




SIGMOD 2025_Revisiting the Design of In-Memory Dynamic Graph Storage_华为.pdf
免费下载

Revisiting the Design of In-Memory Dynamic Graph Storage
JIXIAN SU, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, China
CHIYU HAO, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, China
SHIXUAN SUN, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, China
HAO ZHANG, Huawei Cloud, China
SEN GAO, National University of Singapore, Singapore
JIAXIN JIANG, National University of Singapore, Singapore
YAO CHEN, National University of Singapore, Singapore
CHENYI ZHANG, Huawei Cloud, China
BINGSHENG HE, National University of Singapore, Singapore
MINYI GUO, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, China
The eectiveness of in-memory dynamic graph storage (DGS) for supporting concurrent graph read and
write queries is crucial for real-time graph analytics and updates. Various methods have been proposed, for
example, LLAMA, Aspen, LiveGraph, Teseo, and Sortledton. These approaches dier signicantly in their
support for read and write operations, space overhead, and concurrency control. However, there has been no
systematic study to explore the trade-os among these dimensions. In this paper, we evaluate the eectiveness
of individual techniques and identify the performance factors aecting these storage methods by proposing a
common abstraction for DGS design and implementing a generic test framework based on this abstraction.
Our ndings highlight several key insights: 1) Existing DGS methods exhibit substantial space overhead.
For example, Aspen consumes 3.3-10.8x more memory than CSR, while the optimal ne-grained methods
consume 4.1-8.9x more memory than CSR, indicating a signicant memory overhead. 2) Existing methods
often overlook memory access impact of modern architectures, leading to performance degradation compared
to continuous storage methods. 3) Fine-grained concurrency control methods, in particular, suer from severe
eciency and space issues due to maintaining versions and performing checks for each neighbor. These
methods also experience signicant contention on high-degree vertices. Our systematic study reveals these
performance bottlenecks and outlines future directions to improve DGS for real-time graph analytics.
CCS Concepts: • Information systems
→
Graph-based database models; Data structures; Storage man-
agement.
Additional Key Words and Phrases: dynamic graph storage; graph concurrency control; graph neighbor index;
benchmark framework.
ACM Reference Format:
Jixian Su, Chiyu Hao, Shixuan Sun, Hao Zhang, Sen Gao, Jiaxin Jiang, Yao Chen, Chenyi Zhang, Bingsheng
He, and Minyi Guo. 2025. Revisiting the Design of In-Memory Dynamic Graph Storage. Proc. ACM Manag.
Data 3, 1 (SIGMOD), Article 70 (February 2025), 27 pages. https://doi.org/10.1145/3709720
Authors’ Contact Information: Jixian Su, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai, China, sjx13623816973@sjtu.edu.cn;
Chiyu Hao, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai, China, hcahoi11@sjtu.edu.cn; Shixuan Sun, Shanghai Jiao Tong
University, Shanghai, China, sunshixuan@sjtu.edu.cn; Hao Zhang, Huawei Cloud, Beijing, China, zhanghao687@huawei.
com; Sen Gao, National University of Singapore, Singapore, sen@u.nus.edu; Jiaxin Jiang, National University of Singapore,
Singapore, jxjiang@nus.edu.sg; Yao Chen, National University of Singapore, Singapore, yaochen@nus.edu.sg; Chenyi
Zhang, Huawei Cloud, Hangzhou, China, zhangchenyi@huawei.com; Bingsheng He, National University of Singapore,
Singapore, hebs@comp.nus.edu.sg; Minyi Guo, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai, China, guo-my@cs.sjtu.edu.cn.
