




Data Management For Large Language Models A Survey.pdf
免费下载

Data Management For Large Language Models: A Survey
Zige Wang
1∗
Wanjun Zhong
2†
Yufei Wang
2
Qi Zhu
2
Fei Mi
2
Baojun Wang
2
Lifeng Shang
2
Xin Jiang
2
Qun Liu
2
1
School of Computer Science, Peking University
2
Huawei Noah’s Ark Lab
zigewang@stu.pku.edu.cn
{zhongwanjun1, wangyufei44, zhuqi41, mifei2, puking.w}@huawei.com
{Shang.Lifeng, Jiang.Xin, qun.liu}@huawei.com
Abstract
Data plays a fundamental role in the training
of Large Language Models (LLMs). Effective
data management, particularly in the formula-
tion of a well-suited training dataset, holds sig-
nificance for enhancing model performance and
improving training efficiency during pretrain-
ing and supervised fine-tuning phases. Despite
the considerable importance of data manage-
ment, the current research community still falls
short in providing a systematic analysis of the
rationale behind management strategy selec-
tion, its consequential effects, methodologies
for evaluating curated datasets, and the ongoing
pursuit of improved strategies. Consequently,
the exploration of data management has at-
tracted more and more attention among the re-
search community. This survey provides a com-
prehensive overview of current research in data
management within both the pretraining and
supervised fine-tuning stages of LLMs, cover-
ing various noteworthy aspects of data man-
agement strategy design: data quantity, data
quality, domain/task composition, etc. Looking
toward the future, we extrapolate existing chal-
lenges and outline promising directions for de-
velopment in this field. Therefore, this survey
serves as a guiding resource for practitioners as-
piring to construct powerful LLMs through ef-
fective data management practices. The collec-
tion of the latest papers is available at
https://
github.com/ZigeW/data_management_LLM.
1 Introduction
Large Language Models (LLMs) have shocked
the natural language processing (NLP) community
with their strong performance and emergent abil-
ities (OpenAI, 2023; Touvron et al., 2023a; Wei
et al., 2022). According to previous studies (Ka-
plan et al., 2020; Hoffmann et al., 2022), LLMs’
achievements depend heavily on self-supervised
∗
Work done during Zige Wang’s internship at Huawei
Noah’s Ark Lab.
†
Corresponding author (zhongwanjun1@huawei.com)
pretraining over processed vast volumes of text
data. Recent research (Zhou et al., 2023a; Ouyang
et al., 2022) further enhances LLMs’ instruction-
following ability and performance on downstream
tasks through supervised fine-tuning on deliber-
ately curated instruction datasets.
Constructing a well-suited training dataset,
which we define as data management, is vitally
important and challenging in both the pretraining
and supervised fine-tuning (SFT) stages of LLMs.
In the pretraining stage, constructing datasets with
high-quality and the most useful data is essential
for efficient training (Jain et al., 2020; Gupta et al.,
2021). To equip LLMs with general abilities, het-
erogeneous dataset composition with mixtures of
domains is also required (Gao et al., 2020; Long-
pre et al., 2023b; Shen et al., 2023). However,
many prominent LLMs do not enclose (Anil et al.,
2023; OpenAI, 2023) or only document which
procedures are chosen (Brown et al., 2020; Work-
shop et al., 2022; Touvron et al., 2023a) in the
construction of their pretraining data, leaving the
reason behind it absent. In the SFT stage, the
performance and instruction-following abilities of
LLMs are largely evoked by carefully designed
instruction datasets (Sanh et al., 2022; Ouyang
et al., 2022). Although a handful of instruction
datasets/benchmarks have been proposed with hu-
man annotations (Wang et al., 2022; Köpf et al.,
2023), self-instruct (Wang et al., 2023c; Taori et al.,
2023) or collection of existing datasets (Si et al.,
2023; Anand et al., 2023), practitioners still find it
confusing about the effect of instruction datasets
on the performance of fine-tuned LLMs, leading
to difficulties in choosing proper data management
strategies in LLM fine-tuning practices.
