




VLDB2024_FusionQuery: On-demand Fusion Queries over Multi-source Heterogeneous Data_华为.pdf
免费下载

Fusionery: On-demand Fusion eries over Multi-source
Heterogeneous Data
Junhao Zhu
Zhejiang University
Hangzhou, China
zhujunhao@zju.edu.cn
Yuren Mao
Zhejiang University
Hangzhou, China
yuren.mao@zju.edu.cn
Lu Chen
Zhejiang University
Hangzhou, China
luchen@zju.edu.cn
Congcong Ge
Zhejiang University
Hangzhou, China
gcc@zju.edu.cn
Ziheng Wei
Wuhan University
Wuhan, China
ziheng.wei@whu.edu.cn
Yunjun Gao
Zhejiang University
Hangzhou, China
gaoyj@zju.edu.cn
ABSTRACT
Centralised data management systems (e.g., data lakes) support
queries over multi-source heterogeneous data. However, the query
results from multiple sources commonly involve between-source
conicts, which makes query results unreliable and confusing and
degrades the usability of centralised data management systems.
Therefore, resolving the between-sourced conicts is one of the
most important problems for centralised data management systems.
To solve it, many batch data fusion-based methods have been pro-
posed, which require traversing all the data in the centralised data
management systems and cause scalability and exibility issues.
To address these issues, this paper explores the problem of on-
demand fusion queries, where the between-sourced conicts are
solved with only the query-related data; moreover, we propose an
ecient on-demand fusion query framework, Fusionery, which
consists of a query stage and a fusion stage. In the query stage,
we frame the heterogeneous data query problem as a knowledge
graph matching problem and present a line graph-based method
to accelerate it. In the fusion stage, we develop an Expectation
Maximization-style algorithm to iteratively updates data veracity
and source trustworthiness. Furthermore, we design an incremental
estimation method of source trustworthiness to address the lack of
sucient observations. Extensive experiments on two real-world
datasets demonstrate that Fusionery outperforms state-of-the-
art data fusion methods in terms of both eectiveness and eciency.
PVLDB Reference Format:
Junhao Zhu, Yuren Mao, Lu Chen, Congcong Ge, Ziheng Wei, and Yunjun
Gao. FusionQuery: On-demand Fusion Queries over Multi-source
Heterogeneous Data. PVLDB, 17(6): 1337 - 1349, 2024.
doi:10.14778/3648160.3648174
PVLDB Artifact Availability:
The source code, data, and/or other artifacts have been made available at
https://github.com/JunHao-Zhu/FusionQuery.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons BY-NC-ND 4.0 International
License. Visit https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/ to view a copy of
this license. For any use beyond those covered by this license, obtain permission by
emailing info@vldb.org. Copyright is held by the owner/author(s). Publication rights
licensed to the VLDB Endowment.
Proceedings of the VLDB Endowment, Vol. 17, No. 6 ISSN 2150-8097.
doi:10.14778/3648160.3648174
1 INTRODUCTION
Localised data management systems cannot meet the needs of man-
aging rapidly growing multi-source heterogeneous data, such as
structured, semi-structured, and unstructured data from dierent
organizations. Accordingly, centralised data management systems
(e.g., data lakes [
39
]) have emerged and provide a proper solution
for multi-source heterogeneous data management. When submit-
ting queries in centralised data management systems, we can obtain
richer information from multiple sources, which can facilitate vari-
ous downstream applications, such as question answering [
2
,
45
]
and knowledge reasoning [
5
,
13
]. However, dirty and erroneous
data widely exist in centralised data management systems, which in-
curs serious between-source conicts among the query results from
dierent sources. Such conicts make query results unreliable and
confusing, signicantly degrading the performance of downstream
applications. Therefore, resolving between-source conicts in the
query results is one of the most important problems for centralised
data management systems.
To address this problem, many methods have been proposed.
