




3D Point Cloud Map Based Vehicle Localization Using Stereo Camera.pdf
50墨值下载

3D Point Cloud Map Based Vehicle Localization Using Stereo Camera
Yuquan Xu
1
Vijay John
1
Seiichi Mita
1
Hossein Tehrani
2
Kazuhisa Ishimaru
3
Sakiko Nishino
3
Abstract— Nowadays, the driverless automobiles have be-
come a near reality and are going to become widely available.
For autonomous navigation, the vehicles need to precise localize
itself within a pre-defined map. In this paper, we propose a novel
algorithm for the problem of three-dimensional (3D) point cloud
map (PCL) based localization using a stereo camera. This 3D
point cloud map consists of dense 3D geometric information and
intensity measures of surface reflectivity value generated by the
3D light detection and ranging (LIDAR) scanner based mapping
system. Although some LIDAR based localization algorithms
have been proposed, in this paper we present a comparable
centimeter-level accuracy localization algorithm using much
cheaper and commodity stereo camera. Specifically, at each
candidate position we transform the 3D data points from the
real-world coordinate system to the camera coordinate system
and synthetic the virtual depth and intensity images from the
3D PCL map. We localize the ego vehicle by estimating the
transformation between the real-world and vehicle coordinates
in each frame by matching these virtual images with the stereo
depth and intensity images. In the experiment part, we show
that although the 3D map was generated 3 years ago, the
proposed algorithm still can produce reliable localization results
even in many difficult cases, such as shadow, dynamic objects,
new lane marker and night.
I. INTRODUCTION
Recently, significant attention has been paid to make
our vehicles smarter, both in the autonomously driving and
advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS) application [1],
[2], [3], [4], [5]. A lot of researchers or companies (ex.
Google) have successfully experimented the driverless car
with hundreds of thousands of miles without user interven-
tion and some car manufacturers have begun looking into
commercialization of such technology.
A common way of autonomous driving is to use a prior
map which contains many precise and useful information
of surroundings, such as road geometry, lane locations, lane
labels, traffic signs etc. The use of this prior map can
necessarily transform many difficult real-time algorithms into
a vehicle localization problem. Nowadays many map com-
panies provide precise map services for automated driving
applications. The 3D light detection and ranging (LIDAR)
scanner based mobile mapping system is one of the most
1
Yuquan Xu, Vijay John and Seiichi Mita are with the
Research Center for Smart Vehicles, Toyota Technological
Institute, 2-12-1 Hisakata, Tempaku, Nagoya, Aichi, 468-
8511, Japan
yuquan.xu86@toyota-ti.ac.jp,
vijayjohn@toyota-ti.ac.jp, smita@toyota-ti.ac.jp
2
Hossein Tehrani is with the Driving Assist & Safety Eng. Div. 1,
DENSO CORPORATION, 1-1, Showa cho, Kariya, Aichi, 448-8661 Japan
hossein tehrani@denso.co.jp
3
Kazuhisa Ishimaru and Sakiko Nishino are with the Research &
Development Dept. 2, NIPPON SOKEN INC., Nishio, Aichi, 445-0012,
Japan
, kazuhisa ishimaru@soken1.denso.co.jp,
sakiko
nishino@soken1.denso.co.jp
popular platforms to build highly precise three-dimensional
(3D) point cloud map (PCL), which contains dense 3D points
with latitude, longitude, altitude and intensity information.
Vehicle localization within a given map is a significantly
important issue of the autonomous driving and ADAS ap-
plications and the localization robustness is a critical factor
since the online autonomous platform would no longer be
able to operate when it fails.
Typically, the Global Positioning System (GPS) is a com-
mon sensor used to localize the vehicle. However, in certain
environments such as urban areas, the conventional GPS
can only achieve an accuracy around 10 meters which is
insufficient and does not meet the requirements. On the other
hand, the RTK-GPS which can produce centimeter level
accuracy is too costly to be practical. Therefore, in this work
we are committed to propose an accurate vehicle localization
method against a predefined 3D PCL map with a reasonable
price.
To address this issue, we present a novel 3D point cloud
map based vehicle localization algorithm using the stereo
camera. This study contains the following contributions.
1. The proposed method utilize both the intensity and
depth information to localize the ego car which is robust to
the change of illumination, shadow and other scene appear-
ance. Unlike some feature based algorithm, we directly use
the pixel values of the depth and gray image for localization
and .
2. Design robust metric to compare the depth and intensity
information. For intensity images, to perform direct (whole-
image) localization in the presence of environment and
illumination changes, we adopt the gradient information to
match the intensity images which is popular to match images
utilized in the stereo vision [6][7] and optical flow [8] field.
For the depth images, we use the depth value related metric
