




VLDB 2025_SiriusBI A Comprehensive LLM-Powered Solution for Data Analytics in Business Intelligence_腾讯.pdf
免费下载

SiriusBI: A Comprehensive LLM-Powered Solution for Data
Analytics in Business Intelligence
Jie Jiang
1
, Haining Xie
1
, Siqi Shen
2
, Yu Shen
1
, Zihan Zhang
1
, Meng Lei
1
, Yifeng Zheng
1
, Yang Li
1
,
Chunyou Li
1
, Danqing Huang
1
, Yinjun Wu
3
, Wentao Zhang
2
, Bin Cui
3
, Peng Chen
1
1
Department of Data Platform, TEG, Tencent Inc.
2
Center of Machine Learning Research, Peking University
3
School of Computer Science, Peking University
1
{zeus, hainingxie, willyushen, rylanzhang, garylei, yifengzheng, thomasyngli,
chunyouli, daisyqhuang, felixxfyang, pengchen}@tencent.com
2
{shensiqi1009, wentao.zhang}@pku.edu.cn
3
{wuyinjun, bin.cui}@pku.edu.cn
ABSTRACT
With the proliferation of Large Language Models (LLMs) in Busi-
ness Intelligence (BI), existing solutions face critical challenges in
industrial deployments: functionality deciencies from legacy sys-
tems failing to meet evolving LLM-era user demands, interaction
limitations from single-round SQL generation paradigms inade-
quate for multi-round clarication, and cost for domain adaptation
arising from cross-domain methods migration.
We present SiriusBI, a practical LLM-powered BI system address-
ing the challenges of industrial deployments through three key in-
novations: (a) An end-to-end architecture integrating multi-module
coordination to overcome functionality gaps in legacy systems; (b)
A multi-round dialogue with querying mechanism, consisting of se-
mantic completion, knowledge-guided clarication, and proactive
querying processes, to resolve interaction constraints in SQL gener-
ation; (c) A data-conditioned SQL generation method selection strat-
egy that supports both an ecient one-step Fine-Tuning approach
and a two-step method leveraging Semantic Intermediate Repre-
sentation for low-cost cross-domain applications. Experiments on
both real-world datasets and public benchmarks demonstrate the
eectiveness of SiriusBI. User studies further conrm that SiriusBI
enhances both productivity and user experience.
As an independent service on Tencent’s data platform, SiriusBI
is deployed across nance, advertising, and cloud sectors, serving
dozens of enterprise clients. It achieves over 93% accuracy in SQL
generation and reduces data analysts’ query time from minutes to
seconds in real-world applications.
PVLDB Reference Format:
Jie Jiang, Haining Xie, Siqi Shen, Yu Shen, Zihan Zhang, Meng Lei, Yifeng
Zheng, Yang Li, Chunyou Li, Danqing Huang, Yinjun Wu, Wentao Zhang,
Bin Cui, Peng Chen. SiriusBI. PVLDB, 18(12): 4860 - 4873, 2025.
doi:10.14778/3750601.3750610
PVLDB Artifact Availability:
The source code, data, and/or other artifacts have been made available at
https://github.com/Tencent-SiriusAI/SiriusBI.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons BY-NC-ND 4.0 International
License. Visit https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/ to view a copy of
this license. For any use beyond those covered by this license, obtain permission by
emailing info@vldb.org. Copyright is held by the owner/author(s). Publication rights
licensed to the VLDB Endowment.
Proceedings of the VLDB Endowment, Vol. 18, No. 12 ISSN 2150-8097.
doi:10.14778/3750601.3750610
1 INTRODUCTION
Business Intelligence (BI) [
54
,
83
] is a crucial application scenario in
the data eld, comprising a comprehensive suite of methodologies,
tools, and infrastructures designed to collect, integrate, analyze,
and present raw data from an organization to generate actionable
insights for informed decision-making. BI systems are extensively
used in various sectors, including nance [
55
], environment [
24
],
and social media [
11
,
64
], which signicantly improves the decision-
making process through the provision of real-time analytics and
reporting capabilities [44, 60].
A typical BI system comprises several key components: a data
management module that stores, processes, and aggregates vast
amounts of data; analytic algorithms that transform the data into
actionable insights; and visualization tools that present the infor-
mation in intuitive and user-friendly formats. Among these, data
analytics plays a crucial role in providing decision-making sup-
port, directly determining the correctness and appropriateness of
decisions. Recent advancements in LLMs [
34
,
46
,
89
] have sparked
signicant interest in ChatBI — a new paradigm supported by natu-
ral language interfaces [
1
,
41
]. Concurrently, the demand for a fully
integrated and ecient ChatBI solution is surging, driven by the
need of a more intuitive and accessible mode of data interaction.
This evolution promises to transform how users engage with data,
making insights more available and actionable.
