




Read Consistency in Distributed Database Based on DMVCC.pdf
免费下载
Read Consistency in Distributed Database Based on DMVCC
Jie Shao
†§
, Boxue Yin
§
, Bujiao Chen
§
, Guangshu Wang
§
, Lin Yang
§
Jianliang Yan
§
, Jianying Wang
§
, Weidong Liu
†
†
Tsinghua University
§
Baidu,Inc
†
shao-j14@mails.tsinghua.edu.cn
†
liuwd@mail.tsinghua.edu.cn
§
{yinboxue,chenbujiao,wangguangshu,yanglin05,yanjianliang,wangjianying}@baidu.com
Abstract—In a traditional distributed database system, the
partitions use two-phase locking (2PL) as the concurrency
control protocol to ensure distributed read consistency. But
the read-lock acquired by a read operation is incompatible
with a write-lock, which undermines the performance of the
system. While in a system at the snapshot isolation level, where
partitions use Multi-Version Concurrent Control (MVCC) as
the concurrent control protocol, distributed read inconsistency
may occur. To achieve read consistency and guarantee the
performance at the same time, we propose Distributed Multi-
Version Concurrent Control (DMVCC). With DMVCC, the
system can support snapshot reads, which do not block write
operations, and ensure distributed read consistency. In this
protocol, a transaction obtains a set of consistent snapshot
version numbers at the startup time. The transaction then uses
those numbers to read the corresponding data stored on each
partition. The correctness of the protocol is strictly proved.
We conduct a series of experiments to compare the perfor-
mance of the system when using and not using DMVCC with a
scaled TPC-C benchmark. We observe that our DMVCC based
system outperforms the system using 2PL at both medium (up
to 1.53x speed up) and high contention (up to 2.0x speed up)
levels. Furthermore, when read/write ratio goes up to 1:1, the
throughput of the DMVCC based system is 290% higher than
that of the system using 2PL. The scalability of the system is
also presented.
I. INTRODUCTION
As the data increase, many large-scale services in Baidu
such as Baidu Wallet can no longer store data in a single
database. Being a Chinese counterpart of PayPal, Baidu
Wallet relies on a distributed on-line transaction processing
(OLTP) system as its storage backend. OLTP systems require
concurrency control to guarantee consistency[6], [7], so that
services running on top of them can function correctly. With-
out right concurrency control, Baidu Wallet could transfer
more money than there is from the account, execute the
transfer twice, transfer the wrong amount of money, or
present the wrong balance after a transaction.
While concurrency control is a well-studied field concern-
ing single databases, the performance of protocols such as
two-phase locking (2PL)[6] is limited with high-contention
workloads, especially when the database receives long read-
only transactions. To solve this problem, Multi-Version
Concurrency Control (MVCC)[7], [11], [14] is proposed.
