




基于多任务学习的眼底图像红色病变点分割-郭松,李涛,李宁,康宏,张玉军,王恺.pdf
免费下载

软件学报 ISSN 1000-9825, CODEN RUXUEW E-mail: jos@iscas.ac.cn
Journal of Software,2021,32(11):3646−3658 [doi: 10.13 328/j.cnki.jos.006038] http://www.jos.org.cn
©中国科学院软件研究所版权所有. Tel: +86-10-62562563
基于多任务学习的眼底图像红色病变点分割
∗
郭
松
1
,
李
涛
2,3
,
李
宁
1
,
康
宏
1,4
,
张玉军
5
,
王
恺
1
1
(南开大学 计算机学院,天津 300350)
2
(天津市网络与数据安全技术重点实验室(南开大学),天津 300350)
3
(计算机体系结构国家重点实验室(中国科学院),北京 100190)
4
(北京上工医信科技有限公司,北京 100176)
5
(中国科学院 计算技术研究所,北京 100190)
通讯作者: 王恺, E-mail: wangk@nankai.edu.cn
摘 要: 糖尿病性视网膜病变(糖网病)是导致成年人视觉损失的主要因素之一.早期的眼底筛查可以显著降低这
种视觉损失的可能性.彩色眼底图像由于具有采集便利、对人体无伤害等特点,常被用于大规模的眼底筛查工作.对
眼底图像中的红色病变点而言,微动脉瘤是轻度非增殖性糖网病的主要标志,出血点与中度及重度非增殖性糖网病
的诊断有关,因此,眼底图像中出血点和微动脉瘤的准确分割对糖网病分级诊断具有重要参考价值.提出一种基于多
任务学习的分割模型 Red-Seg 来对出血点和微动脉瘤进行分割.该网络包含两个分支,每个分支处理一种病变点.设
计了一种两阶段训练算法,并且两个阶段使用不同的损失函数:第 1 阶段使用改进的 Top-k 带权交叉熵损失函数,将
模型训练集中在难分样本上;第 2 阶段将最小化假阳性和假阴性作为 Red-Seg 模型训练的优化目标,进一步减少病
变点误分.最后,在 IDRiD 数据集上进行模型验证,并与其他病变点分割方法进行对比.实验结果表明,在应用 Red-
Seg 模型进行微动脉瘤和出血点红色病变点分割时,两阶段训练算法可以显著减少病变点误分情况,尤其是出血点
分割的准确率和召回率都提高 2.8%.同时,与 HED、FCRN、DeepLabv3+和 L-Seg 等图像级分割模型相比,Red-Seg
模型在微动脉瘤分割上获得了更好的 AUC_PR.
关键词: 眼底图像;糖网病;微动脉瘤分割;出血点分割;多任务学习
中图法分类号: TP3
91
中文引用格式: 郭松,李涛,李宁,康宏,张玉军,王恺.基于多任务学习的眼底图像红色病变点分割.软件学报,2021,32(11):
3646−3658. http ://www.jos.org.cn/1000-9825/6038.htm
英文引用格式: Guo S, Li T, Li N, Kang H, Zhang YJ, Wang K. Red lesion segmentation of fundus image with multi-task
learning. Ruan Jian Xue Bao/Journal of Software, 2021,32(11):3646−3658 (in Chinese). http://www.jos.org.cn/1 000-9825/6038 .
