




VLDB2024_《TDSQL:Tencent Distributed Database System》_腾讯云.pdf
免费下载
TDSQL: Tencent Distributed Database System
Yuxing Chen
Anqun Pan*
Hailin Lei
Tencent Inc.
{axingguchen,aaronpan,
harlylei}@tencent.com
Anda Ye
Shuo Han
Yan Tang
Tencent Inc.
{andaye,shuohan,
allenytang}@tencent.com
Wei Lu
Yunpeng Chai
Renmin University of China
lu-wei@ruc.edu.cn
ypchai@ruc.edu.cn
Feng Zhang
Xiaoyong Du
Renmin University of China
fengzhang@ruc.edu.cn
duyong@ruc.edu.cn
ABSTRACT
Distributed databases have become indispensable in contemporary
computing and data processing, owing to their pivotal role in en-
suring high availability and scalability. They eectively cater to the
requirements of data management and high-concurrency access.
However, developing a distributed database system that is well-
suited for diverse application scenarios, particularly for large-scale
applications, presents several challenges. These challenges include
ensuring data consistency and achieving high levels of performance.
This paper presents TDSQL, a distributed database system that
prioritizes core design principles of distributed systems, including
high availability, strong consistency, and scalability. In particular,
TDSQL has achieved high performance through over a decade of
practical experience and optimization in various modules, such
as the kernel, synchronous replication, and transaction process-
ing, in large-scale application scenarios. By conducting the TPC-C
benchmark test, TDSQL demonstrated outstanding performance,
achieving a throughput of 814 million tpmC across 1650 database
nodes, with a jitter rate of less than 0.2%. This jitter rate is an order
of magnitude lower than the standard required, showcasing the
system’s stability and reliability. During the 8-hour TPC-C standard
stress test, TDSQL successfully completed over 860 billion trans-
actions and processed 40 trillion order details, with zero forced
rollbacks and zero data inconsistency.
PVLDB Reference Format:
Yuxing Chen, Anqun Pan, Hailin Lei, Anda Ye, Shuo Han, Yan Tang, Wei
Lu, Yunpeng Chai, Feng Zhang, and Xiaoyong Du. TDSQL: Tencent
Distributed Database System. PVLDB, 17(12): 3869 - 3882, 2024.
doi:10.14778/3685800.3685812
1 INTRODUCTION
In recent years, the exponential growth in data volume and com-
plexity has led to performance challenges for traditional centralized
databases. Distributed database systems have emerged as a promis-
ing solution, oering high scalability [
12
,
15
,
26
,
55
], availability
[
9
,
60
,
61
], and performance [
18
,
32
,
43
,
50
,
71
,
80
]. However, in
distributed scenarios, new challenges arise, such as the trade-o
between performance [
46
,
53
] and consistency [
8
,
17
,
54
,
64
,
70
].
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons BY-NC-ND 4.0 International
License. Visit https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/ to view a copy of
this license. For any use beyond those covered by this license, obtain permission by
emailing info@vldb.org. Copyright is held by the owner/author(s). Publication rights
licensed to the VLDB Endowment.
Proceedings of the VLDB Endowment, Vol. 17, No. 12 ISSN 2150-8097.
doi:10.14778/3685800.3685812
*Anqun Pan is the corresponding author.
T
encent
D
istributed
SQL
(TDSQL), developed by Tencent Cloud
[
13
], is a database system specically designed to address the per-
formance requirements of large-scale applications, e.g., e-commerce
and banking scenarios, while also ensuring consistency, including
strong synchronization [22, 44, 53, 59].
TDSQL is specically designed to deliver high-performance and
reliable databases for enterprises of all sizes. TDSQL has undergone
iterative developments and meticulous optimizations to enhance
its distributed functionalities, particularly focusing on improving
distributed transaction processing capabilities. A noteworthy char-
acteristic of TDSQL is its share-nothing architecture, which facil-
itates horizontal scaling across multiple nodes. This architecture
empowers TDSQL to eectively handle substantial data volumes
and manage high concurrency, with performance scaling that ap-
proaches linearity. Our TPC-C benchmark test has demonstrated
the capability of TDSQL in eciently processing data exceeding
the 10 PB threshold while maintaining scalability on a single cluster
equipped with over 100,000 physical cores. As an increasing num-
ber of nancial industry enterprises, such as banks and securities
rms, adopt TDSQL, it also oers a range of advanced features to
ensure high availability. These features encompass auto-failover,
data replication, primary-secondary switching, and recovery [79].
