




DeltaEdit.pdf
100墨值下载

DeltaEdit: Exploring Text-free Training for Text-Driven Image Manipulation
Yueming Lyu
1,2
, Tianwei Lin
3
, Fu Li
3
, Dongliang He
3
, Jing Dong
2
*
, Tieniu Tan
2,4
1
School of Artificial Intelligence, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences
2
CRIPAC, Institute of Automation, Chinese Academy of Sciences
3
VIS, Baidu Inc.
4
Nanjing University
yueming.lv@cripac.ia.ac.cn, jdong@nlpr.ia.ac.cn
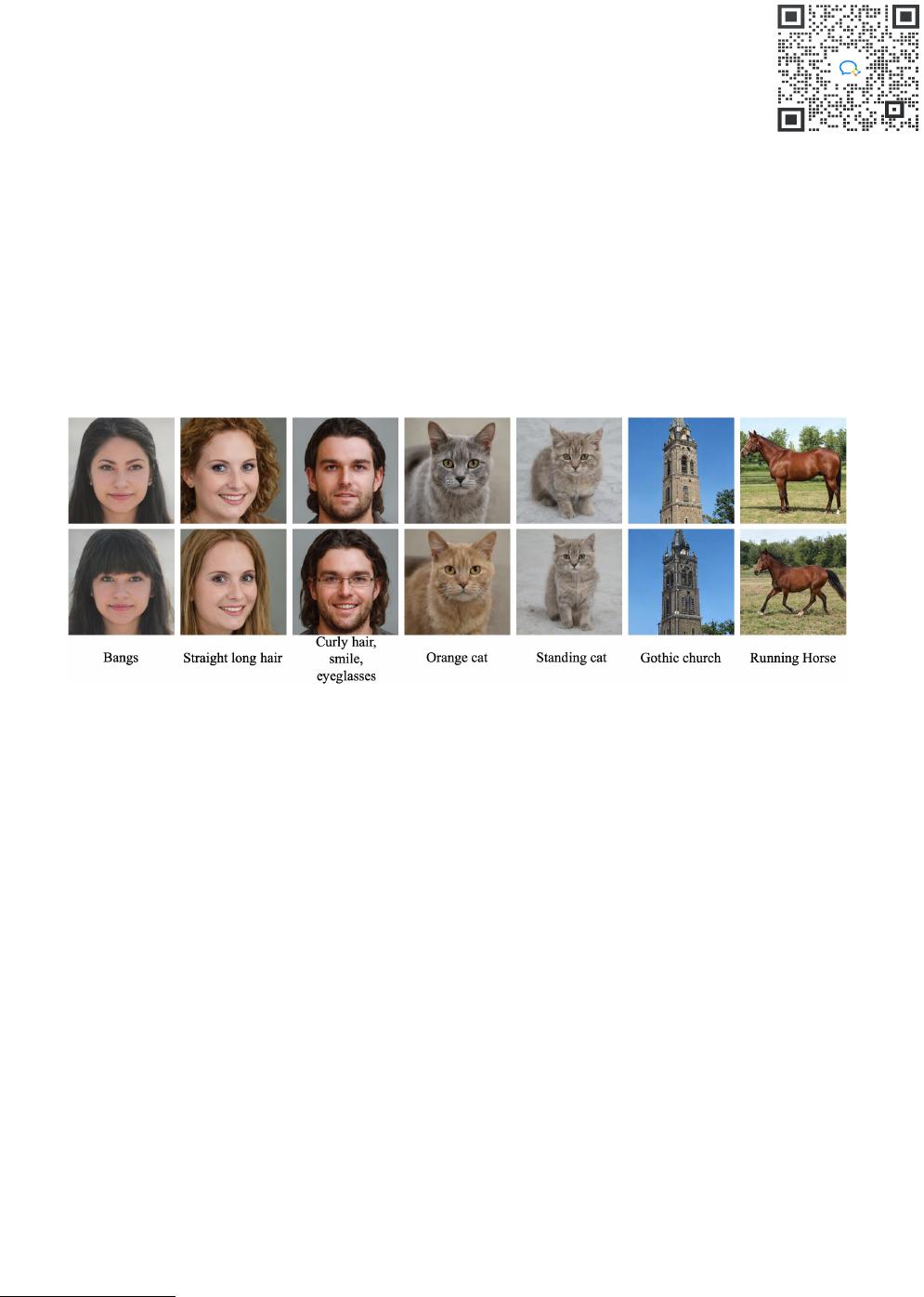
Figure 1. Examples of text-driven manipulations of multiple StyleGAN imagery categories induced by our DeltaEdit with text-free training.
