




CnosDB:一种面向大规模数据的灵活分布式时序数据库.pdf
免费下载

CnosDB: A Flexible Distributed
Time-Series Database for Large-Scale
Data
Yu Yan
1
, Bo Zheng
2
, Hongzhi Wang
1(
B
)
,JinkaiZhang
1
, and Yutong Wang
1
1
Harbin Institute of Technology, Harbin, China
{yuyan,wangzh}@hit.edu.cn, harbour.zheng@cnosdb.com
2
Cnosdb Inc., Beijing, China
Abstract. With the development of the Internet of Things, the time
series data generated by monitors, analyzers, and detection instruments
in the industry has surged. The management of very large-scale time
series data faces great challenges. However, the current distributed time
series database is still poor in terms of data storage efficiency and data
writing speed. In order to achieve the fast writing and high efficient stor-
age of billions or even tens of billions of data points, we propose a cloud
native distributed time series database, CnosDB. Our system integrates
various data compression algorithms to achieve high compression rate in
each data type. And we propose a three-layer storage policy to achieve
fast writing under the premise of ensuring rapid time-based batch oper-
ations. In this paper, introduce the architecture and key techniques of
CnosDB, and describe three key demo scenarios of our system.
1 Introduction
With the advent of big data, the scale of time series data surge in the indus-
try, such as monitors, analyzers, and detection instruments in the electric power
industry [10] and the chemical industry. Industrial data has three typical fea-
tures: Fast Generation Speed [9]: Each monitoring point can generate large
amount of data one second. Unique Timestamp [8]: Each piece of data has a
dependent and unique timestamp. Wide Collection Range [13]: The conven-
tional real-time monitoring system has thousands of monitoring points, which
are generated data every second.
Faced with the real-time and large amount of time series data, traditional
databases such as MySQL can no longer meet the requirements for massive
data storage and management, and various types of time series databases have
emerged.
Recently, in order to achieve efficient management of large-scale time series
data, some time series database management systems have been developed. In
the early days, researchers used other databases as the backend and developed
a middleware for time series data management, such as TimescaleDB [3], [6],
etc. Without own storage engines, middleware-based methods cannot effectively
c
The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG 2023
X. Wang et al. (Eds.): DASFAA 2023, LNCS 13946, pp. 696–700, 2023.
https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-30678-5
_58
CnosDB: A Flexible Distributed Time-Series Database for Large-Scale Data 697
compress data and has weak aggregation capabilities. Later, the storage struc-
ture based on time series data gradually appeared [5][1]. Graphite [5] designs
the Whisper storage structure for time series data, which can store data at fixed
time intervals and accelerate the writing speed of time series data. However, it
does not support data shard. Time series data is stored in the file system which
conducts bad scalability. To achieve high scalability, InfluxDB [7], FreeTSDB [4]
and TDengine [2] have been proposed. They design more flexible shard archi-
tectures, which can realize the addition and deletion of data nodes. However, its
writing speed and storage efficiency still cannot meet the demand of large-scale
time series data. In fact, no management system that can efficiently handle very
large-scale time series data access now has been proposed. The industry urgently
needs a scalable database that can efficiently manage large-scale time series data.
Motivated by this, we analyze the features of time series data, and develop
a scalable and efficient time series data management system. Considering the
demands of large-scale time series data, we pay more attention to the efficiency
of data writing policy and data compression. Our CnosDB has the following
advantages:
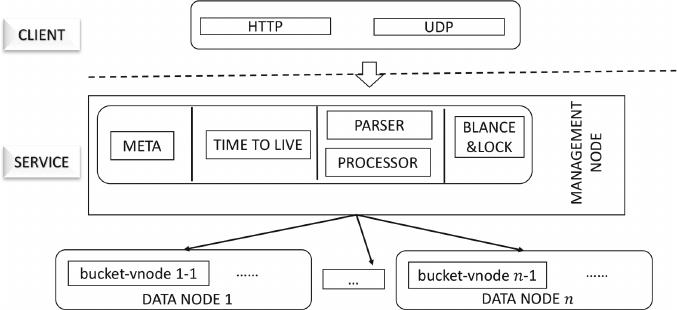
Fig. 1. System Architecture
– High Compression Rate. The system integrates compression algorithms for
time series data, integers, floating point numbers and other data types, which
can compress each type of data to the greatest extent.
– Fast Data Writing. We designed a new storage policy based on the features
of time series data and adopted a hierarchical shard (called bucket-vnode),
which reach higher performance by using disk batch sequential writing.
– Friendly UI. CnosDB provides friendly user interface. Our system not only
supports command line interaction but also provides a friendly graphical
interface.
of 5
免费下载
【版权声明】本文为墨天轮用户原创内容,转载时必须标注文档的来源(墨天轮),文档链接,文档作者等基本信息,否则作者和墨天轮有权追究责任。如果您发现墨天轮中有涉嫌抄袭或者侵权的内容,欢迎发送邮件至:contact@modb.pro进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,墨天轮将立刻删除相关内容。
下载排行榜


评论