




云存储多卷负载均衡的LSM键值存储系统_徐鹏_PingCAP.pdf
免费下载

小 型 微 型 计 算 机 系 统
Journal of Chinese Computer Systems
收稿日期:2021-10-12 基金项目:国家自然科学基金面上项目(No.62072196)资助;国家自然科学基金创新研究群体项目(No.61821003)资助。 作
者简介:徐鹏,男,1991 年生,博士研究生,研究方向为云存储、键值存储系统等;周元辉,男,1997 年生,博士研究生,研究方向为大数据存储、键
值存储系统、非易失性内存和学习索引等;陈书宁,男,1994 年生,硕士,公司员工,研究方向为键值存储系统、分布式存储等;刘玮,男,1994 年
生,学士,公司员工,研究方向为键值存储系统、分布式存储等;李大平,男,1992 年生,博士研究生,研究方向为大数据、存储系统节能等;万继
光,男,1972 年生,博士,教授,通讯作者,CCF 会员,研究方向为大数据存储、键值存储系统、文件系统、分布式存储和智能化存储等。
云存储多卷负载均衡的 LSM 键值存储系统
徐 鹏
1
,周元辉
1
,陈书宁
2
,刘玮
2
,李大平
1
,万继光
1
1
(武汉光电国家研究中心, 华中科技大学 武汉 430074)
2
(北京平凯星辰科技发展有限公司 北京 100192)
E-mail:jgwan@hust.edu.cn
摘 要:单个云存储卷的 IOPS 和带宽性能受到限制,通过组合使用多个云存储卷的方式能以较低的费用获得更高的性能。但是,
现有工作缺乏针对多云存储卷优化的 LSM 键值存储系统探究。首先将现有多路径或哈希负载均衡的方案应用于使用多云存储卷
的 LSM 键值存储系统,相对单个大容量卷的性能有显著提升;但是,现有多卷负载均衡方案的写数据策略,无法感知 LSM 键值存
储系统的数据布局特点,导致各成员卷之间仍然存在负载不均衡的问题,不能充分发挥出多卷的最大性能。为此,提出一种基于
LSM 键值存储系统的多卷负载均衡方案 TANGO。在日志结构归并树由 compation 新生成的 sstable 落盘之前,先根据统计的各个
成员卷的关键信息,判断 sstable 与各成员卷的键范围重叠情况,然后选择键范围重叠最小的成员卷进行写入;针对读为主的负
载,无法通过 compation 达到负载均衡,TANGO 采用后台数据迁移方式进一步达到负载均衡。在亚马逊云存储卷上的评估表明,
相比相同存储容量的单卷,采用了 TANGO 方案的同等容量的多卷可提高 7 倍左右的性能;相比其它多卷方案,TANGO 能提升 20%
以上的性能,且各成员卷间负载更加均衡。
关键词:云存储;多卷;键值存储;日志结构归并树;负载均衡
中图分类号:TP392 文献标识码:A
TANGO: A Balancer for LSM Stores with Multiple Cloud Volumes
XU Peng
1
, ZHOU Yuan-hui
1
, CHEN Shu-ning
2
, LIU Wei
2
, LI Da-ping
1
, and WAN Ji-guang
1
1
(Wuhan National Laboratory for Optoelectronics, School of Computer Science & Technology in Huazhong University of Science and Technology, and Key Laboratory
of Information Storage System Ministry of Education of China, Wuhan, 430074)
2
(PingCAP©, Beijing, 100192)
Abstract: Cloud service providers (e.g., AWS) limit the IOPS and bandwidth provisioned for a cloud storage volume, so users can join
multiple volumes together to get higher IOPS and bandwidth at almost no extra cost. However, few existing works focus on LSM stores
with multiple cloud volumes. Even when naively marrying existing multi-path based or hash-based workload balancing approaches to build
an LSM store using multiple small cloud volumes, we observe a significant improvement when compared to using a single large cloud
volume. Existing work, on the other hand, is unaware of key-value distributions of LSM stores among volumes, resulting in I/O pressure
imbalance and, as a result, is inefficient for unleashing aggregated performance of multiple volumes and yields suboptimal performance. In
this paper, we propose TANGO, an LSM store-based I/O balancer for multiple cloud volumes. It effectively uses LSM compactions to
prevent potential I/O jams to a single volume by sensing LSM data layouts and collected data distributions among volumes. TANGO also
actively offloads I/O pressures from bottleneck volumes through selective duplications. Evaluation results on AWS EBS volumes
demonstrate that, TANGO improves performance by up to 7× when compared to a single cloud volume with the same cost. TANGO also
achieves a more balanced I/O among volumes when joining multiple volumes for LSM stores, outperforming existing approaches by 20%.
