D upsampler. Further-
more, the generated images are not well aligned with the
given 3D pose, due to the lack of explicit 3D consistency reg-
ularization. This misalignment would introduce large label
noise in the dataset, limiting the performance in downstream
tasks. In addition to these findings, the camera parameters
are fixed after training, making them challenging to align the
output resolution with arbitrary downstream data.
In this paper, we propose Lift3D, a new paradigm for syn-
thesizing 3D training data by lifting pretrained 2D GAN
to 3D generative radiance field. Compared with the 3D
GANs that rely on a 2D upsampler, we invert the gener-
ation pipeline into 2D-to-3D rather than 3D-to-2D to achieve
higher-resolution synthesis. As depicted in Fig. 1, we first
take advantage of a well-disentangled 2D GAN to generate
multi-view images with corresponding pseudo pose annota-
tion. The multi-view images are then lifted to 3D represen-
tation with NeRF reconstruction. In particular, by distilling
from pretrained 2D GAN, lift3D achieves high-quality syn-
thesis that is comparable to SOTA 2D generative models. By
decoupling the 3D generation from generative image synthe-
sis, Lift3D can generate images that are tightly aligned with
the sampling label. Finally, getting rid of 2D upsamplers,
Lift3D can synthesize images in any resolution by accumu-
lating single-ray evaluation. With these properties, we can
leverage the generated objects to augment existing dataset
with enhanced quantity and diversity.
To validate the effectiveness of our data generation frame-
work, we conduct experiments on image-based 3D object
detection tasks with KITTI [16] and nuScenes [4] datasets.
Our framework outperforms the best prior data augmen-
tation method [24] with significantly better 3D detection
accuracy. Furthermore, even without any labeled data, it
achieves promising results in an unsupervised manner. Our
contributions are summarized as follows:
•
We provide the first exploration of using 3D GAN to
synthesize 3D training data, which opens up a new
possibility that adapts NeRF’s powerful capabilities of
novel view synthesis to benefit downstream tasks in 3D.
•
To synthesize datasets with high-resolution images and
accurate 3D labels, we propose Lift3D, an inverted 2D-
GIRAFFE HD Ours
Position Rotation
Position Rotation
Figure 2. We compare our generation result with GIRAFFE
HD [45]. We zoom in or rotate the sampled 3D box to control
the generation of models. The rotation of the 3D box introduces
artifacts to images generated by GIRAFFE HD. All images are
plotted with sampled 3D bounding boxes.
to-3D data generation framework that disentangles 3D
generation from generative image synthesis.
•
Our experimental results demonstrate that the synthe-
sized training data can improve image-based 3D detec-
tors across different settings and datasets.
2. Related Work
Data Generation for Downstream Tasks
Benefiting
from low data acquisition costs, learning from synthesized
data is an attractive way to scale up the training data. Several
studies like [1, 3, 14, 31] leverage graphic engines to synthe-
size training data without human annotation. However, they
rely on pre-built 3D assets to mimic the world, which is also
a non-negligible effort in the whole pipeline.
Without any burden of collecting 3D assets, generative
models can also be considered as a neural rendering alterna-
tive to graphics engines. For example, BigDatasetGAN [23]
generates classification datasets by conditioning the genera-
tion process on the class labels. SSOD [27] samples dataset
with 2D bounding boxes via generative image synthesis. Our
method goes further, utilizing 3D GAN to generate training
data with 3D annotation, greatly reducing labeling effort in
3D data.
3D-aware Generative Image Synthesis
Recently, Gen-
erative Adversarial Networks (GANs) [18] have made great
progress in generating high-resolution photorealistic 2D im-
ages. One natural extension of the 2D GANs is to endow
their 3D controllable ability as 2D images are projections
of the 3D world. To provide the 3D-aware ability, recent
2
of 10
100墨值下载
【版权声明】本文为墨天轮用户原创内容,转载时必须标注文档的来源(墨天轮),文档链接,文档作者等基本信息,否则作者和墨天轮有权追究责任。如果您发现墨天轮中有涉嫌抄袭或者侵权的内容,欢迎发送邮件至:contact@modb.pro进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,墨天轮将立刻删除相关内容。
下载排行榜


评论