




RPTQ Reorder-based Post-training Quantization for Large Language Models.pdf
100墨值下载

RPTQ: Reorder-based Post-training Quantization for
Large Language Models
Zhihang Yuan
∗
Houmo AI
Lin Niu
∗
Jiawei Liu Wenyu Liu Xinggang Wang
†
Huazhong University of Science & Technology
Yuzhang Shang
Illinois Institute of Technology
Guangyu Sun
Peking University
Qiang Wu
Houmo AI
Jiaxiang Wu
Tencent AI Lab
Bingzhe Wu
†
Tencent AI Lab
Abstract
Large-scale language models (LLMs) have demonstrated impressive performance,
but their deployment presents challenges due to their significant memory usage.
This issue can be alleviated through quantization. In this paper, we identify that
the challenge in quantizing activations in LLMs arises from varying ranges across
channels, rather than solely the presence of outliers. To address this challenge,
we introduce a quantization method called RPTQ, which utilizes a reorder-based
approach. By rearranging the channels and quantizing them in clusters, RPTQ
effectively mitigates the impact of range differences between channels. To mini-
mize the overhead of the reorder operation, we fuse it into the layer norm operation
and weights in linear layers. In our experiments, RPTQ achieved a significant
breakthrough by utilizing 3-bit activation in LLMs for the first time, resulting
in a substantial reduction in memory usage. For instance, quantizing OPT-175b
can lead to a memory consumption reduction of up to 80%. The code is in
https://github.com/hahnyuan/RPTQ4LLM.
1 Introduction
Large-scale language models (LLMs) have demonstrated impressive performance in various tasks,
but their deployment poses challenges due to their enormous model size. For example, the OPT-
175B model [
40
] contains 175 billion parameters, which require significant memory to store As the
sequence length and batch size increase, the problem of memory consumption becomes more severe
because activations. In some cases, the key and value cache can consume more than 100 times the
memory of the weights. However, a single GPU or server does not possess sufficient memory capacity
to store such massive weights and activations. To address this issue, LLMs are often divided into
multiple chunks and stored on different devices. However, this requires data to be transferred between
devices during computation, leading to significant bandwidth and energy consumption [1; 30].
To address the challenges posed by LLMs’ high memory usage, model quantization has emerged
as a promising solution. This technique involves quantizing both the weights and activations of
LLMs using low-bit integers, resulting in a significant reduction in storage and computational costs.
Specifically, quantization reduces memory requirements for saving weights and activations and
∗
Equal contribution. hahnyuan@gmail.com, linniu@hust.edu.cn. This work was done when Lin Niu and
Jiawei Liu were interns at Houmo AI.
†
Corresponding author. xgwang@hust.edu.cn, bingzhewu@tencent.com.
Preprint. Under review.
arXiv:2304.01089v4 [cs.CL] 17 May 2023
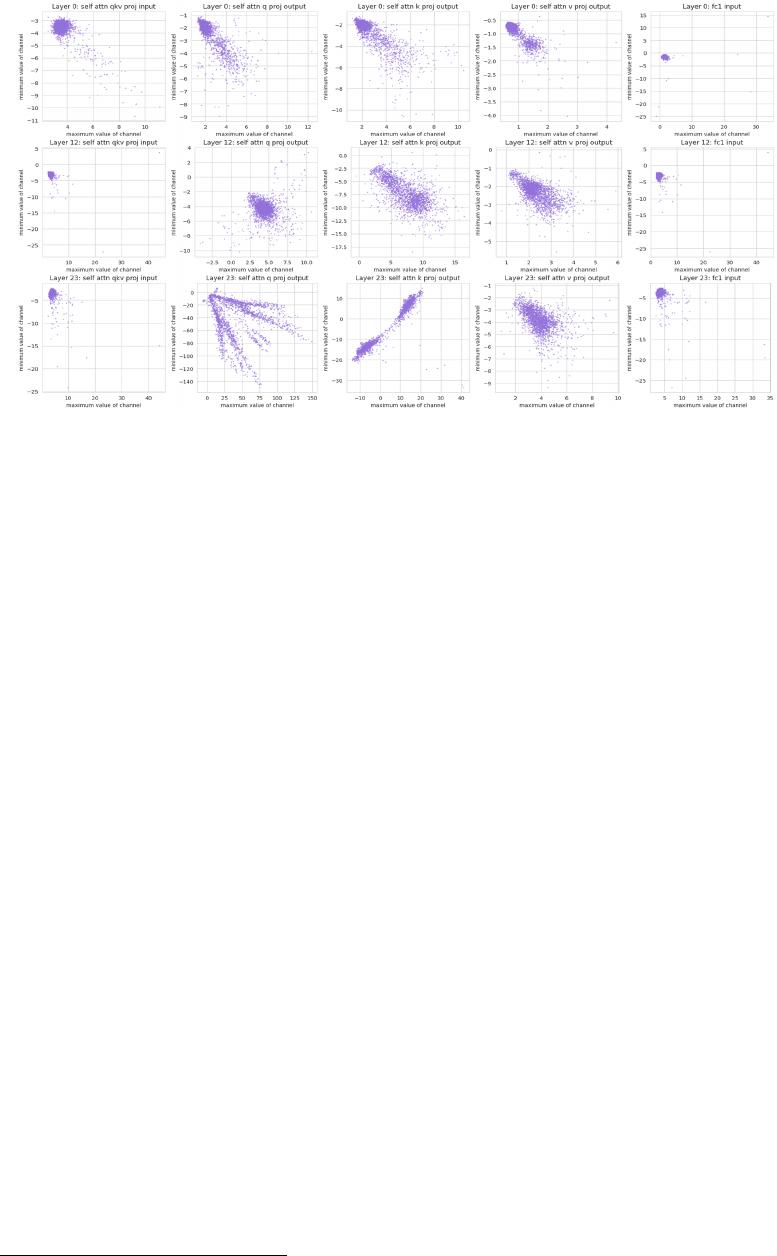
Figure 1: Demonstration of the distribution of different channels in OPT decoder layers. Each point
is (maximum value, minimum value) of a channel in the activation.
accelerates compute-intensive operations like Matrix Multiplication and linear layers. By quantizing