For read operations, a client is allowed to read historical data
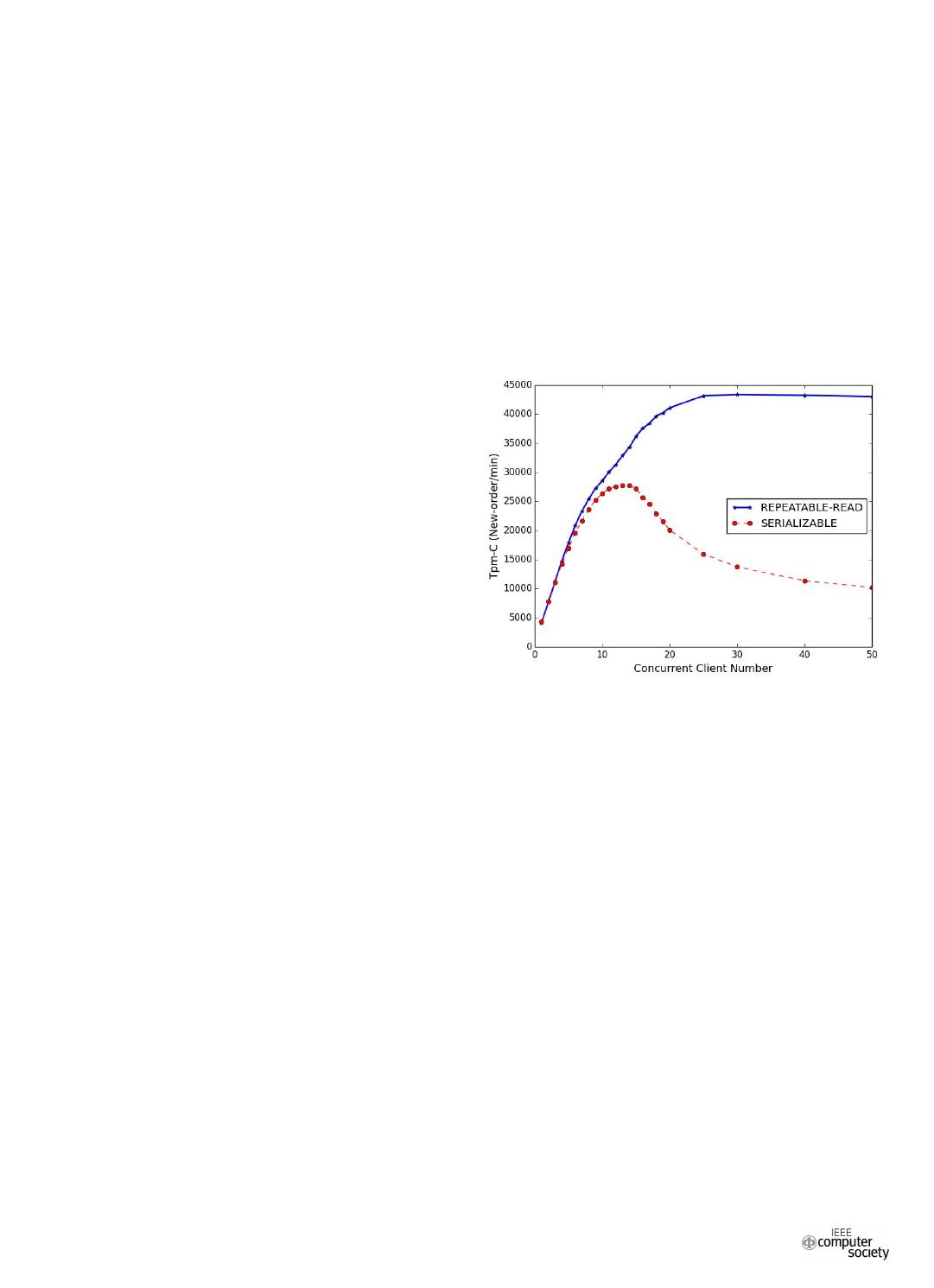
Figure 1: The throughput of a single database at different
isolation levels as the client number increases
to avoid read-write conflicts. This improve the performance
intensely[16].
To prove that, we set up a simple experiment that com-
pares the performances of a single database at different
isolation levels. In this experiment, we use MySQL[1] as our
database, which has different concurrency control methods.
2PL is used at the serializable isolation level, while MVCC
is used at the repeatable read level. TPC-C[2] is used as
our benchmark. The database contains 5 warehouses. The
experimental setup remains the same in Section V. Figure 1
shows the results:
• When the number of clients is less than 10, the perfor-
mance of the system remains almost unchanged at the
repeatable read level and at the serializable level since
there is little contention.
• As the number of clients increases, the throughput of
the database at the serializable isolation level drops
sharply. Meanwhile, the throughput of the system at the
repeatable read level almost remains the same. That is
to say the drop is caused by read and write conflicts
instead of resource limitation.
