




ICDE 2025_MemQ:A Graph-Based Query Memory Prediction Framework for Effective Workload Scheduling.pdf
免费下载
MemQ: A Graph-Based Query Memory Prediction
Framework for Effective Workload Scheduling
Yang Wu
1
, Xuanhe Zhou
2
, Xiaoguang Li
3
, Jinhuai Kang
3
, Chunxiao Xing
4
,
Tongliang Li
5
, Xinjun Yang
5
, Wenchao Zhou
5
, Feifei Li
5
, Yong Zhang
4,∗
1
Department of Computer Science, Tsinghua University, Beijing, China
2
Department of Computer Science, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai, China
3
Business-intelligence of Oriental Nations Corporation Ltd., Beijing, China
4
Beijing National Research Center for Information Science and Technology, Beijing, China
5
Alibaba Group, Hangzhou, China
Emails: {wu-y22}@mails.tsinghua.edu.cn, {zhouxh}@cs.sjtu.edu.cn, {lixiaoguang1, kangjinhuai}@bonc.com.cn,
{litongliang.ltl, xinjun.y, zwc231487, lifeifei}@alibaba-inc.com, {xingcx, zhangyong05}@tsinghua.edu.cn,
Abstract—Query memory prediction is an essential yet un-
derexplored problem in self-driving databases, particularly for
high-concurrency workload scheduling where efficient resource
utilization is critical. Existing works mainly focus on cost and
latency estimation (e.g., using plan representation learning), while
memory prediction poses new challenges such as requiring (1)
numerous memory-specific training data, (2) memory-relevant
query plan featurization strategies, and (3) a prediction model
suitable for capturing the complexities of memory usage in query
operations. Moreover, most learning-based approaches do not
consider transferability across different datasets and database
systems.
This paper introduces MemQ, a graph-based memory pre-
diction framework designed for effective workload scheduling.
First, we build a comprehensive training dataset for memory
prediction by executing diverse query workloads across multiple
datasets and recording their diverse peak memory consumptions.
Second, our MemQ model leverages operator-level features of
query plans, achieving high prediction accuracy, compact model
size, and fast training and inference times. Third, we integrate the
MemQ model into memory-aware First Fit Decreasing (FFD) and
Bidrectional Fit (BF) scheduling strategy to optimize resource
utilization. Extensive experiments demonstrate the effectiveness
of our homogeneous query plan graph model. Moreover, our
FFD scheduling strategy reduces makespan (total query execution
time) by up to 55% and decreases retry counts by over 99%
compared to default strategies when batch executing analytical
queries on PostgreSQL. Furthermore, our novel BF strategy
reduces makespan by 15.17% and reduces sum of total time
by 41.41% compared with FFD strategy when batch executing
mixed workloads.
Index Terms—query memory prediction, homogeneous opera-
tor graph, workload scheduling, first fit decreasing
I. INTRODUCTION
In modern database systems, efficient query processing
is essential to meet the demands of growing data volumes
and increasing query complexity. These systems must handle
This Work was supported by National Key R&D Program of China
(2023YFB4503600), NSF of China (61925205, 62232009, 62102215),
Business-intelligence of Oriental Nations Corporation Ltd., Alibaba Research
Intern Program.
diverse query types while optimizing resource utilization under
high concurrency requests. One key issue arises when queries
consume excessive memory, leading to allocation failures [29],
prolonged execution times, degraded system performance, and
even potential database shutdowns [1]. On the other hand,
insufficient memory allocation results in suboptimal resource
utilization [2]. Addressing these issues requires memory pre-
diction strategy that can balance resource allocation and sys-
tem performance [15], [27].
Recent advancements in machine learning for databases
(ML4DB) [16] have introduced query plan representation
learning [45] as a cornerstone for tasks like cost estimation
and query optimization [8], [19]. While significant progress
has been made in latency and cost prediction [12], [21],
[35], [39], [44], the domain of memory prediction remains
relatively underexplored. The key challenges of query memory
prediction are summarized as follows:
C1: Lack of Ground-Truth Data. Learned query memory
prediction methods demand a vast number of precise mem-
ory usage data for model training. Profiling memory usage
across diverse workloads and database systems is both time-
consuming and resource-intensive.