Abstract
Text-driven image manipulation remains challenging
in training or inference flexibility. Conditional genera-
tive models depend heavily on expensive annotated train-
ing data. Meanwhile, recent frameworks, which lever-
age pre-trained vision-language models, are limited by ei-
ther per text-prompt optimization or inference-time hyper-
parameters tuning. In this work, we propose a novel frame-
work named DeltaEdit to address these problems. Our key
idea is to investigate and identify a space, namely delta im-
age and text space that has well-aligned distribution be-
tween CLIP visual feature differences of two images and
CLIP textual embedding differences of source and target
texts. Based on the CLIP delta space, the DeltaEdit network
is designed to map the CLIP visual features differences to
the editing directions of StyleGAN at training phase. Then,
in inference phase, DeltaEdit predicts the StyleGAN’s edit-
ing directions from the differences of the CLIP textual fea-
tures. In this way, DeltaEdit is trained in a text-free manner.
Once trained, it can well generalize to various text prompts
for zero-shot inference without bells and whistles. Code is
available at https://github.com/Yueming6568/
DeltaEdit
*
Corresponding author.
Text-driven image manipulation has aroused widespread
research interests in both academic and industrial commu-
nities given its significance for real-world applications. It
aims at editing the content of images according to user-
provided natural language descriptions while preserving
1. Introduction
text-irrelevant content unchanged.
Existing approaches [3,12,17,19,33] typically train con-
ditional generative models from scratch with a large amount
of manually annotated image-text pairs. This procedure
requires expensive labor annotation, which obstacles the
training flexibility. Recently, some CLIP+StyleGAN ap-
proaches [11, 16, 20, 31, 41] have been proposed to perform
text-driven image manipulation by utilizing the CLIP’s re-
markable semantic representation of image-text modali-
ties, and well-trained StyleGAN’s high-quality generation
power. Given one text prompt, these methods either lever-
age iterative optimization [16, 20, 33] or learn the corre-
sponding mapping network [4, 20, 35], or require to tune
the complex hyper-parameters online to discover the spe-
cific editing direction [20]. Namely, for different text
prompts, they must implement different optimization pro-
cesses, which is not flexible during training or inference,
and cannot well generalize to any other unseen text.
We consider that the key to alleviate these problems is
1
arXiv:2303.06285v1 [cs.CV] 11 Mar 2023
to precisely build the relationships between the text feature
space and the StyleGAN’s [8] latent visual space within one
model. Manually collecting relevant textual data to train
one model is a possible way [31, 43], but it could only
learn the sub-relationships and lead to limited generaliza-
tion. Therefore, it is challenging but desired to explore how
to construct the full mapping between two feature spaces
without any textual supervision to restrict the generalization
ability.
To achieve this goal, we figure out a text-free training
paradigm, where a text-driven image manipulation model
is trained on easily collected image data instead of textual
data, but the model can be well generalized to input of text
prompts for zero-shot inference. The key of approaching
this is to identify a well semantically aligned feature space
for image and text modalities. Within such an aligned space,
image features can be utilized as pseudo text conditions to
achieve text-free training.