However, all these methods rely on batch data fusion before query
processing [9, 11, 16–18, 31, 32, 36, 37, 40, 50, 55], which traverses
all data within a centralised data management system and resolves
all conicts at once. Batch data fusion-based methods face three
following dilemmas. 1) Poor scalability. Enterprises today store
million-scale data (or even larger scale) in their centralised data
management systems. Conducting data fusion on such a large scale
data at once is time-consuming and even infeasible in practice. 2)
Slow response to data updates. In scenarios where data updates
frequently, such as centralised data management systems for stock
data, the prolonged batch data fusion can lead to data staleness,
resulting in outdated information. 3) Binding with data match-
ing. Typically, data fusion is regarded as the last step of a data
integration pipeline [
10
,
19
,
34
], when the schemas of dierent data
sources have been unied [
15
,
29
] and the records across sources
referring to the same data item have been detected [
21
,
35
,
47
].
The processes before data fusion are collectively termed as (across-
source) data matching. Without accurate data matching, one cannot
nd matched data values describing the same attribute of an entity,
let alone perform eective data fusion and nd out truths from
candidate values.
1337
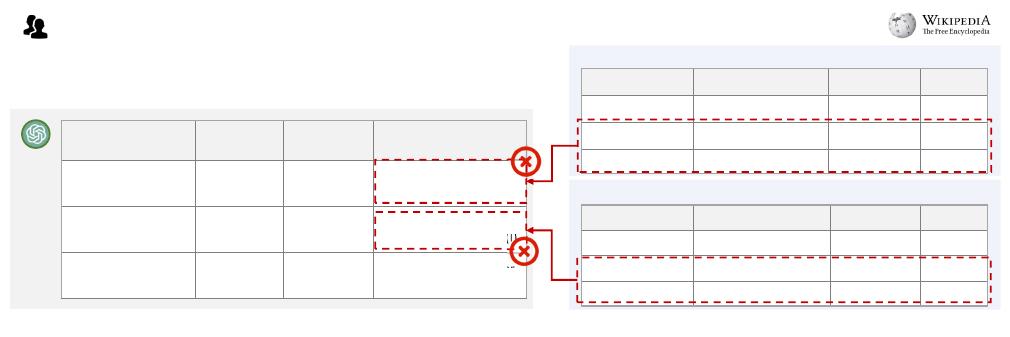
Please generate a table regarding "united states house of representatives elections,
2004 in Ohio", the attributes are ["district", "incumbent", "first elected", "candidates"].
and the values under "district" column are ["Ohio's_1st_congressional_district",
"Ohio's_2nd_congressional_district“, "Ohio's_3rd_congressional_district"]. The values
under other columns are missing, which you should fill in with your knowledge.
District Incumbent
First
Elected
Candidates
Ohio's_1st_congressi
onal_district
Steve Chabot
(R)
1994
Steve Chabot (R), Emily
Johnson (D), Alex Smith (I)
Ohio's_2nd_congressi
onal_district
Rob Portman
(R)
1993 (special)
Rob Portman (R), Sarah
Davis (D), James White (I)
Ohio’s_3rd_congressi
onal_district
Mike Turner
(R)
2002 (special)
Mike Turner (R), Jennifer
Lee (D), Robert Green (I)
Party Candidate Votes %
Republican Steve Chabot 173,430
59.83
Democratic Greg Harris 116,235 40.10
Independent Rich Stevenson 198 0.07
Ohio's 1st Congressional District election, 2004
Ohio's 2nd Congressional District election, 2004
Party Candidate Votes %
Republican Rob Portman 227,102
71.70
Democratic Charles W. Sanders 89,598 28.29
Independent James J. Condit, Jr. 60 0.02
(a) ChatGPT for table generation (b) Retrieved relevant data for verification
2004 United States House of Representatives
Elections in Ohio
Figure 1: (a) ChatGPT generates values in tuples; (b) Fusionery retrieves relevant data from third-party sources for verication
and aggregates conicts to provide reliable data.
To avoid the above dilemmas, this paper proposes the on-demand
fusion query, which resolves the between-source conicts with
only the query-related data and avoids accessing all the data in a
centralised data management system. The advantages of the on-
demand fusion query could be concluded in three aspects. (I) Real-
time data fusion. It only utilizes the query-related data, which
commonly makes up only a small proportion of the data in a cen-
tralised data management system and can be processed in real-time.