Key words: Cloud Storage; Multiple Volume; Key-Value Storage; Log-Structured Merge Tree; Workload Balance
1 引言
建设“数字化中国”是《十四五规划》提出的重要目标
之一,数字化建议意味着海量的数据
[ 1 ]
。随着网络技术的
不断进步,在一些场景下,用户通过网络获取数据的速度接
近甚至是超过了从本地存储中获取数据的速度。因此,数据
上云是一大趋势,云存储具有数据可靠性高
[ 2 ][ 4 ]
、扩展性
强
[ 3 ][ 5 ]
、按需付费和性能稳定等特点,能够为用户提供丰
富的服务
[ 19 ][ 20 ]
。但是单个云存储卷(以下简称卷)可使用
的最大 IOPS 和带宽受到限制
[ 18 ]
,无法满足用户的高性能,
特别是 IOPS 需求。基于云存储服务商的对云存储卷的计费
规则和实际性能测试,我们发现相比单个卷,在容量相同时,
组合使用多个小容量的卷能够以相同的费用获得更高的
IOPS 和带宽性能。然而,测试表明,简单组合使用多个卷的
2 小 型 微 型 计 算 机 系 统
方式会导致各个成员卷之间的负载严重不均衡,不能充分发
挥出多卷所累加的最大性能。
为充分发挥多卷的性能,需要基于实际的存储系统进行
分析和优化。日志结构归并树(Log-structured Merge-tree,
LSM)
[ 6 ]
以读性能为代价的设计思想极大地提升了写性能,
因此已被广泛应用于各大互联网服务厂商的键值存储系统
(例如,Facebook 的 RocksDB
[ 7 ]
和 Cassandra
[ 14 ]
、Google
的 BigTable
[ 8 ]
和 LevelDB
[ 9 ]
以及阿里云的 X-Engine
[ 15 ]
),
成为了各类存储系统的重要组成部分。对此,本文旨在充分
发挥应用在 LSM 键值存储系统的多卷性能。
LSM 的数据分层设计使得 LSM 键值存储系统在处理读请
求时产生大量的 I/O 请求
[ 21 ][ 22 ][ 24 ]
。虽然键值对在 L
i
层内
的各 sstable 之内和之间均保持有序且不存在重复,但是 L
i
层与 L
i+1
层之间的键值对则不然。因此,在查找键值对时,
LSM 键值存储系统必须逐层进行查找,且在未命中目标键值
对或遍历完所有的层之前无法确保查询结果的正确性。相较
于将写请求在内存中进行聚合之后再批量地写入存储的设
计
[ 23 ]
,在最坏情况下,LSM 键值存储系统处理读请求时需
要向每一层发出随机 I/O 请求,导致大量的读 I/O 放大。因
而,依赖于随机 I/O 请求的读性能受到卷的 IOPS 性能和键
值对在 LSM 各层分布的影响。
现有的多卷负载均衡方案仅依靠写数据策略来最终决
定数据在成员卷之间的分布,不仅无法充分应对多变的读负
载(例如顺序读写、随机读写或昼夜变化等
[ 16 ][ 17 ]
)的问题,
同时依然存在将 LSM 不同层键范围重合度高的 sstable(或
者一部分)分配到同一个成员卷的问题,导致成员卷之间的
读负载严重不均衡。
因此,需要将在多卷的成员卷之间迁移读负载热数据的
方式作为现有多卷负载均衡方案的补充。而为了实现读负载
均衡,需要实现键范围在各个成员卷之间均匀分布,从而避
免读负载的热数据引起单个成员卷的 I/O 压力超过其购买
的 IOPS 性能、进而造成多卷整体性能无法充分发挥的问题。
为此,以提升多卷读性能为目标,提出一种基于 LSM 键
值存储系统的多卷负载均衡方案 TANGO。TANGO 通过优化 LSM