To address these challenges, A systematic anal-
ysis of data management is required regarding the
rationale behind management strategy selection
and its consequential effect, the evaluation of cu-
rated training datasets, and the pursuit of improved
arXiv:2312.01700v1 [cs.CL] 4 Dec 2023
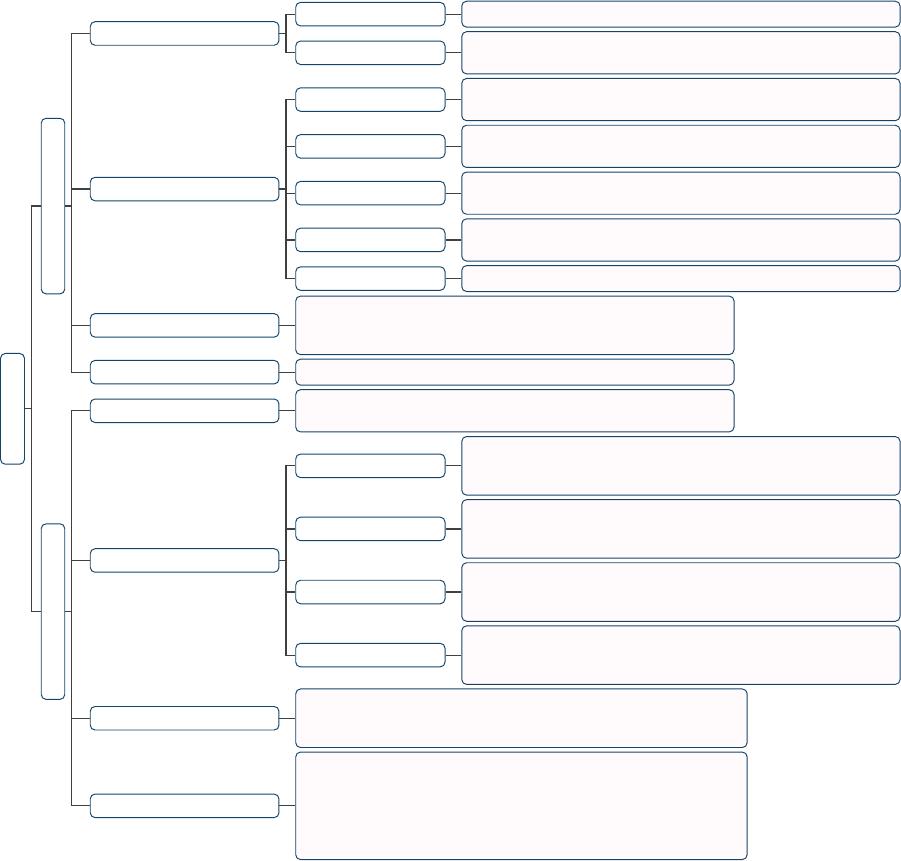
Data Management
Pretraining (§2)
Data Quantity (§2.1)
Scaling Laws Kaplan et al. (2020), DeepMind Chinchilla Scaling Law (Hoffmann et al., 2022)
Data Repetition
Villalobos et al. (2022), Muennighoff et al. (2023), Hernandez et al. (2022),
Xue et al. (2023), D4 (Tirumala et al., 2023)
Data Quality (§2.2)
Deduplication
Lee et al. (2021), Kandpal et al. (2022), Silcock et al. (2022),
SemDeDup (Abbas et al., 2023), Kaddour (2023)
Quality Filtering
Gao (2021), Kreutzer et al. (2022), Gunasekar et al. (2023), Li et al. (2023b),
RefinedWeb (Penedo et al., 2023), Marion et al. (2023), Longpre et al. (2023b)
Toxicity Filtering
Luccioni and Viviano (2021), Xu et al. (2021), Welbl et al. (2021),
Longpre et al. (2023b)
Social Bias
Dodge et al. (2021), Meade et al. (2022), Gururangan et al. (2022)
Feng et al. (2023)
Diversity & Age
Lee et al. (2023a), D2 Pruning (Maharana et al., 2023), Longpre et al. (2023b)
Domain Composition (§2.3)
Longpre et al. (2023b), CodeGen2 (Nijkamp et al., 2023),
SlimPajama-DC (Shen et al., 2023), DSIR (Xie et al., 2023b),
DoReMi (Xie et al., 2023a), DoGE (Fan et al., 2023)
Data Management Systems (§2.4) Data-Juicer (Chen et al., 2023a), Oasis (Zhou et al., 2023c)
Supervised Fine-Tuning (§3)
Data Quantity (§3.1)
Ji et al. (2023), LIMA (Zhou et al., 2023a), Yuan et al. (2023),
Chen et al. (2023b), DMT (Dong et al., 2023), Song et al. (2023)
Data Quality (§3.2)
Instruction Quality
INSTRUCTEVAL (Chia et al., 2023), LIMA (Zhou et al., 2023a),
Ding et al. (2023), Wang et al. (2023d), Li et al. (2023a),
Instruction Mining (Cao et al., 2023)
Instruction Diversity
UltraChat (Ding et al., 2023), LIMA (Zhou et al., 2023a),
Alpaca (Taori et al., 2023), #InsTag (Lu et al., 2023),
Explore-Instruct (Wan et al., 2023)
Instruction Complexity
#InsTag (Lu et al., 2023), WizardLM (Xu et al., 2023),
WizardCoder (Luo et al., 2023), Orca (Mukherjee et al., 2023),
Tree-Instruct (Zhao et al., 2023a), CELLO (He et al., 2023)
Prompt Design
Mishra et al. (2022), Khashabi et al. (2022), Gonen et al. (2022),
Yin et al. (2023b), Kung and Peng (2023), UIT (Liang et al., 2023),
Weber et al. (2023), Gudibande et al. (2023), Song et al. (2023)
