




基于虚拟力的WSNs能量高效分簇路由协议-赵小强,崔砚鹏,郭铮,刘敏,李雄,文秦.pdf
免费下载

软件学报 ISSN 1000-9825, CODEN RUXUEW E-mail: jos@iscas.ac.cn
Journal of Software, 2022,33(2):622640 [doi: 10.13328/j.cnki.jos.006159] http://www.jos.org.cn
©中国科学院软件研究所版权所有. Tel: +86-10-62562563
基于虚拟力的 WSNs 能量高效分簇路由协议
赵小强
1,3
,
崔砚鹏
2
,
郭
铮
1,3
,
刘
敏
1,3
,
李
雄
1,3
,
文
秦
1,3
1
(西安邮电大学 通信与信息工程学院, 陕西 西安 710121)
2
(泛网无线通信教育部重点实验室(北京邮电大学), 北京 100876)
3
(陕西省信息通信网络及安全重点实验室(西安邮电大学), 陕西 西安 710121)
通信作者: 崔砚鹏, E-mail: cuiyanpeng94@bupt.edu.cn
摘 要: 作为无线传感器网络(wireless sensor networks, WSNs)的关键技术之一, 分簇路由协议因其可扩展性较强
及能耗较低等优势, 逐渐成为 WSNs 路由协议的研究热点. 如何对簇首进行最佳化选取, 是提高分簇路由协议性
能的关键. 通过揭示不同场景中的簇首数量及网络能耗之间的映射关系, 以能耗最小化为目标, 构建了簇首最佳
规模及最佳位置的计算理论; 面向不同规模的网络讨论了簇间多跳策略的使用条件, 提出了虚拟簇首及其虚拟力
的概念, 构建了虚拟簇首与边界、节点及其他虚拟簇首之间的 3 种虚拟力模型, 讨论了不同虚拟力的最佳距离阈
值; 为实现网络能耗的最小化及均衡化, 设置了关于剩余能量及距离因子的适应度函数, 形成了基于虚拟力的能
量高效路由协议. 实验结果表明: 在多种规模的网络中, 与基于适应度值的改进灰狼优化器、改进的低能耗自适
应聚类层次结构协议以及改进的分布式能量高效分簇算法相比, 该算法使簇首分布更均匀、节点能耗更低且更
均衡.
关键词: 无线传感器网络; 分簇路由协议; 簇首最佳数量; 虚拟力
中图法分类号: TP393
中文引用格式: 赵小强, 崔砚鹏, 郭铮, 刘敏, 李雄, 文秦. 基于虚拟力的 WSNs 能量高效分簇路由协议. 软件学报, 2022,
33(2): 622–640. http://www.jos.org.cn/1000-9825/6159.htm
英文引用格式: Zhao XQ, Cui YP, Guo Z, Liu M, Li X, Wen Q. Energy-efficient Clustering Routing Protocol for Wireless Sensor
Networks Based on Virtual Force. Ruan Jian Xue Bao/Journal of Software, 2022, 33(2): 622640 (in Chinese). http://www.jos.org.cn/
1000-9825/6159.htm
Energy-efficient Clustering Routing Protocol for Wireless Sensor Networks Based on Virtual
Force
ZHAO Xiao-Qiang
1,3
, CUI Yan-Peng
2
, GUO Zheng
1,3
, LIU Min
1,3
, LI Xiong
1,3
, WEN Qin
1,3
1
(School of Communication and Information Engineering, Xi’an University of Posts and Telecommunications, Xi’an 710121, China)
2
(Key Laboratory of Universal Wireless Communications, Ministry of Education (Beijing University of Posts and Telecommunications),
Beijing 100876, China)
3
(Shaanxi Key Laboratory of Information Communication Network and Security (Xi’an University of Posts and Telecommunications),
Xi’an 710121, China)
Abstra ct : As one of the key technologies of wireless sensor networks (WSNs), clustering routing protocol has gradually become a
research hotspot of WSNs routing protocol due to its advantages of strong scalability and low energy consumption. How to select the
optimal cluster head is the key to improve the performance of cluster routing protocol. In this study, by revealing the mapping relationship
among cluster head number and the network energy consumption in different scenarios, with the goal of minimizing energy consumption,