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution International 4.0 License.
© 2025 Copyright held by the owner/author(s).
ACM 2836-6573/2025/2-ART70
https://doi.org/10.1145/3709720
Proc. ACM Manag. Data, Vol. 3, No. 1 (SIGMOD), Article 70. Publication date: February 2025.
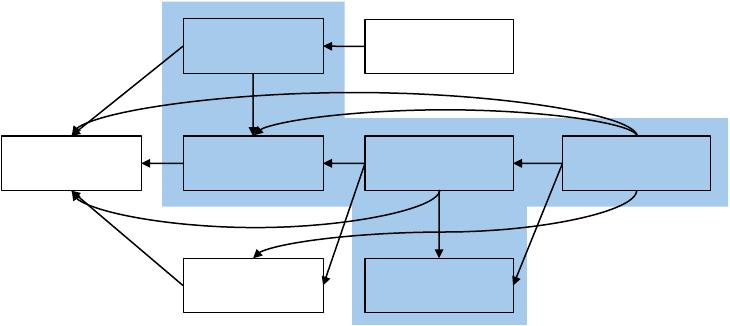
70:2 Jixian Su et al.
STINGER
[HPEC’2012]
LLAMA
[ICDE’2015]
Aspen
[PLDI’2019]
GraphOne
[FAST’2019]
Terrace
[SIGMOD’2021]
Teseo
[VLDB’2021]
LiveGraph
[VLDB’2020]
Sortledton
[VLDB’2022]
Fig. 1. Comparison of DGS methods from previous experiments. An edge from
𝑥
to
𝑦
indicates that
𝑥
’s
experiments include 𝑦. Shaded methods are transactional approaches.
1 Introduction
Graph storage is the foundation for ecient in-memory graph data processing. As graph data
often require frequent updates [
45
,
46
], in-memory dynamic graph storage (DGS) is essential
for supporting concurrent graph read and write queries, enabling real-time graph analytics and
updates. To address this need, a variety of DGS methods have been proposed [
12
,
14
,
15
,
24
,
30
,
37
,
42
,
62
], as shown in Figure 1. STINGER [
15
], GraphOne [
30
], and Terrace [
42
] do not provide
concurrency control, meaning read and write queries can only execute alternately. In contrast, the
other approaches support concurrent read and write queries with serializability [
44
], i.e., the results
of executing concurrent queries are equivalent to some serial execution order. LLAMA [
37
] and
Aspen [
14
] primarily focus on batch updates with a single-writer model, while recent methods have
shifted toward optimizing individual updates to support a broader range of applications, which
has attracted signicant research interest [
12
,
24
,
62
]. Despite their varied update strategies, these
approaches all enable concurrent read and write queries, thus called transactional approaches in
this paper.
These approaches dier signicantly in their support for read and write operations, space
overhead, and concurrency control. First, they employ dierent graph container designs to support
ecient read and write operations. For instance, LLAMA [
37
] and LiveGraph [
62
] store a vertex’s
neighbor set
𝑁 (𝑢)
in a dynamic array, enabling fast scan operations with continuous storage and
simple append inserts, but at the cost of expensive search operations. Recent approaches like
Aspen [
14
], Teseo [
12
], and Sortledton [
24
] use a segmented strategy, dividing
𝑁 (𝑢)
into small
blocks (e.g.,
|𝐵| =
256), storing each block as a sorted array, and linking them with a block index
(e.g., a skip list). This design balances insert, scan, and search eciency. Moreover, these approaches
propose additional optimizations, such as adaptive indexing to use dierent data structures for
varying neighbor set sizes to further accelerate graph operations.
Second, although existing methods all use multi-version concurrency control (MVCC) to maxi-
mize parallelism among queries [
55
], they dier in version granularity. Coarse-grained methods
like LLAMA and Aspen use the typical single-writer-multiple-reader scheme with copy-on-write
(CoW) [
10
]. For each update, they create a new graph snapshot, while read queries work on the
snapshot at their start. Recent works such as LiveGraph, Teseo, and Sortledton use a ne-grained
strategy, maintaining version information for each neighbor and synchronizing read and write
Proc. ACM Manag. Data, Vol. 3, No. 1 (SIGMOD), Article 70. Publication date: February 2025.
of 27
免费下载
【版权声明】本文为墨天轮用户原创内容,转载时必须标注文档的来源(墨天轮),文档链接,文档作者等基本信息,否则作者和墨天轮有权追究责任。如果您发现墨天轮中有涉嫌抄袭或者侵权的内容,欢迎发送邮件至:contact@modb.pro进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,墨天轮将立刻删除相关内容。
下载排行榜


文档被以下合辑收录
评论