htm
Red Lesion Segmentation of Fundus Image with Multi-task Learning
GUO Song
1
, LI Tao
2,3
, LI Ning
1
, KANG Hong
1,4
, ZHANG Yu-Jun
5
, WANG Kai
1
1
(College of Computer Science, Nankai University, Tianjin 300350, China)
2
(Tianjin Key Laboratory of Network and Data Sci ence Technology (N ankai University), Tianjin 300350, China)
3
(State Key Laboratory of Computer Architecture (Chinese Academy of Sciences), Beijing 100190, China)
∗ 基金项目: 国家自然科学基金(61872200); 国家重点研发计划(2016YFC0400709, 2018YFB2100300); 天津市自然科学基金
(18YFYZCG00060, 19JCZDJC31600); 天津市教学成果奖重点培育项目(PYGJ-018)
Foundation item: National Natural Science Foundation of China (61872200); National Key Research and Development Program of
China (2016YFC0400709, 2018YFB2100300); Natural Science Foundation of Tianjin Municipality (18YFYZCG00060, 19JCZDJC316
00); Key Cultivation Proj ect of Education Achievement Aw ard of Tianjin Municipality (PYGJ-018)
收稿时间: 2019-07-18; 修改时间: 2019-11-04; 采用时间: 2020-03-27
郭松 等:基于多任务学习的眼底图像红色病变点分割
3647
4
(Beijing Shanggong Medical Technology Co. Ltd., Beijing 100176, China)
5
(Institute of Computing Technology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100190, China)
Abstra ct : Diabetic retinopathy (DR) is the leading cause of vision loss for adult individuals, and early fundus screening can
significantly reduce this visual loss. Color fundus image is often used in large-scale fundus screening due to the acquisition convenience
and its human-harmless. As a kind of red lesions in fundus images, the appearance of microaneurysms is the main marker of mild
non-proliferative DR, and hemorrhage, as another kind of red lesions, is r elated to moderate and severe non-proliferative DR. So that red
lesions in fundus images are important indicators for th e screening of DR. This s tudy proposes a multi-task n etwork, named Red-Seg, for
red lesion segmentation. The network contains two individual branches, each is used for one kind of lesion segmentation. Meantime, a