TDSQL was ocially launched on Tencent Cloud [
13
] and has
gained widespread adoption across 30,000 enterprises in various in-
dustries, including e-commerce, nance, government, and telecom-
munications. As a result, it has emerged as the market leader in
China’s distributed relational database market [
30
]. Signicantly,
TDSQL holds the distinction of being the rst domestically de-
veloped database in China to be utilized in both internet-based
distributed banking core systems and traditional banking core sys-
tems. It has also played a pioneering role in assisting domestic
banks with migrating their core systems from centralized to dis-
tributed architectures. Currently, 7 out of the top 10 banks in China
have already adopted TDSQL for services such as deposits, loans,
payments, general ledger, and common operations.
This paper shares our experiences in designing, developing, and
optimizing the TDSQL, a large-scale distributed database system.
We conducted the ocial TPC-C benchmark test [
58
] on TDSQL.
The results were impressive compared to open reports [
57
], as TD-
SQL achieved a remarkable performance of 814 million tpmC across
1650 database nodes (surpassing the second place by 15% overall
and 8% per node) with a jitter rate less than 0.2%, which is an order
of magnitude lower than the standard required. Throughout the
8-hour stress test, TDSQL demonstrated exceptional performance
by handling a staggering volume of over 860 billion transactions
and processing an astonishing 40 trillion order details, all without
3869
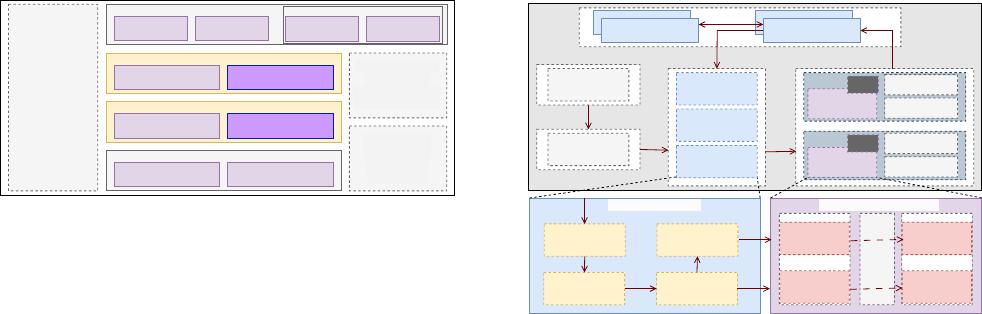
Services
Audit services
Data migration
Data validation
Data subscription
Data governance
SQL firewall
Injection detection.
Scheduling system
Fault migration
Resource scheduling
Capacity scheduling
Backup system
Physical backup
Logical backup
Data recovery
Physical machine Virtual machine
Resouce layer
Noshard cluster Distributed cluster
Storage layer
SQL rewrite Distributed transaction
Compute layer
Operations and
maintenance
Real-time
monitoring
Performance
analysis
Cluster heath
diagnosis
Performance
analysis
Cluster heath
diagnosis
Figure 1: System design overview.
a single transaction of forced rollback or inconsistency. In Tencent
Cloud deployments, TDSQL proved to be highly cost-eective dur-
ing the TPC-C test, with a remarkably low cost of 1.27 CNY/tpmC,
which is only one-third of what comparable vendors oer.
The main contributions of this paper are summarized as follows:
•
We introduce the core design and architecture of the TDSQL
distributed database system. (Section 2)
•
We detail implementations and optimizations of various
modules in TDSQL. We focus on practical experiences gained
from large-scale application scenarios. (Section 3)
•
We conducted the ocial TPC-C benchmark test on TDSQL,
achieving remarkable performance in terms of throughput
(tmpC) and cost (price per tpmC). We also demonstrate our
advantages via the real workload of the banks. (Section 4)
2 DESIGN OVERVIEW
Our primary focus is on designing TDSQL to facilitate rapid scale-
out on commodity hardware, ensuring high performance for large-
scale concurrent transactions and complex queries. Also, we aim to
maintain data consistency and high availability even in the pres-
ence of hardware failures or other extreme scenarios. This section
introduces our system design, core architecture, and applications.