2016 IEEE 23rd International Conference on High Performance Computing
978-1-5090-5411-4/16 $31.00 © 2016 IEEE
DOI 10.1109/HiPC.2016.11
142
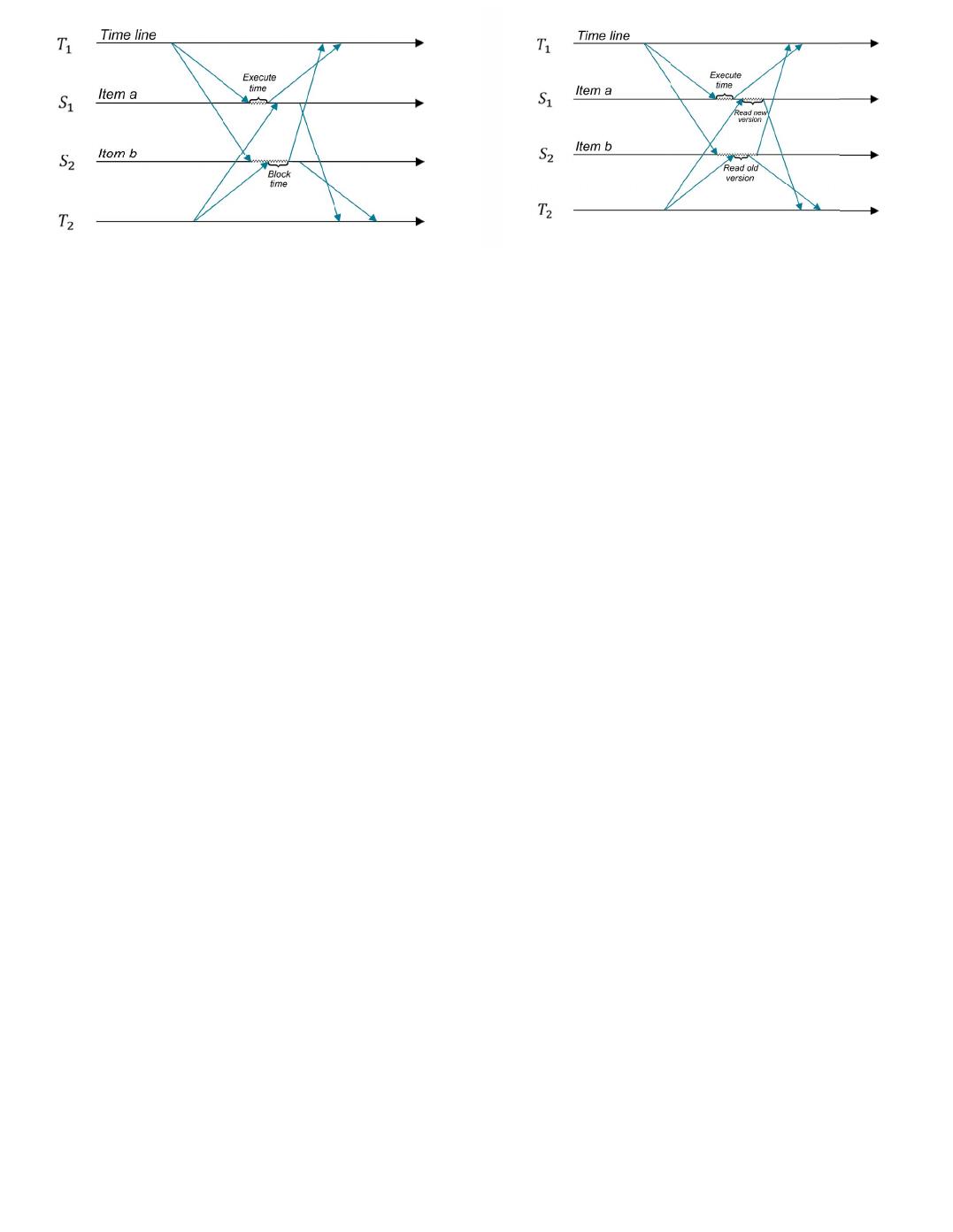
(a) partitions using 2PL
(b) partitions using MVCC
Figure 2: How transactions read data using 2PL and using MVCC
As Figure 1 shows, if the distributed database uses MVCC
as the concurrency control protocol, the system may have
a better performance. Unfortunately, the distributed system
requires that the transactions use 2PL in every partition
1
[1].
