




Table of Wait Events and Potential Causes.docx
免费下载
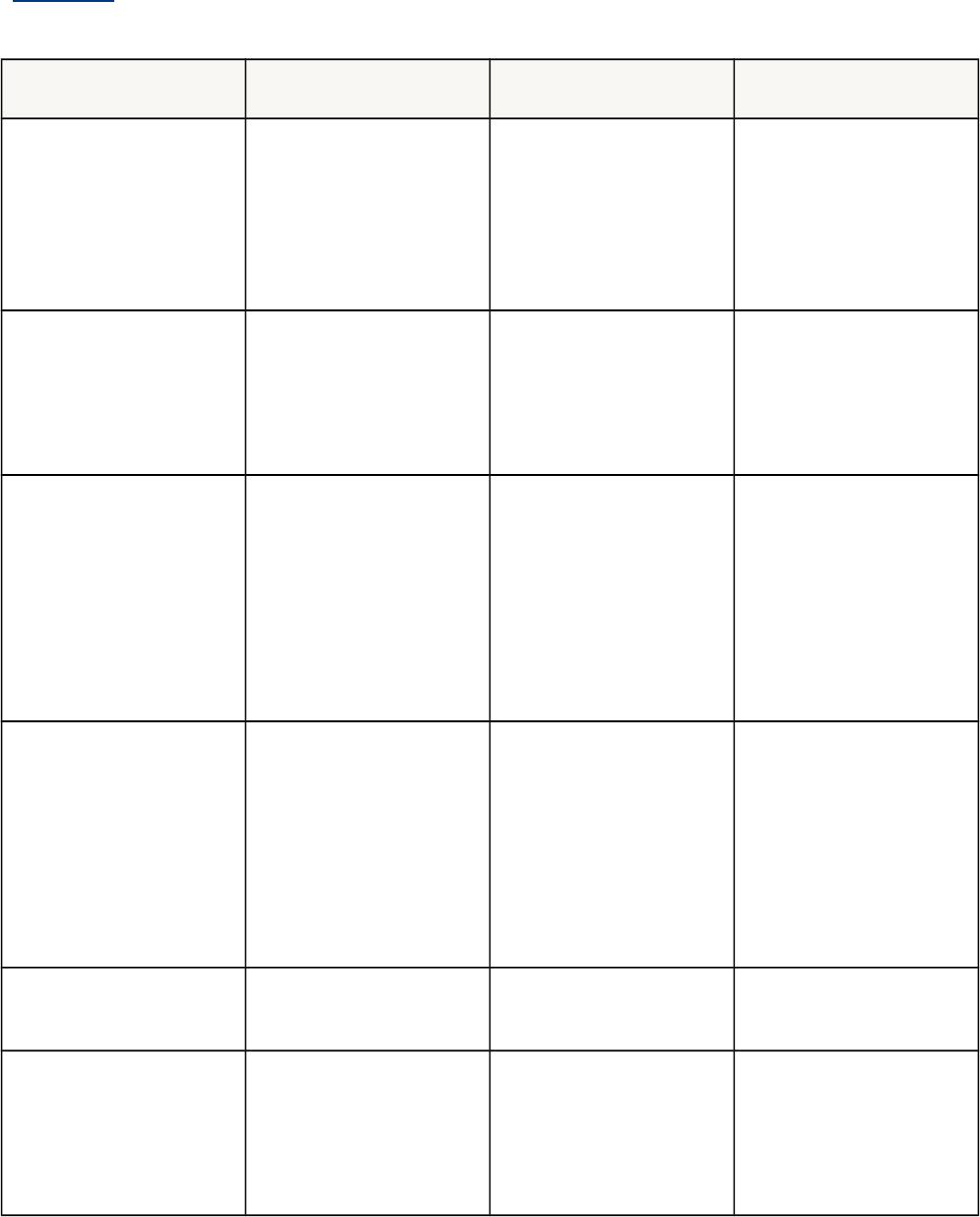
Table of Wait Events and Potential Causes
Table 10-1 links wait events to possible causes and gives an overview of the Oracle data
that could be most useful to review next.
Table 10-1 Wait Events and Potential Causes
Wait Event General Area Possible Causes Look for / Examine
buffer busy waits Buffer cache, DBWR
Depends on buffer
type. For example,
waits for an index
block may be caused
by a primary key that
is based on an
ascending sequence.
Examine V$SESSION
while the problem is
occurring to determine
the type of block in
contention.
free buffer waits
Buffer cache, DBWR,
I/O
Slow DBWR (possibly
due to I/O?)
Cache too small
Examine write time
using operating system
statistics. Check buffer
cache statistics for
evidence of too small
cache.
db file scattered read
I/O, SQL statement
tuning
Poorly tuned SQL
Slow I/O system
Investigate V$SQLAR
EA to see whether
there are SQL
statements performing
many disk reads.
Cross-check I/O
system
and V$FILESTAT for
poor read time.
db file sequential read
I/O, SQL statement
tuning
Poorly tuned SQL
Slow I/O system
Investigate V$SQLAR
EA to see whether
there are SQL
statements performing
many disk reads.