Task Composition (§3.3)
Wei et al. (2021), Wang et al. (2022), Sanh et al. (2022), Chung et al. (2022),
Flan 2022 (Longpre et al., 2023a), ELM (Jang et al., 2023), Chen et al. (2023b)
DMT (Dong et al., 2023), OPT-IML (Iyer et al., 2022), Tulu (Wang et al., 2023b)
Data-Efficient Learning (§3.4)
AlShikh et al. (2023), Attendu and Corbeil (2023), Ivison et al. (2023),
Instrucion Mining (Cao et al., 2023), AlpaGasus (Chen et al., 2023c),
OpenChat (Wang et al., 2023a), DiverseEvol (Wu et al., 2023),
Dynosaur (Yin et al., 2023a), MAmmoTH (Yue et al., 2023),
DMT (Dong et al., 2023), LoBaSS (Zhou et al., 2023b),
Data-Juicer (Chen et al., 2023a)
Figure 1: Taxonomy of research in data management for pretraining and supervised fine-tuning of Large Language
Models (LLM).
strategies. Therefore, this survey aims to provide a
comprehensive overview of current research in data
management as shown in Figure 1. In Section 2, we
focus on pretraining data management, including
the research on data quantity, data quality, domain
composition, and data management systems. In
Section 3, we discuss the data quantity, data qual-
ity, task composition, and data-efficient learning in
the SFT stage of LLMs. In Section 4, looking into
the future, we present the existing challenges and
promising future directions in training data man-
agement for LLMs. Through this survey, we are
devoted to offering a guiding resource to practi-
tioners attempting to build powerful LLMs with
effective and efficient data management practices.
2 Pretraining of LLM
Data management is found to be important in
the pretraining of many prominent LLMs (Ope-
nAI, 2023; Touvron et al., 2023a; Wei et al.,
2022). While most do not report their data man-
agement procedures or only report the strategies
they adopted, the reason for choosing the specific
strategy and the effects of data management strate-
gies are crucial for building stronger LLMs. In this
section, we first review the research studying train-
ing dataset scaling law with/without data repetition.
Then, data quality regarding deduplication, qual-
ity filtering, toxicity filtering, social bias, and data
diversity and age are explored. After that, domain
composition and domain reweighting methods are
of 17
免费下载
【版权声明】本文为墨天轮用户原创内容,转载时必须标注文档的来源(墨天轮),文档链接,文档作者等基本信息,否则作者和墨天轮有权追究责任。如果您发现墨天轮中有涉嫌抄袭或者侵权的内容,欢迎发送邮件至:contact@modb.pro进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,墨天轮将立刻删除相关内容。
下载排行榜


评论