To meet the growing demand for big data analytics and decision-
making in BI, the data community has proposed numerous eective
approaches. However, when applying existing work in real-world
BI scenarios, we identify the following three challenges:
C1: Functionality Deciencies. While traditional business in-
telligence systems [
8
] integrate core components spanning data
management, SQL generation, and insight discovery to form com-
plete analytics pipelines, their reliance on heuristic rules and con-
ventional AI/ML techniques limits generalization ability in dy-
namic scenarios. Although LLM-based methods have advanced
task-specic performance, few oer comprehensive BI capabilities
comparable to their traditional counterparts. For example, MAC-
SQL [
75
] and CHESS [
68
] optimize NL2SQL accuracy but treat SQL
execution as terminal outputs, neglecting downstream tasks like
attribution analysis. While Lian et al. [
46
] extend their pipeline with
Apache Superset for visualization, they fail to introduce knowledge
bases to support dynamic grounding of domain-specic context, a
4860
SELECT `industry_aggregation_id` AS `industry`,
SUM(`gross_profit`) AS `total_gross_profit`
FROM `table1`
WHERE YEAR(`ftime`) = 2023
GROUP BY `industry`
SELECT `industry_aggregation_id` AS `industry`,
SUM(`shouldincome_after`) AS `total_income`
FROM `table1`
WHERE YEAR(`ftime`) = 2023
GROUP BY `industry`
ORDER BY `total_income` DESC LIMIT 5
SELECT `industry_aggregation_id` AS `industry`,
SUM(`shouldincome`) AS `total_revenue`
FROM `table1`
WHERE YEAR(`ftime`) = 2023 AND
QUARTER(`ftime`) = 2
GROUP BY `industry`
ORDER BY ` total_revenue ` DESC LIMIT 3
Chat 1
Chat 2
Chat 3
✅
✅
✅
SELECT `industry_aggregation_id` AS `industry`,
SUM(`gross_profit`) AS `total_gross_profit`
FROM `table1`
WHERE YEAR(`ftime`) = 2023
GROUP BY `industry`
SELECT `industry_aggregation_id` AS `industry`,
SUM(`shouldincome`) AS `total_income`
FROM `table1`
WHERE YEAR(`ftime`) = 2023
GROUP BY `industry_aggregation_id`
ORDER BY `total_income` DESC LIMIT 5
SELECT `industry_aggregation_id` AS `industry`,
SUM(`shouldincome`) AS `total_revenue`
FROM `table1`
WHERE YEAR(`ftime`) = 2023 AND
QUARTER(`ftime`) = 2
GROUP BY `industry`
ORDER BY ` total_revenue ` DESC LIMIT 3
Chat 1
Chat 2
Chat 3
✅
✅
SELECT `industry_aggregation_id` AS `industry`,
SUM(`gross_profit`) AS `total_gross_profit`
FROM `table1`
WHERE YEAR(`ftime`) = 2023
GROUP BY `industry`
SELECT `customer_name` ,
SUM(`shouldincome_after`) AS `total_income`
FROM `table1`
GROUP BY `customer_name`
ORDER BY `total_income`
DESC LIMIT 5
SELECT `industry_aggregation_id` AS `industry`,
SUM(`shouldincome`) AS `total_revenue`
FROM `table1`
WHERE QUARTER(`ftime`) = 2
GROUP BY `industry`
ORDER BY `total_revenue`
DESC LIMIT 3
Chat 1
Chat 2
Chat 3
✅
Query 1: Gross profit of
various industries in 2023,
summarize and output.
Query 2: Which are the top
five in terms of income?
Query 3: Top three in terms of
revenue including tax for the
second quarter.
DescriptionColumn
Dateftime
Revenue
including tax
shouldincome
Gross profitgross_profit
············
SRD
MRD SiriusBI MRD-Q
Which are the top five in
terms of income?
Does income mean
`shouldincome` or
`shouldincome_after` ?
`shouldincome_after`
OK, then the query is "What are
the top five industries in terms
of tax-excluded revenue in
2023?"
Querying
2023?
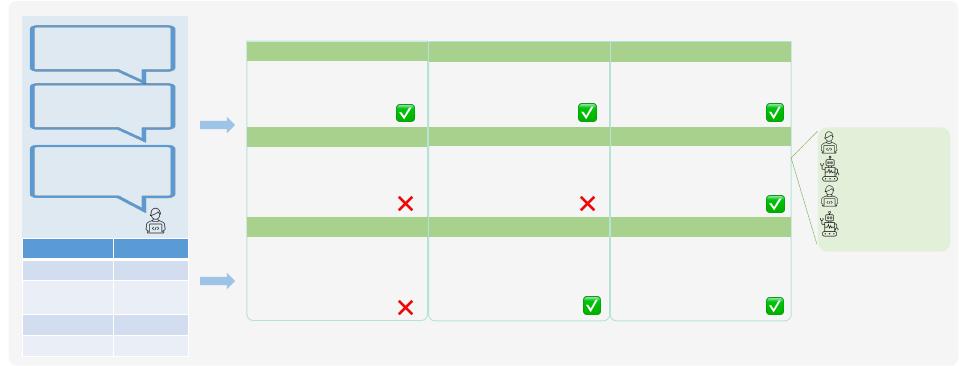
Figure 1: Demonstration of multi-round user requests. Compared with SiriusBI, SRD misses the omitted year information in
conversations, while MRD fails to identify the user’s ambiguous intent.
critical requirement for real-world BI adaptation [
12
]. This func-
tional fragmentation forces users to manually coordinate tools (e.g.,
SQL editors, dashboard platforms, knowledge retriever), which im-
poses signicant cognitive load and reduces operational eciency,
as evidenced by industry report [36].