In this paper, we first approach text-free training by a
na
¨
ıve solution, which naturally uses the CLIP image fea-
tures as pseudo text conditions. However, it fails to perform
well-disentangled image manipulation with user-provided
text descriptions, which mainly because there is still a
modality gap between the image and text feature spaces [15]
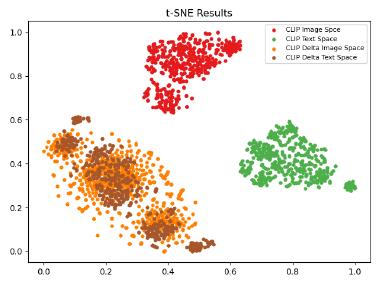
(illustrated in Figure 2). Notably, it is the direction of CLIP
features that is semantically meaningful as all features are
normalized to a unit norm [20, 41], and CLIP feature differ-
ences of paired visual-textual data both mean similar se-
mantic changes. Though gap exists between features of
each individual modality, we have demonstrated that the
CLIP feature space for image-text differences are more con-
sistent and semantically better aligned (shown in Figure 2).
We term this feature space as the CLIP Delta space. Po-
tentially, constructing pseudo text conditions in the better
aligned CLIP delta space will enable more fine-grained and
better disentangled edits for the text-free trained manipula-
tion model.
Based on the above analysis, we propose our DeltaEdit
framework. Specifically, we learn a coarse-to-fine mapping
network from the CLIP image feature differences of two
images to their editing direction at the S style space, then
directly applying the learned mapping onto the differences
of two texts’ CLIP features could obtain the corresponding
editing direction at S space. The predicted editing direction
shall then be able to change image attributes from one text
description to the other text description. As shown in Fig-
ure 1, we also demonstrate DeltaEdit can well generalize to
various target text-prompts without bells and whistles.
To summarize, our main contributions are as follows:
• We push the frontiers of text-free training for image
manipulation, which largely eliminates the training or
inference inflexibility and poor generalization suffered
by previous methods.
Figure 2. Feature space analysis on the MultiModal-CelebA-
HQ [33] dataset. Paired CLIP image-text features (marked in red
and green) and paired CLIP delta image-text features (marked in
orange and brown) are visualized in 2D using t-SNE visualization.
• We investigate and identify the CLIP delta image-
text feature space is better semantically aligned than
the original CLIP space. Furthermore, we propose
our DeltaEdit framework to learn the mapping from
image-feature change to StyleGAN’s S style space
change and seamlessly generalize to predict editing di-
rection from text-feature change.
• Extensive experiments on a variety of datasets, includ-
ing FFHQ and LSUN, verify the effectiveness and ef-
ficiency of our method. Results show DeltaEdit can
well generalize to various edits conditioned on differ-
ent target text-prompts without bells and whistles.
2. Related Work
2.1. Vision-Language Representations
Learning generic vision-language representations is of
great importance in the multi-modal field. Following the
success of BERT [2], many large scale pre-trained vision-
language models [13, 18, 26, 29, 39] are proposed. A re-
cent development, CLIP [21], is extremely powerful for
joint vision-language learning. It is trained on 400 mil-
lion (image, text) pairs and learns a joint multi-modal se-
mantic space for both images and texts. Benefit from
the excellent image/text representation ability, it has been
widely used in various directions, such as domain adapta-
tion [5], image segmentation [22, 40], and image genera-
tion [4, 14, 16, 27, 35, 42].
2.2. Text-Guided Generation and Manipulation
The goal of text-guided image generation [1, 23, 28, 34,
37, 38] is to generate realistic images according to given
text descriptions. As a pioneering work, Reed et al. [23]
embed the text features as the conditional input for a GAN-
based one-stage architecture. After that, StackGAN [37]
2
of 17
100墨值下载
【版权声明】本文为墨天轮用户原创内容,转载时必须标注文档的来源(墨天轮),文档链接,文档作者等基本信息,否则作者和墨天轮有权追究责任。如果您发现墨天轮中有涉嫌抄袭或者侵权的内容,欢迎发送邮件至:contact@modb.pro进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,墨天轮将立刻删除相关内容。
下载排行榜


评论