A MVCC-based distributed database system at the non-
serializable level leads to distributed read inconsistency,
which refers to the circumstance where only some of the
updates of a distributed transaction are visible to other
transactions. We will explain that in detail in Section II.
Many transactions in Baidu Wallet such as account checking
and statistic analysis do not need to read the latest data. But a
global consistent snapshot is still needed. So in this paper we
propose DMVCC (Distributed Multi-Version Concurrency
Control), a distributed concurrency protocol that ensures
distributed read consistency and the performance at the same
time.
DMVCC is a two-phase protocol based on two-phase
commit (2PC)[6], [19]. A set of distributed transaction
managers (DTMs) run the protocol on behalf of clients. At
the beginning of a transaction, the DTM connects with the
consistency coordinator to obtain global consistent snapshot
version numbers. In the prepare phase, the transaction uses
the snapshot version number to read data items stored on
each partition. In the commit phase, the DTM collects the
snapshot versions from each partition and sends them to
the consistency coordinator. The consistency coordinator
then calculates the new global consistent snapshot version.
With DMVCC, the system guarantees that all or none of
the updates of a distributed transaction is visible to other
transactions.
The rest of the paper proceeds as follows. Section II
presents a case of distributed read inconsistency and the way
to avoid it. Section III elaborates the design of a DMVCC-
based system. In Section IV, we prove the correctness of
DMVCC. Section V sets up the experiments and presents
1
In our design, we call each database a partition.
the results of our experimental evaluation. Then we discuss
the related work in Section VI and present the conclusion
in section VII.
II.
OVERVIEW
This section begins with a review of why we can not use
MVCC in a distributed system. Then we will explain how
the distributed multi-version concurrency control works.
A. A case of distributed read inconsistency
Application programmers usually prefer the highest isola-
tion level to simplify the reasoning of correctness in the face
of concurrent transactions[6], [17]. To guarantee distributed
consistency, a distributed transaction runs standard concur-
rency control schemes such as standard 2PL combined with
two-phase commit (2PC)[6], [8], [9].
To give a more intuitive explanation, we demonstrate a
simplified process of money transferring in Baidu Wallet,
during which the system reads the balance data from the
account to ensure consistency. As is shown below, there are
two distributed transactions T
1
and T
2
and two partitions S
1
and S
2
, which contain data items a and b respectively. In
transaction T
1
, account A transfers 10 dollars to account B.
Transaction T
2
then reads the data of the current account
balance of A and B.
T
1
: UPDATAa=a-10 UPDATAb=b+10
T
2
: READ a READ b
Firstly, let us see how distributed transactions work on
each partition which uses standard 2PL as the concurrency
control protocol and 2PC as the distributed commit protocol.
Suppose partition S
1
and S
2
receive T
1
and T
2
’s subtransac-
tions sequentially. The process is shown in Figure 2(a). We
can see that T
2
arrives when T
1
is committed on partition S
1
but not yet committed on partition S
2
because of network
latency or thread scheduling on S
2
. Since T
1
is committed
143
of 10
免费下载
【版权声明】本文为墨天轮用户原创内容,转载时必须标注文档的来源(墨天轮),文档链接,文档作者等基本信息,否则作者和墨天轮有权追究责任。如果您发现墨天轮中有涉嫌抄袭或者侵权的内容,欢迎发送邮件至:contact@modb.pro进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,墨天轮将立刻删除相关内容。
下载排行榜


评论