the calculation theory of optimal number of cluster heads is constructed. The conditions of using multi-hop strategy among clusters are
discussed for different scale networks; the concept of virtual cluster head and its three virtual force models is proposed. Three virtual
基金项目: 国家自然科学基金-雅砻江联合基金(U1965102); 陕西省创新人才推进计划-物联网科技创新团队(2019TD-028)
收稿时间: 2020-06-30; 修改时间: 2020-08-11; 采用时间: 2020-09-29
赵小强 等: 基于虚拟力的 WSNs 能量高效分簇路由协议
623
force models between virtual cluster head and boundaries, node and other virtual cluster heads are constructed, and the optimal distance
thresholds for different virtual forces and the differences are discussed. In order to realize the minimization and equalization of network
energy consumption, the fitness function of residual energy and distance factor is set up to form an energy efficient routing protocol based
on virtual force. The experimental results show that in networks of various scales, compared with the fitness-value based improved gray
wolf optimizer, the improved low-energy adaptive clustering hierarchy protocol and the modified distributed energy efficient clustering
algorithm, the algorithm proposed in this studymakes the cluster head more uniform, the node energy consumption lower and more
balanced, and the network life is effectively extended.
Key words: wireless sensor networks (WSNs); clustering routing protocol; optimal number of cluster heads; virtual force
1 引 言
作为一种由低功耗微型传感器节点组成的, 具有无线通信感知、数据处理和存储能力的自组织网络, 无
线传感器网络(wireless sensor networks, WSNs)
[1]
凭借其部署便捷、抗毁能力强及成本低等特点, 为信息感知带
来了一场新的变革, 在智慧农业及风能资源监测等领域得到了广泛应用
[2]
. 传感器节点在多数应用场景中常
被不规则地部署, 且节点的地理位置常因环境的变化而变化(如基于系留汽艇的风能资源监测节点), 因此,
WSNs 需具备自组织能力, 且能以较低的成本提供安全可靠的通信与控制业务. 尽管 WSNs 的自组织形式常
因场景业务的不同而存在差异, 但多数传感器节点的任务是从目标监测区域对数据进行感测、收集与预处理,
并基于预设的路由协议将监测数据通过无线传输的方式发送至基站, 完成对目标监测区域的实时全面监控,
实现诸多服务质量(如网络寿命、吞吐量和可靠性等)的性能提升
[3]
.
根据网络结构的差异, WSNs 路由协议可被分为以数据为中心的协议、基于位置的协议、分簇路由协议与
基于服务质量的协议等多类
[4]
. 其中, 分簇路由协议因其可扩展性较强、负载及能耗较低且支持数据融合等优
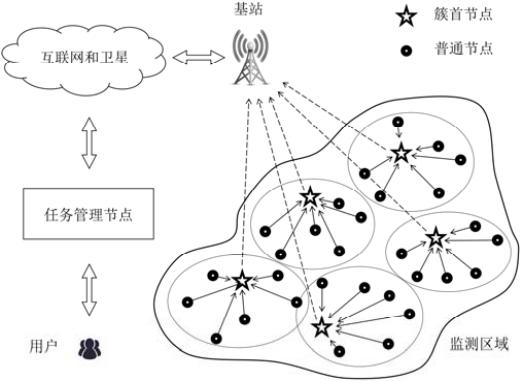
势, 逐渐成为 WSNs 路由协议的研究热点之一. 如图 1 所示, 在分簇路由协议中, 所有节点被群集划分, 簇内
的某个节点被选举为簇首, 一方面负责协调簇内成员的监测及数据传输任务, 另一方面向其他簇首或基站进
行数据转发, 因此具备减少能耗与延长网络寿命的能力. 然而, 由于承担了大量数据的融合与转发任务, 簇首
节点常比其他节点更早地耗尽能量. 鉴于 WSNs 的应用场景限制, 节点的更换或其能源的二次供应往往难以
实现, 一旦部分节点因能量耗尽而失效, 将给整个网络带来无法挽救的灾难
[5]
. 因此, 如何对簇首进行最佳化
选取, 实现能耗的最小化、均衡化并延长网络的生命周期, 成为 WSNs 分簇路由协议面临的挑战.
图 1 WSNs 的分簇路由结构
根据簇首选举机制的差异, 现有的分簇路由协议可被分为经典分簇路由协议及基于群体智能优化的分簇
of 19
免费下载
【版权声明】本文为墨天轮用户原创内容,转载时必须标注文档的来源(墨天轮),文档链接,文档作者等基本信息,否则作者和墨天轮有权追究责任。如果您发现墨天轮中有涉嫌抄袭或者侵权的内容,欢迎发送邮件至:contact@modb.pro进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,墨天轮将立刻删除相关内容。
下载排行榜


评论