to compare the depth information from the stereo vision and
PCL map.
3. A Particle Filter based framework is proposed to online
localize the vehicle.
We evaluate our system in challenging experiments using
the camera data collected from 2014 to 2016 and localize the
vehicle within the predefined map built in 2013. Experiment
results show that our algorithm can successfully localize
the ego vehicle on many difficult scenes including shadow,
dynamic objects, new lane marker and night case.
II. R
ELATED WORK
Vehicle localization is a very important issue in the smart
vehicle field and many efforts have been made over past
decades. GPS based vehicle localization algorithm is widely
2017 IEEE Intelligent Vehicles Symposium (IV)
June 11-14, 2017, Redondo Beach, CA, USA
978-1-5090-4804-5/17/$31.00 ©2017 IEEE 487
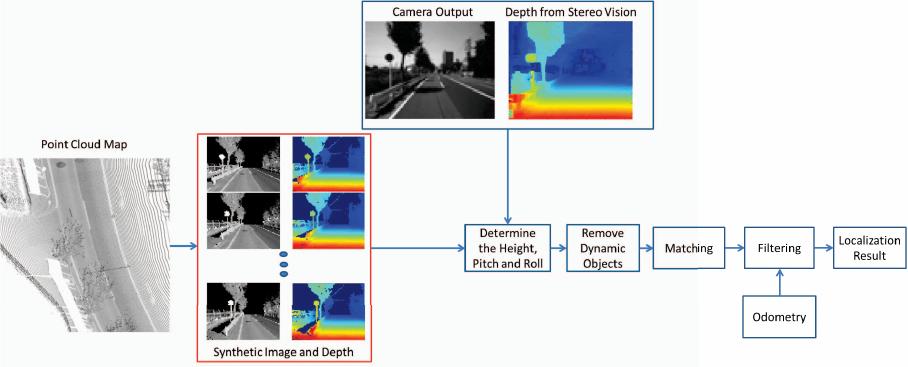
Fig. 1. The flowchart of the proposed method
used to localize the vehicle in the real world, but the
conventional GPS receiver usually suffers from the problem
of low accuracy and intermittent missing signals [9]. Simul-
taneously Localization And Mapping (SLAM) algorithm is
anther typical strategy to estimate the position and build the
surrounding map at the same time. Levinson et al. [10] used
LIDAR based method which first create a ground map from
LIDAR intensity and then use the particle filtering to localize
the vehicle in the map with LIDAR and inertial measurement
unit (IMU).
However, since the high accuracy LIDAR is too expensive,
many researchers use the vision system for SLAM [11][12]
instead. Typically some robust image feature descriptors,
eg. SIFT [13] and SURF [14]), are used to reconstruct
a sparse feature based map and recover the position of
the vehicle. However, these feature based algorithms have
limitations when used over long periods of time [15] and
environmental change [13]. Several recent works try to learn
the robust descriptors [16], but these algorithms need lots
of data from the same place but under variant lighting or
weather conditions to train, which is not easy to acquire.
Recent dense and semi-dense approaches using the monoc-
ular or stereo camera are proposed to visual localization
and SLAM [17][18]. However, these algorithm also test in
a short periods of time and use a pixel value based cost
function, and are not robust to the shadow and lighting
changes. Although the SLAM based vehicle localization
algorithms make great improvement recently and the loop
closure detection [19] techniques are used, it still suffers from
the error accumulation and divergence.
To handle the divergence problem, many researchers try to
localize the vehicle with a predefined map such as 3D PCL
map or RoadDNA system announced by Tomtom. Successful
map-based localization algorithms have be proposed by using
3D LIDAR sensors [20] [21] [22], which can produce robust
results under different conditions but is too expensive for
real-application. Alternately, monocular cameras are used for
the vehicle localization with 3D PCL map. Wolcott et al. [23]
and Pascoe et al. [24] both proposed the monocular camera
based vehicle localization algorithms within a 3D PCL map
generated by LIDAR sensors. Pascoe et al. [25] proposed a
direct visual localization algorithm in changing city environ-
ments. Although these monocular camera based algorithms
have used some information-theoretic methods to matching
metric such as Normalized Information Distance (NID) or
Normalized Mutual Information (NMI), these intensity based
metric is not as reliable as using the depth information from
the stereo vision, since the depth information is theoretically
invariant with the change of illumination, shadow and other
scene appearance.
III. M
ETHOD
A. Priori Map & Synthetic Images
In this paper, we want to solve the problem about estimat-
ing the accurate position of the ego vehicle within a prior
existing map using stereo camera. This kind of high precise
3D PCL map can be generated by some mapping companies.
Mobile Mapping System (MMS) is one of the most popular
mapping approaches to generate the high quality surrounding
map. In this study, the 3D PCL map we used is provided
by AISAN TECHNOLOGY CO., LTD.
1
in 2013, which
employs one Odometer, one RTK-GPS, and two 2-D LI-
DARs (Sick, LSM551). This dense 3D PCL map includes
geometry information (latitude, longitude and altitude) and
intensity information. In this paper, we transform the latitude,
longitude and altitude to the real-world coordinate system
which is defined at the origin of the Universal Transverse
Mercator (UTM) coordinate. Our stereo camera is off-line
calibrated and rectified. As a result, as long as we obtain a
candidate 6 DOF transformation from real-world coordinate
system to the camera coordinate, we can make use of camera
intrinsic matrix to generate a virtual image pair including
one intensity image and one depth image with size 60 × 80
as showed in Fig. 1. Fig. 1 gives a brief flowchart of the
1
http://www.whatmms.com/
488
of 6
50墨值下载
【版权声明】本文为墨天轮用户原创内容,转载时必须标注文档的来源(墨天轮),文档链接,文档作者等基本信息,否则作者和墨天轮有权追究责任。如果您发现墨天轮中有涉嫌抄袭或者侵权的内容,欢迎发送邮件至:contact@modb.pro进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,墨天轮将立刻删除相关内容。
下载排行榜


评论