C2: Complexity of Query Plans. Modern query plans involve
various operator patterns and complex predicates. Memory
usage is influenced by factors such as intermediate data
sizes, join algorithms, and aggregation strategies, leading to
substantial variability.
C3: Transferability across Datasets. Memory usage can
vary significantly across different datasets due to variations in
data distributions, such as skewness or irregularities. Queries
involving skewed joins or large group-by aggregations can
trigger unexpected memory spikes.
C4: Transferability across Systems. In different database
systems, the memory management and query execution strate-
gies can be significantly different. Models trained for one
system often fail to generalize to others without substantial
adaptation. It is tricky to develop transferable prediction
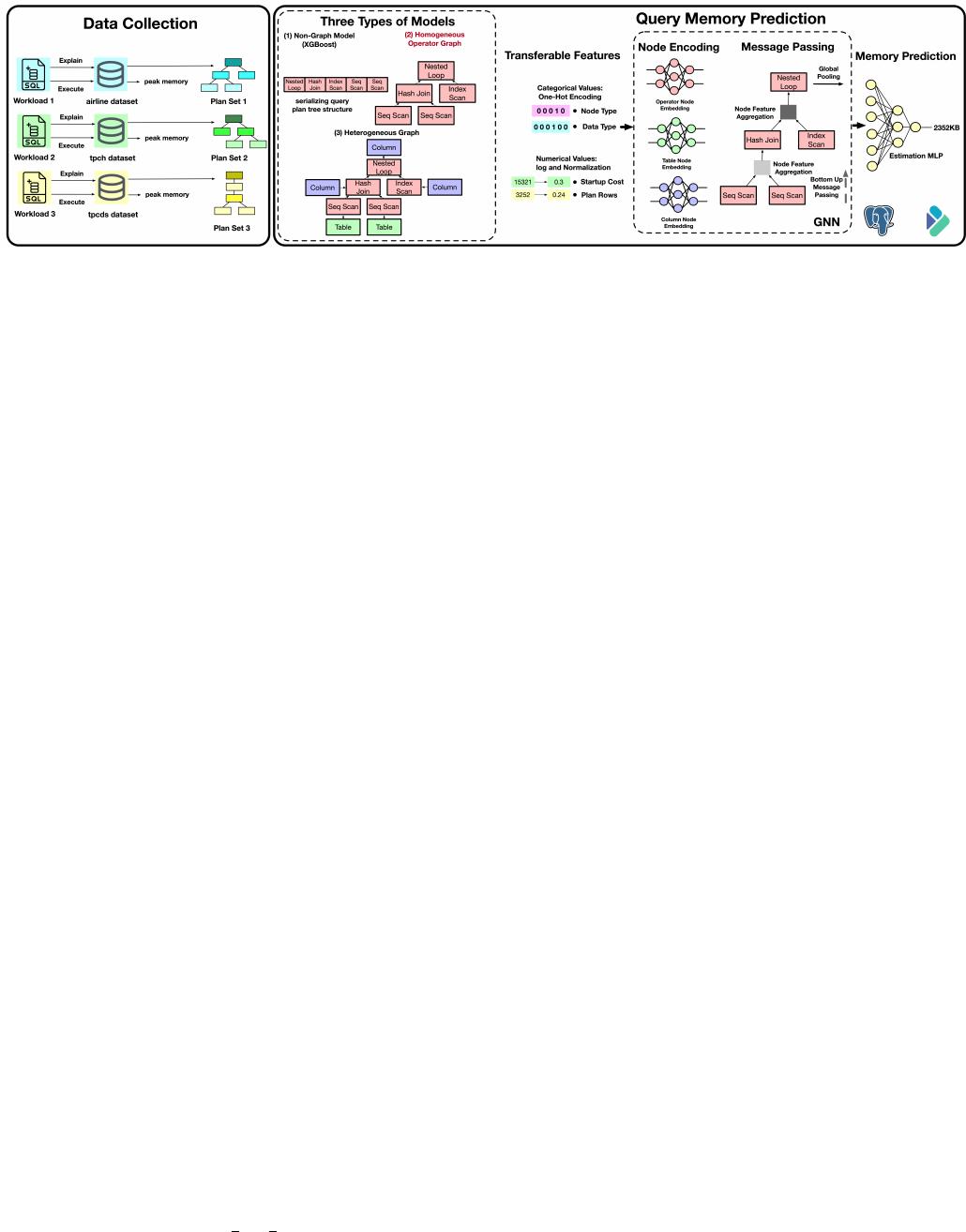
Fig. 1. Data Collection and Query Memory Prediction in MemQ Framework
models that work across heterogeneous systems with minimal
modification [26], [38].