(II) Adaptive to data updates. Both the query step and data fusion
step in the on-demand fusion query can be completed in real-time;
thus, it can be adaptive to frequent data updates. (III) Free of data
matching. By matching data from various sources with users’ in-
tents (i.e., queries), on-demand fusion queries eectively sidestep
the need for explicit across-source data matching. The advantages
include: (1) well-dened query constraints provide clear match crite-
ria; (2) many-to-many comparisons in across-source data matching
are reduced to one-to-many comparisons, taking less time com-
plexity. Despite the progress made by a few studies [
23
,
42
,
51
],
two challenges have still existed in developing on-demand fusion
queries over heterogeneous multi-source data.
Challenge I: How to support unied queries across multi-source
heterogeneous data? Due to the data type heterogeneity (i.e., struc-
tured, semi-structured, and unstructured data) and the semantic
heterogeneity (i.e., dierent sources involve dierent vocabularies)
of heterogeneous multi-source data, there is still no proven solution
for unied queries across multi-source heterogeneous data.
To solve data type heterogenity, we convert heterogeneous data
into knowledge graphs and formulate it as a knowledge graph
matching problem. Due to the richness of semantic information on
both nodes and edges, knowledge graph matching is much more
complex than plain graph matching. Specically, the search space
of the knowledge graph matching is exponential to the scale of
the knowledge graph. Given a query graph with
|𝑉
𝑞
|
nodes and
|𝑅
𝑞
|
edges, a data graph with
|𝑉
𝑑
|
nodes and
|𝑅
𝑑
|
edges, taking
the simplest solution BFS as an example, the time complexity is
𝑂 ((|𝑉
𝑞
| + |𝑅
𝑞
|)(|𝑉
𝑑
| + |𝑅
𝑑
|))
in the best case, which is infeasible
in practice. To speed up knowledge graph matching, we introduce
knowledge line graph transformation to decouple semantic infor-
mation from graph structure, reducing the time complexity of graph
matching to
𝑂 (|𝑅
𝑞
||𝑅
𝑑
|)
. To solve semantic heterogeneity, we fo-
cus on approximate matching in semantic information encoded by
pre-trained language models, which excel in capturing semantic
relations between words. For example, it can capture similar mean-
ings for dierent terms, such as "spouse", "wife" and "husband";
meanwhile it can also identify dierent meanings for the similar
words like "Apple Inc" and "Big Apple".
Challenge II: How to perform high-quality data fusion in the
on-demand setting? The performance of data fusion is highly de-
pendent on data-hungry probability estimations. In the on-demand
setting, we only have a small amount of query-related data; thus,
it is necessary to cope with the data starvation of data fusion and
develop a novel on-demand data fusion method.
To this end, we develop an Expectation Maximization (EM)-style
learning strategy that consists of two steps. (i) The data veracity
estimation learns the probability that a data item is a correct an-
swer to the query and (ii) the source trustworthiness estimation
learns the probability that a data source provides the correct data.
The two steps are repeated iteratively until convergence. Besides,
considering that observed data is limited, we propose an incremen-
tal estimation for source trustworthiness based on the historical
estimate and the current query results. Furthermore, to improve
the eectiveness and eciency of data fusion, we design an au-
tonomous semantic matching threshold update mechanism to strike
a balance between retrieval precision and recall.
Incorporating optimization strategies addressing challenges men-
tioned above, we propose Fusionery, an ecient framework for
on-demand fusion queries over heterogeneous data.
1.1 Motivating Example
There are several potential applicatioins for Fusionery, such as
retrival-based data cleaning [
3
,
12
] and veried generative AI [
43
].
Here, we reinforce the motivations for Fusionery by illustrating
a real-world application in the realm of the veried generative AI.
1338
of 13
免费下载
【版权声明】本文为墨天轮用户原创内容,转载时必须标注文档的来源(墨天轮),文档链接,文档作者等基本信息,否则作者和墨天轮有权追究责任。如果您发现墨天轮中有涉嫌抄袭或者侵权的内容,欢迎发送邮件至:contact@modb.pro进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,墨天轮将立刻删除相关内容。
下载排行榜


文档被以下合辑收录
评论