的合并操作过程以实现多卷的读写负载均衡。在合并操作新
生成的 sstable 落盘前,先根据统计的多卷中各个成员卷的
关键信息,判断该 sstable 与各个成员卷的键范围重叠情
况,选择键范围重叠最小的成员卷执行写入;针对读为主的
负载,无法通过 compation 达到负载均衡,TANGO 采用后台
数据迁移方式进一步达到负载均衡。由此,针对每个键范围
数据的读 I/O 请求会被均匀分散至多个成员卷,实现多卷读
负载均衡的目标,从而充分发挥多卷的性能。
本文的主要贡献如下:
1)将现有多路径负载均衡或哈希负载均衡的方案应用
于使用多云存储卷的 LSM 键值存储系统,并对云存储卷进行
了大量的组合测试,通过实验证明同等存储容量下多卷性能
更好;但是,各成员卷之间仍然存在负载不均衡的问题,不
能充分发挥出多卷的最大性能。进一步通过实验和观察,发
现了基于 LSM 键值存储系统的多卷中各成员卷 I/O 负载严
重不均衡的原因。以上发现为设计更为高效的多卷性能优化
方案提供了依据。
2) 针对 1)中分析的结果,提出一种基于 LSM 键值存
储系统的多卷负载均衡方案 TANGO。在 LSM 中合并操作新生
成的 sstable 确定落盘的目标卷之前,先根据统计的多卷中
各个成员卷的关键信息,判断要写入 sstable 与各个成员卷
的键范围重叠情况,选择键范围重叠最小的成员卷写入。
TANGO 也通过选择性复制的热点数据迁移方法进一步均衡
读请求热点数据分布。TANGO 方案从读和写两个角度对多卷
性能进行优化,弥补了现有多卷使用方案应对 LSM 键值存储
系统的读请求热数据分布严重不均的缺点。
3) 在亚马逊云的弹性块存储卷上实现了 TANGO 以及对
比方案,并将它们进行了详细的对比和分析,从多卷整体性
能、各成员卷平均性能、成员卷实时性能和迁移开销等方面
验证了 TANGO 的高效性。
2 背景及相关工作
2.1 LSM 键值存储系统架构
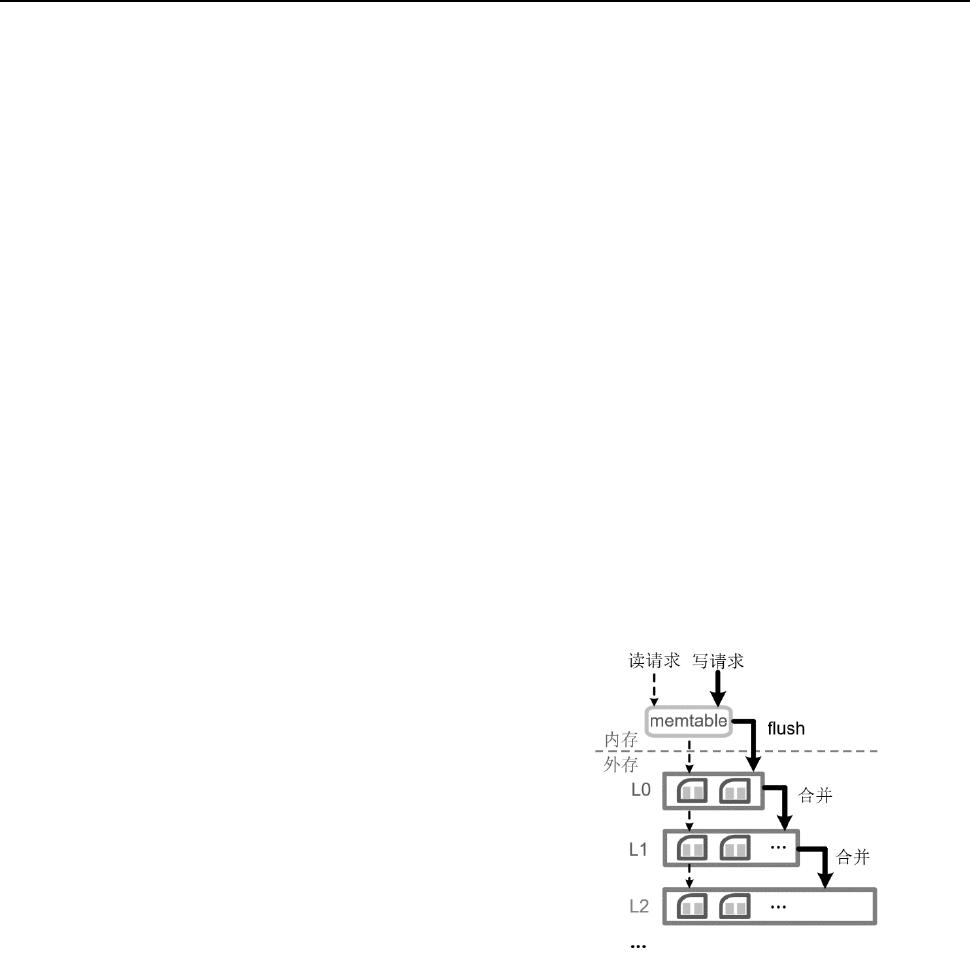
图 1 LSM 架构示意图
Fig.1 Overview of the LSM store
如图 1 所示,基于 LSM 的键值存储系统中包含多层存储
结构(L
0
至 L
n
层),每层存储容量有限,但每层的容量随层
数的增加而逐层增大。所有到来的写请求都会被缓存至内存
的缓存区 memtable,而后写入到一个固定大小的 sstable
中,该 sstable 会被放入 L
0
层。L
0
层中数据总量达到设定阈
值时会触发合并操作(compaction),该操作将 L
0
层和 L
1
层
有键范围重叠的多个 sstable 进行整理,合并重复数据、删
去无效数据后,对剩下的键值对以键为序进行排序,并且将
键范围相近的数据放在一起构成新的 sstable,之后再写入
到 L
1
层中。其它 L
i
至 L
i+1
层的合并操作以此类推。
具体而言,操作通常需要执行以下 3 个步骤:
①读:将选定的 L
i
和 L
i+1
层 sstable 读取到内存。
②归并:将键值对从这些 sstable 数据块中的紧凑格式
of 10
免费下载
【版权声明】本文为墨天轮用户原创内容,转载时必须标注文档的来源(墨天轮),文档链接,文档作者等基本信息,否则作者和墨天轮有权追究责任。如果您发现墨天轮中有涉嫌抄袭或者侵权的内容,欢迎发送邮件至:contact@modb.pro进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,墨天轮将立刻删除相关内容。
下载排行榜


评论