C2: Interaction Limitations. In the context of ChatBI, the
NL2SQL task is becoming increasingly vital, as it facilitates seam-
less interaction between natural language queries and structured
data retrieval, thereby enhancing the eciency and accuracy of
data analytics. The evolution of NL2SQL techniques reveals a crit-
ical architectural mismatch: while traditional methods (schema-
based [
25
,
26
,
50
,
87
] or parsing-based [
30
,
40
,
56
,
77
]) and modern
LLM-driven approaches (prompt engineering [
58
,
75
] or ne-tuning
techniques [
42
,
59
]) predominantly optimize for Single-Round
Dialogue (SRD) precision. This SRD-centric paradigm introduces a
signicant continuity gap in Multi-Round Dialogues (MRD): real-
world BI workows often require iterative investigation through
successive queries, where later queries tend to omit previously
provided contextual information, resulting in semantic ambiguity
beyond the initial query. For instance, in the MRD NL2SQL task
illustrated in Figure 1, the user issues three queries; notably, the
second and third queries omit the time condition “2023” because it
was specied in the rst query. Single-round NL2SQL approaches
demand nearly perfect input specicity, which explains its failure
to generate correct SQL statements for the second and third queries
in Figure 1. Worse still, due to the intricate nature [
48
] of MRD,
few approach has been devoted to addressing this task. Lian et al.’s
MRD solution [
46
] is the rst attempt towards this task. Never-
theless, their solution is absent of user-guided clarication loops
for intent resolution and domain-grounded dialogue act modeling.
As demonstrated in Figure 1, the basic MRD approach still exhibit
performance degradation beyond the rst dialogue round.
C3: Cost for Domain Adaptation. Cross-domain deployment
of NL2SQL models faces the challenge of cost surges in domain
knowledge transfer, primarily caused by insucient model general-
ization capability. Structural dierences in database schema across
domains (e.g., nested tables in nance vs. wide tables in advertising)
necessitate repetitive model adaptation [
48
], while semantic gaps
between industry-specic operators (e.g., nancial window func-
tions vs. e-commerce promotional rules) exacerbate logical devia-
tions in SQL generation [
38
]. Critically, domain knowledge transfer
relies heavily on expert-annotated data, with manual annotation
costs growing with domain complexity [
39
]. Our real-world deploy-
ment statistics show that direct model migration leads to business
logic errors in approximately two-thirds of generated SQL queries.
Meanwhile, adapting models through traditional ne-tuning re-
quires 5.5 person-days on average to label 200 seed queries within
existing databases—forming critical bottlenecks for enterprise-level
scalability.
To address the aforementioned challenges, we propose SiriusBI,
which implements a comprehensive LLM-powered solution for
ChatBI scenarios. This system leverages the capabilities of LLMs to
empower various modules, thereby enhancing both the eciency
and user experience in data analytics. Specically, for the issue of
functionality deciencies (C1), SiriusBI introduces an end-to-end
integrated architecture that seamlessly orchestrate core modules
including knowledge management, multi-round dialogue analysis,
SQL generation, and data insight provision, thereby ensuring a
closed-loop pipeline from natural language queries to nal decision-
making reports.
For the issue of interaction limitations (C2), we introduce the
MRD-Q (Multi-Round Dialogue with Querying) module. As a
supplement to the basic multi-round dialogue analysis module
proposed by Lian et al. [
46
], MRD-Q incorporates an intent querying
module to clarify user queries through follow-up questions. This
approach enables the system to accurately identify the user’s true
intent, even when the initial query is incomplete or ambiguous,
thus facilitating precise responses, as shown in Figure 1.
To enable economic domain adaptation (C3), SiriusBI introduces
a strategy switching mechanism that dynamically selects between
one-step and two-step SQL generation paradigms based on data
conditions. This mechanism optimizes the trade-o between com-
putational cost and performance, ensuring ecient adaptation to
4861
of 14
免费下载
【版权声明】本文为墨天轮用户原创内容,转载时必须标注文档的来源(墨天轮),文档链接,文档作者等基本信息,否则作者和墨天轮有权追究责任。如果您发现墨天轮中有涉嫌抄袭或者侵权的内容,欢迎发送邮件至:contact@modb.pro进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,墨天轮将立刻删除相关内容。
下载排行榜


评论