




VLDB2024_Optimizing Distributed Tiered Data Storage Systems with DITIS_华为.pdf
免费下载

Optimizing Distributed Tiered Data Storage Systems with DITIS
Sotiris Vasileiadis
Cyprus University of Technology
Limassol, Cyprus
sr.vasileiadis@edu.cut.ac.cy
Matthew Paraskeva
Cyprus University of Technology
Limassol, Cyprus
mp.paraskeva@edu.cut.ac.cy
George Savva
Cyprus University of Technology
Limassol, Cyprus
gec.savva@edu.cut.ac.cy
Andreas Efstathiou
Cyprus University of Technology
Limassol, Cyprus
andreasefstathiouudt@gmail.com
Edson Ramiro Lucas Filho
Cyprus University of Technology
Limassol, Cyprus
edson.lucas@cut.ac.cy
Jianqiang Shen
Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
Shenzhen, China
shenjianqiang@huawei.com
Lun Yang
Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
Shenzhen, China
yanglun12@huawei.com
Kebo Fu
Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
Shenzhen, China
fukebo@huawei.com
Herodotos Herodotou
Cyprus University of Technology
Limassol, Cyprus
herodotos.herodotou@cut.ac.cy
ABSTRACT
Modern data storage systems are characterized by a distributed
architecture as well as the presence of multiple storage tiers and
caches. Both system developers and operators are challenged with
the complexity of such systems as it is hard to evaluate how a con-
guration change will impact the workload or system performance
and identify the best conguration to satisfy some performance
objective. DITIS is a new simulator that models the end-to-end
execution of le requests on distributed tiered storage systems that
addresses the aforementioned challenges eciently without any
costly system redeployments. The demonstration will showcase
the key functionalities and benets oered by DITIS, including
(i) analyzing workload traces to understand their characteristics
and the behavior of the underlying storage system; (ii) running
simulations with dierent congurations to evaluate their impact
on performance; and (iii) running optimizations over custom search
spaces to nd the best conguration that satises a given objective.
PVLDB Reference Format:
Sotiris Vasileiadis, Matthew Paraskeva, George Savva, Andreas Efstathiou,
Edson Ramiro Lucas Filho, Jianqiang Shen, Lun Yang, Kebo Fu,
and Herodotos Herodotou. Optimizing Distributed Tiered Data Storage
Systems with DITIS. PVLDB, 17(12): 4393 - 4396, 2024.
doi:10.14778/3685800.3685883
PVLDB Artifact Availability:
The source code, data, and/or other artifacts have been made available at
https://github.com/cut-dicl/ditis-ui.
1 INTRODUCTION
Modern data storage systems exhibit considerable complexity due
to their distributed nature and the need to balance data and load
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons BY-NC-ND 4.0 International
License. Visit https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/ to view a copy of
this license. For any use beyond those covered by this license, obtain permission by
emailing info@vldb.org. Copyright is held by the owner/author(s). Publication rights
licensed to the VLDB Endowment.
Proceedings of the VLDB Endowment, Vol. 17, No. 12 ISSN 2150-8097.
doi:10.14778/3685800.3685883
across the storage nodes [
7
]. In addition, these systems incorporate
multiple storage tiers, encompassing numerous HDDs and SSDs,
along with multiple cache levels of DRAM and NVRAM. Conse-
quently, new data management policies are required to optimize
performance and resource utilization. Furthermore, these systems
integrate diverse redundancy mechanisms, including replication
and erasure coding, to ensure data durability and fault tolerance.
The multifaceted architecture of modern data storage systems
necessitates sophisticated management strategies to harness their
full potential, for both system developers and operators. For devel-
opers, evaluating the impact of new policies for caching, tiering,
and other mechanisms is cumbersome and time-consuming as it
requires system redeployments. Hence, it is very dicult to explore
the design space for promoting changes in the system. For opera-
tors, it is challenging to evaluate how their workloads will behave
after a system reconguration or upgrade as well as determine the
best system conguration that will satisfy their objectives.
Simulation presents a logical approach to address the aforemen-
tioned challenges. Numerous simulators concentrate on modeling
particular aspects of storage systems, including caching and tier-
ing policies [
6
], scheduling [
5
], network communication [
1
], and
le system behavior [
2
]. Some simulators are also available for
simulating either single-node multi-tier storage systems [4, 10] or
distributed single-tier storage systems [
8
,
9
]. However, none of
the current simulators can fully encompass the complexity and
nuances of contemporary storage systems that feature multiple
storage nodes, diverse storage tiers, and various cache levels.
DITIS [
3
] is a new comprehensive simulator that models the end-
to-end execution of le requests on distributed multi-tier storage
systems. The key novelties of DITIS include (i) an architecture based
on an adaptation of the actor model instead of the typical event-
oriented or process-oriented models; (ii) a machine learning-based
initialization process for placing data to the appropriate tier/cache
before the simulation begins; and (iii) ne-grained but ecient
performance cost models for HDD, SSD, NVRAM, DRAM, and net-
work communications. Moreover, DITIS is extremely congurable
with 131 conguration parameters touching all aspects of a storage
system (e.g., number of nodes/tiers/caches, device and network
4393
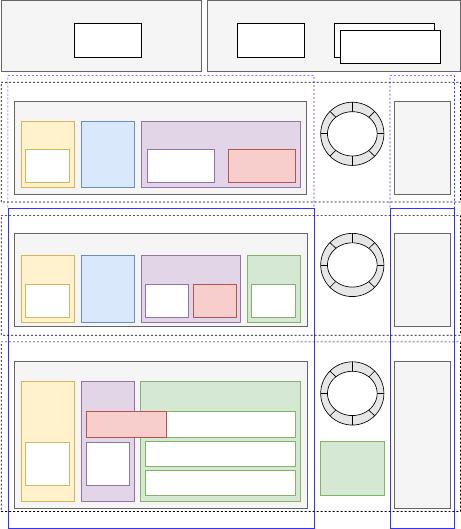
Storage NodeStorage Node
Access Layer
Persistence Layer
Workload Replay^*
Application
Application^