Cross-check I/O
system
and V$FILESTAT for
poor read time.
enqueue waits (waits
starting with enq:)
Locks
Depends on type of
enqueue
Look
at V$ENQUEUE_STA
T.
library cache latch
waits: library cache, lib
rary cache pin,
and library cache lock
Latch contention SQL parsing or sharing Check V$SQLAREA t
o see whether there are
SQL statements with a
relatively high number
of parse calls or a high
number of child
cursors
(column VERSION_C
OUNT). Check parse
statistics
in V$SYSSTAT and
their corresponding
rate for each second.
log buffer space Log buffer, I/O
Log buffer small
Slow I/O system
Check the
statistic redo buffer all
ocation retries in V$S
YSSTAT. Check
configuring log buffer
section in configuring
memory chapter.
Check the disks that
house the online redo
logs for resource
contention.
log file sync I/O, over- committing
Slow disks that store
the online logs
Un-batched commits
Check the disks that
house the online redo
logs for resource
contention. Check the
number of transactions
(commits + rollbacks)
each second,
from V$SYSSTAT.
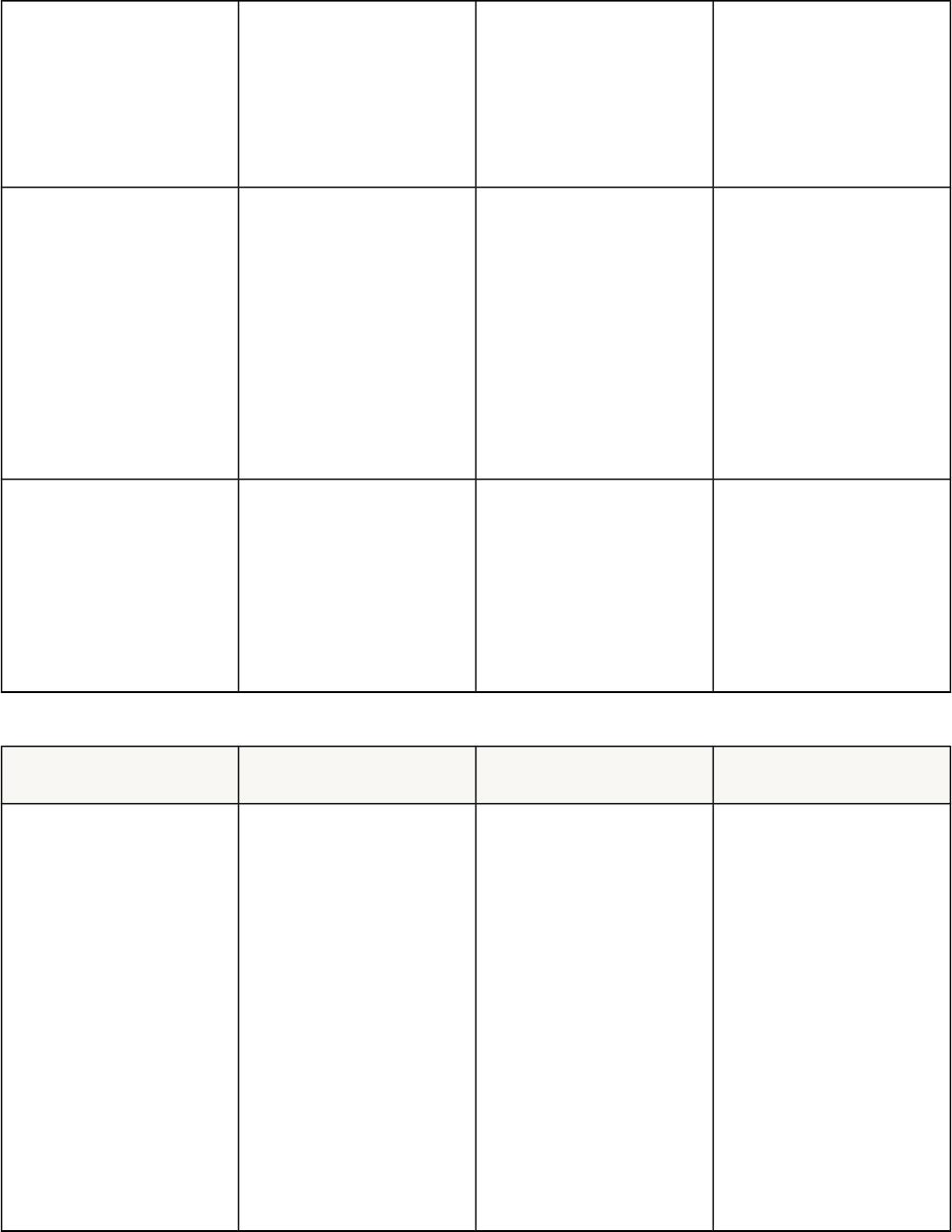
Table 10-3 Latch Wait Event
Latch SGA Area Possible Causes Look For:
Shared pool, library
cache
Shared pool Lack of statement
reuse
Statements not using
bind variables
Insufficient size of
application cursor
cache
Cursors closed
explicitly after each
execution
Frequent logins and
logoffs
Underlying object
structure being
modified (for example
truncate)
Sessions
(in V$SESSTAT) with
high:
1. parse time CPU
2. parse
time elapsed
3. Ratio of
parse count
(hard) / execute count
4. Ratio of
parse count
(total) / execute count
Cursors
(in V$SQLAREA/V$S
QLSTATS) with:
1. High ratio of
of 4
免费下载
【版权声明】本文为墨天轮用户原创内容,转载时必须标注文档的来源(墨天轮),文档链接,文档作者等基本信息,否则作者和墨天轮有权追究责任。如果您发现墨天轮中有涉嫌抄袭或者侵权的内容,欢迎发送邮件至:contact@modb.pro进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,墨天轮将立刻删除相关内容。
下载排行榜


评论