2.1 System Design
Figure 1 shows the design overview of TDSQL, as follows:
Resource Layer. Starting from the bottom, the resource layer is
the IaaS layer service, which can be physical machines or virtual
machines, enabling TDSQL to manage the database instances.
Storage Layer. The storage layer, on top of the resource layer,
emphasizes two storage forms in TDSQL: Noshard and distributed.
Noshard is a centralized database, which supports high availability,
data consistency, and 24/7 automatic failover. The distributed one
additionally provides horizontal scalability.
Compute Layer. The compute layer, on top of the storage layer,
serves as the computation engine. The compute layer primarily han-
dles SQL-related processing, such as lexical analysis, syntax parsing,
and SQL rewriting. This layer does not store data but focuses on
real-time SQL computation, making it more CPU-intensive.
Management Layer. With management layer, DBAs can operate
TDSQL via a web interface without the need to log in to the back-
end. The management platform allows for the management of the
distribution, scaling, and migration of compute and storage nodes.
Intelligent DBA. When faults occur, Intelligent DBA (e.g., [
3
])
nodes can try to analyze the causes of the faults, and identify reasons
SQL Engine
SQL Engine
SQL Engine
Primary
Data Node
Secondary 1
Secondary M
Set 1
Primary
Data Node
Secondary 1
Secondary M
Set N
Client
Load balance
ZooKeeperScheduler
Management
Compute
Storage
Agent
Agent
Connection Pool
Parser Optimizer
Txn Manager
Buffer Pool
Log Buffer
In-memory
B-tree
Redo Log
Disk
OS
cache
SQL Compute Engine InnoDB-like Storage Engine
Figure 2: System core architecture.
for slow SQL queries, sudden IO abnormalities, or machine failures.
For example, SSDs experience an aging process, resulting in slower
response times. It can also tune performance parameters [
25
,
40
,
76
].
Others. There are several other supporting and managing modules.
For example, the scheduling system is responsible for overall re-
source scheduling, including adding and deleting database instances
There is also a backup system, which serves as a cold backup center,
supporting distributed storage systems such as HDFS and mount-
able distributed storage like Ceph [
68
]. We also provide auxiliary
service modules, such as auditing, database migration services [
19
]
between TDSQL and other databases, data validation, SQL rewall,
injection detection, and other security-related modules.
2.2 System Core Architecture
TDSQL adopts a core architecture known as storage-compute sep-
aration [
63
]. As shown in Figure 2, the core architecture consists
of three key parts: storage, compute, and management. TDSQL is
built upon TXSQL [
14
], an open-source MySQL branch maintained
by Tencent, which is fully compatible with MySQL’s syntax and
APIs. Figure 2 shows the key functionalities related to our opti-
mizations in the SQL engine and data node. It includes numerous
optimizations and xes (e.g., consistency issues in § 3.3.1), extensive
development (
∼
3 million lines of code) of distributed features (e.g.,
physical replication in § 3.1 and lock optimizations in § 3.3.2), and
performance enhancements specic to distributed properties (e.g.,
memory model optimization in § 3.3.4). A description of the core
architecture is provided below.
Management Module includes the Scheduler cluster, which helps
users automatically schedule and run various types of jobs [
81
],
such as primary-secondary switches, managing resource additions
in replication instances, or collecting monitoring data. TDSQL com-
bines Scheduler and ZooKeeper [
28
] to activate specied resource
plans within a time window, fullling various complex resource
and job management requirements.
Storage Module consists of Set units, including Data nodes and
Agents. Data nodes store replicas, and in high availability scenarios,
a Set often contains one primary replica and two secondary replicas,
across three physical nodes. Agents are auxiliary modules that
3870
of 14
免费下载
【版权声明】本文为墨天轮用户原创内容,转载时必须标注文档的来源(墨天轮),文档链接,文档作者等基本信息,否则作者和墨天轮有权追究责任。如果您发现墨天轮中有涉嫌抄袭或者侵权的内容,欢迎发送邮件至:contact@modb.pro进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,墨天轮将立刻删除相关内容。
下载排行榜


文档被以下合辑收录
评论