two-stage training algorithm is presented where different loss functions are used in different stages. In the first stage, modified Top-k
balanced cross-entropy loss is used to push th e network focuses on hard-to-classify s amples. And, in the second s tage, false positive and
false negative are integrat ed as loss function into training to reduce misclassification furth er. At last, extensive experiments are employed
on the IDRiD dataset, and the lesion segmentation results are compared with other methods. Experimental results show that proposed
two-stage training algorithm can lead to much higher pr ecision and recall, which means this method can reduce misclassification in some
certain. Specifically for hemorrhage segmentation, both recall and precision increased by at least 2.8%. Meanwhile, compared with other
image-level lesion segmentation models, such as HED, FCRN, DeepLabv3+, and L-Seg, Red-Seg achieves much higher AUC_PR on
microaneurysm segmentation.
Key words: fundus image; diabetic retinopathy; microaneurysms segmentation; hemorrhage segmentation; multi-task learning
糖尿病性视网膜病变(简称糖网病,diabetic retinopat hy,简称 DR) 是糖尿病引起的眼部疾病,是致盲的主要原
因之一.据报道,在美国、欧洲和亚洲,大约 1/3 的糖尿病患者患有一定程度的糖网病
[1]
.研究表明,通过早期筛查,
可以显著降低糖网病的致盲率,而糖网筛查的主要方法是分析彩色眼底图像.按照国际眼科中心定义的糖网病
分级标准,与糖网病相关的眼底病变点主要包括软渗、硬渗、出血点、微动脉瘤、静脉串珠等
[1]
,其中,出血点
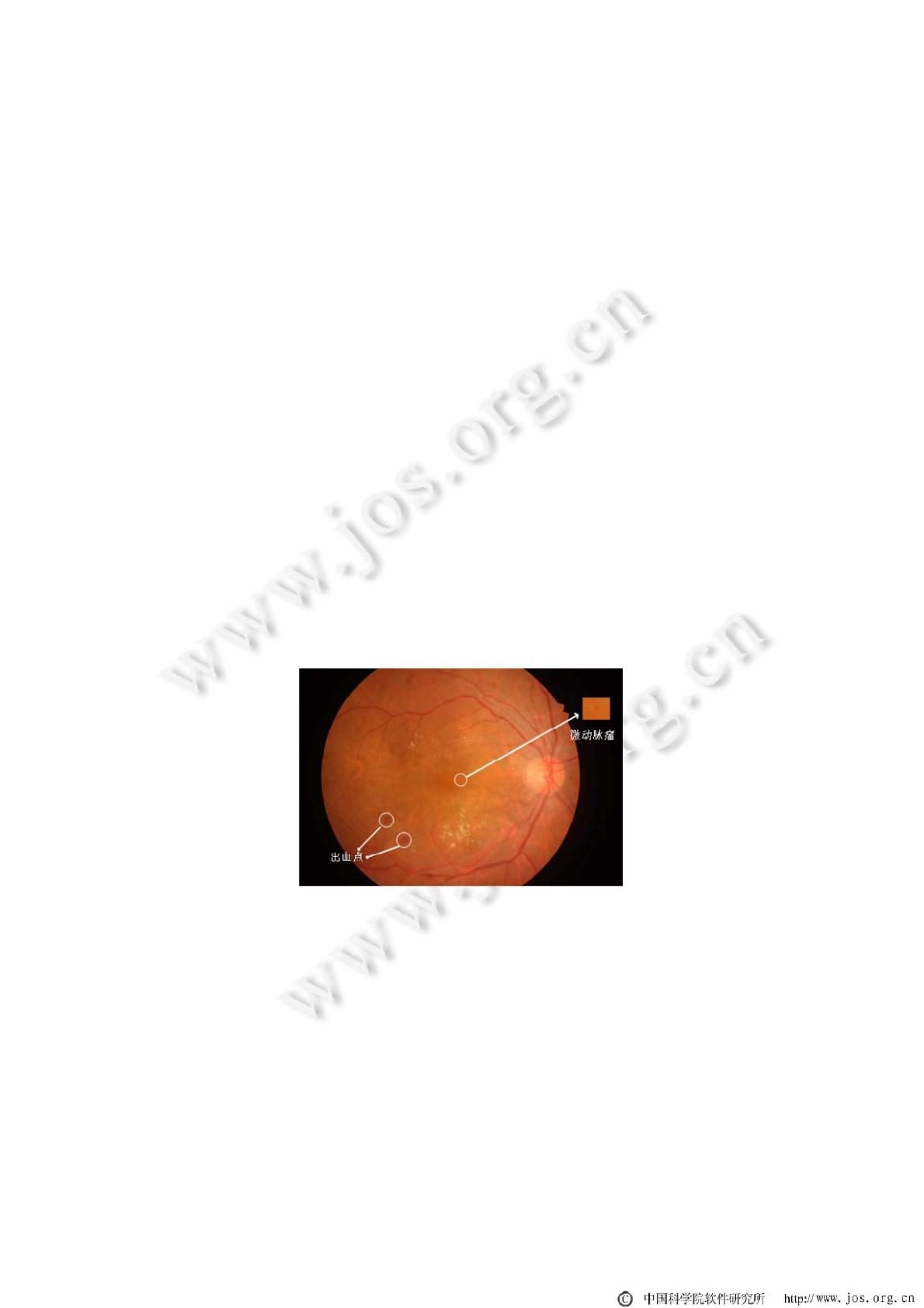
和微动脉瘤的颜色偏红(如图 1 所示),统称为红色病变点.轻度非增殖性糖网病在眼底图像上的表现是只存在微
动脉瘤(microaneu ry sm,简称 MA),中度及重度非增殖性糖网病的表现之一是眼底存在出血点(hemorrhage,简称
HE).因此,眼底红色病变点的识别和检测对糖网病的分级诊断具有重要的指示意义.但由于病变点形态大小不
一,导致人工进行病变点分析耗时耗力,并且与大规模待检人员相比,眼科医生严重匮乏,这使得大规模的糖网
筛查难以有效开展.因此,开发一种自动化的眼底图像病变点分析工具非常必要.
Fig.1 A fundus image from the IDRiD dataset
图 1 IDRiD 数据集中的眼底图像
目前,大量工作表明,深度学习方法在眼底图像分析领域获得了比传统方法更优的性能,比如在糖网病筛
查、眼底血管分割、眼底视杯视盘分割、病变点检测等领域
[2−10]
.Google 在 2016 年提出了一种基于深度学习
模型的糖网病筛查算法,首先通过多位职业眼科医生对将近 13 万张眼底图像进行病变等级标注,然后采用
inception-v3 网络对其进行训练和测试,在由 1 万多张图像组成的测试集上获得了 90.3 %的敏感性和 98.1%的特
of 13
免费下载
【版权声明】本文为墨天轮用户原创内容,转载时必须标注文档的来源(墨天轮),文档链接,文档作者等基本信息,否则作者和墨天轮有权追究责任。如果您发现墨天轮中有涉嫌抄袭或者侵权的内容,欢迎发送邮件至:contact@modb.pro进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,墨天轮将立刻删除相关内容。
下载排行榜


评论