C5: Real-Time Efficiency. Practical usage of query memory
prediction model such as workload scheduling requires balanc-
ing prediction accuracy with computational efficiency. Models
must be lightweight, fast to train, and efficient during inference
to avoid bottlenecks in high-concurrency environments.
This paper addresses these challenges by introducing
MemQ, a graph-based memory prediction framework. The
framework encompasses dataset collection specifically for
memory prediction, query memory prediction over homoge-
neous operator graph, and workload scheduling using First
Fit Decreasing (FFD) or Bidirectional Fit (BF) strategy. The
framework is designed to handle complex query plans and
can be transferable across different datasets and even database
systems, and meanwhile maintain a relatively small size while
ensuring efficiency.
A. Contributions
The main contributions of this work are as follows:
• We are the first to formalize the task of memory prediction
at the query level and introduce a graph-based query memory
prediction framework MemQ
1
.
• We design a tool to execute hundreds of thousands of queries
and collect comprehensive memory consumption data (C1).
We make this dataset publicly available
2
to facilitate future
studies.
• Our query memory prediction model leverages the structural
features of query plans (C2) and is designed to be transferable
across datasets (C3) and database systems (C4) while main-
taining a lightweight architecture for fast training and efficient
inference (C5).
• We propose memory-aware FFD and BF scheduling al-
gorithms that leverage query-level memory predictions to
optimize query execution order and concurrency (C5).
• Extensive experiments demonstrate MemQ model’s superi-
ority on query memory prediction in accuracy, transferability,
and efficiency. Our memory-aware FFD scheduling strategy
achieves up to 55% reduction in execution time and a
99% reduction in query retries for batch execution of 900
1
https://github.com/earthwuyang/pg mem pred
2
https://cloud.tsinghua.edu.cn/d/9ad34a4caafe405ebcc7/
queries on PostgreSQL. Furthermore, when executing a mixed
workload of 100 queries, BF strategy reduces makespan by
15.17% and reduces sum of total time by 41.41% compared
with FFD strategy.
B. Paper Organization
The remainder of this paper is structured as follows: Sec-
tion II formalizes the Query Memory Prediction problem
and introduces MemQ. Section III presents its application on
workload scheduling. Section IV provides a comprehensive
evaluation of MemQ. Section V discusses the key findings
and points out potential future directions.
II. MEMQ: A GRAPH-BASED QUERY MEMORY
PREDICTION FRAMEWORK
In this section, we formalize the Query Memory Prediction
(QMP) problem and introduce the main techniques in MemQ,
including dataset construction, query featurization (e.g., the
homogeneous graph), and prediction model construction.
A. Problem Definition
The Query Memory Prediction problem involves estimating
the peak memory consumption M
q
of a query q during its
execution, which can be written as:
θ = arg min
θ
E
q∈Q
[L(M
q
, f(q; θ))] (1)
where L is the loss function, Q denotes the set of all possible
queries, f (q; θ) is a predictive model parameterized by θ.
The objective of query memory prediction is to learn θ that
minimizes the prediction error between M
q
and f(q; θ) across
diverse workloads and environments.
B. Framework of MemQ
In MemQ, dataset collection, query memory prediction are
illustrated in Figure 1 and workload scheduling is presented
in Figure 3. These components are detailed below.
C. Dataset Collection
First, we construct a dataset involving diverse query mem-
ory prediction scenarios by combining publicly available real-
world datasets [24], i.e., airline, carcinogenesis, credit, em-
ployee, financial, geneea, hepatitis, and walmart, with the
standard benchmarks like TPC-H and TPC-DS [25], [36].
of 14
免费下载
【版权声明】本文为墨天轮用户原创内容,转载时必须标注文档的来源(墨天轮),文档链接,文档作者等基本信息,否则作者和墨天轮有权追究责任。如果您发现墨天轮中有涉嫌抄袭或者侵权的内容,欢迎发送邮件至:contact@modb.pro进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,墨天轮将立刻删除相关内容。
下载排行榜


文档被以下合辑收录
评论