weights and activations, storage and communication overhead is reduced, leading to improved
efficiency and faster inference times. Quantization methods are typically divided into two categories:
post-training quantization (PTQ) and quantization-aware training (QAT). While QAT methods can
lead to higher accuracy in most cases, they require significant computational resources to train
the models, making them less practical for LLMs that already have significant training costs. In
contrast, PTQ methods can quantize pre-trained models without additional training, making them
more practical for larger models that require significant computational and memory resources. This
paper focuses on PTQ for LLMs.
In this paper, we highlights the challenge of quantizing the activations of LLMs, which is attributed
to the significant variations in the values across different channels
2
, as shown in Figure 1. Two
observations can be made from this figure: 1) Some channels exhibit significant outliers, with
maximum or minimum values that are hundreds of times larger than those of other channels. Previous
studies [
34
;
11
] have also identified this issue and proposed special treatment for outliers. 2) Different
channels exhibit significant difference in the range of values. Quantizing different channels using the
same quantization parameter can lead to substantial quantization errors. Even if two channels have
the same absolute value of outliers, they can exhibit strong difference in the range of numerical values.
For instance, one channel may have a range of -100 to -50, while another channel may have a range
of 80 to 100. Using the same quantization parameters for them can lead to significant quantization
errors, which is a challenge that has not been effectively addressed in previous works.
To address the issue of quantizing activations with channels that have significantly different ranges, we
propose a method called RPTQ. This method involves clustering channels in activations that exhibit
similar value ranges, followed by the quantization with the same quantization parameter to the values
within each cluster. Consequently, channels displaying considerable discrepancies in numerical ranges
can utilize distinct quantization parameters, leading to a significant reduction in quantization error.
Furthermore, we propose strategies to avoid explicit reordering, thereby decreasing computational
overhead and enhancing inference efficiency. We propose a modified layer norm operation to yield
reordered activations directly, obviating the necessity for explicit channel adjustments during the
inference process. In addition, we reorganize the weights of linear layers to enable them to directly
accept and produce activations in a sorted order.
Our experiments demonstrate that RTPQ is an effective solution for addressing the issue of quantizing
the activations of LLMs. Clustering the channels in only a small number of clusters can significantly
reduce quantization errors and improve the accuracy of quantized LLMs. The results show that RPTQ
2
For simplicity, we use the term "channel" to refer to the dimension of the hidden size. See Appendix A.1 for
more results.
2
of 18
100墨值下载
【版权声明】本文为墨天轮用户原创内容,转载时必须标注文档的来源(墨天轮),文档链接,文档作者等基本信息,否则作者和墨天轮有权追究责任。如果您发现墨天轮中有涉嫌抄袭或者侵权的内容,欢迎发送邮件至:contact@modb.pro进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,墨天轮将立刻删除相关内容。
下载排行榜


评论