Workload Initializer^*
Trace ParserTrace Parser
File Home Layer
Persistence Module^
Redundancy
Policy*
Block
Balancer*
File Home Module^
Metadata
Manager
Storage Pool
Manager
Cold Storage Pool
SATA/NL-SAS SSDs or HDDs
Warm Storage Pool
SAS SSDs
Hot Storage Pool
NVMe SSDs
Access Module^
Metadata
Manager
Cache
Dataflow
Manager
Dataflow
Policies*
Dataflow
Manager
Dataflow
Policies*
Dataflow
Manager
Dataflow
Policies*
Cache
Manager
L2 Cache
Policies*
Cache
Manager
L0 Cache
Policies*
L0 Data
Cache
Cache
Manager
L1 Cache
Policies*
L1 Data
Cache
Tiering
Manager
Tiering
Policies*
L2 Data Cache
File Home
Module^
Access
Module^
Persistence
Module^
Application
Connector*
File
Balancer*
Figure 1: DITIS architecture. Components marked with ^ are
actors and with
∗
are pluggable policies.
characteristics, etc.) as well as extensible with 44 pluggable policies
controlling all aspects of data ow, caching, and tiering decisions.
This demonstration aims at showcasing the benets to both
storage system developers and operators from using DITIS to:
•
Understand workload characteristics and the behavior of the
underlying storage system;
•
Evaluate the impact of dierent storage conguration setups and
policies to the workload performance; and
•
Optimize the storage conguration to satisfy a workload or sys-
tem objective such as maximizing throughput or cache hit ratio.
2 DITIS SIMULATOR
DITIS is a simulator designed for distributed and tiered le-based
storage systems, capable of handling up to three storage tiers plus
three levels of caches. It allows for the conguration of various
storage media devices such as HDD, SSD, NVRAM, and DRAM, each
with specic performance characteristics. The simulator calculates
the duration of I/O requests for each tier, cache, and network using
detailed performance cost models for each device type.
2.1 System Architecture
DITIS requires two inputs to simulate a workload execution on
a storage system: (1) a text le containing a workload trace with
le requests containing details like process ID, timestamp, le op-
eration, oset, length, le size, and original duration; and (2) a
storage conguration that denes the storage system’s behavior
and structure, allowing for the customization of components of the
storage system, specifying their performance characteristics, and
determining which policies to use during the simulation. The main
system components of DITIS, shown in Figure 1, are:
•
Workload Initializer: Sets up the initial state of the system
(e.g., creates pre-existing les) before the trace is executed.
•
Workload Replay: Controls the order and timing of submitting
and simulating the le requests from the workload trace.
•
Application: Represents external applications (processes) that
submit le requests to the storage system in parallel.
•
Application Connector: Balances incoming application con-
nections to the available Access Modules.
•
Access Module: Represents a storage system’s access compo-
nent running on a storage node or a system’s client.
•
File Balancer: Distributes les and le requests to File Home
Modules based on full le paths.
•
File Home Module: Maintains a partition of the system’s names-
pace on a storage node.
•
Block Balancer: Distributes data blocks and block requests to
Persistence Modules based on a block IDs (or addresses).
•
Persistence Module: Stores and processes data blocks in tiered
storage pools on a storage node.
•
Redundancy Policy: Controls the redundancy policy of blocks
(e.g., using erasure coding, replication, or RAID).
DITIS generates an output trace, accurately capturing the sequence
of le requests from the input trace but with a simulated duration
for each operation. Alongside, DITIS produces a detailed report
containing information and statistics about the workload execution
and the storage system (described in Section 3).
2.2 Simulation Process
Following the Actor Model, the key components of the system are
treated as actors (marked with ^ in Figure 1). These actors main-
tain their own private state, process messages received from other
actors, and send messages to other actors enabling asynchronous
message exchange, while respecting a simulation clock. This ap-
proach ensures the sequence and timing of events accurately reect
those of a real distributed multi-threaded system. In DITIS, the
process for handling I/O requests begins when an Application con-
nects to an Access Module and sends a le request (e.g., a read
request) to the storage system. If the request can be served by the
Access Module (e.g., perform the read from the local cache), a re-
spond is sent back to the Application. Otherwise, the request is
forwarded to the appropriate File Home Module for processing.
The request can be completed there or forwarded as one or more
block requests to the appropriate Persistence Module(s). There, the
request is served from the appropriate storage pool and returned
upstream. While the requests are getting processed, all relevant
decisions are made by pluggable policies, such as cache admission,
eviction, and prefetching, tier migrations, block redundancy, etc.
At each step, the duration is calculated based on several pluggable
performance cost models, while taking into account the potential
concurrent execution of requests as well as resource contention.
2.3 Performance Cost Modeling
The performance cost models for all devices and network are de-
signed to be pluggable, thus making it easy to replace to accommo-
date dierent simulation needs or advancements in technology.
4394
of 4
免费下载
【版权声明】本文为墨天轮用户原创内容,转载时必须标注文档的来源(墨天轮),文档链接,文档作者等基本信息,否则作者和墨天轮有权追究责任。如果您发现墨天轮中有涉嫌抄袭或者侵权的内容,欢迎发送邮件至:contact@modb.pro进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,墨天轮将立刻删除相关内容。
下载排行榜


文档被以下合辑收录
评论