




Database Meets Deep Learning Challenges and.pdf
10墨值下载

Database Meets Deep Learning: Challenges and
Opportunities
Wei Wang
†
, Meihui Zhang
‡
, Gang Chen
§
,
H. V. Jagadish
#
, Beng Chin Ooi
†
, Kian-Lee Tan
†
†
National University of Singapore
‡
Beijing Institute of Technology
§
Zhejiang University
#
University of Michigan
†
{wangwei, ooibc, tankl}@comp.nus.edu.sg
‡
meihui zhang@bit.edu.cn
§
cg@zju.edu.cn
#
jag@umich.edu
ABSTRACT
Deep learning has recently become very popular on ac-
count of its incredible success in many complex data-
driven applications, such as image classification and speech
recognition. The database community has worked on
data-driven applications for many years, and therefore
should be playing a lead role in supporting this new
wave. However, databases and deep learning are differ-
ent in terms of both techniques and applications. In this
paper, we discuss research problems at the intersection
of the two fields. In particular, we discuss possible im-
provements for deep learning systems from a database
perspective, and analyze database applications that may
benefit from deep learning techniques.
1. INTRODUCTION
In recent years, we have witnessed the success of
numerous data-driven machine-learning-based ap-
plications. This has prompted the database com-
munity to investigate the opportunities for integrat-
ing machine learning techniques in the design of
database systems and applications [84]. A branch of
machine learning, called deep learning [57, 38], has
attracted worldwide interest in recent years due to
its excellent performance in multiple areas including
speech recognition, image classification and natural
language processing (NLP). The foundation of deep
learning was established about twenty years ago in
the form of neural networks. Its recent resurgence is
mainly fueled by three factors: immense computing
power, which reduces the time to train and deploy
new models, e.g. Graphic Processing Unit (GPU)
enables the training systems to run much faster
than those in the 1990s; massive (labeled) training
datasets (e.g. ImageNet) enable a more comprehen-
sive knowledge of the domain to be acquired; new
deep learning models (e.g. AlexNet [55]) improve
the ability to capture data regularities.
Database researchers have been working on sys-
tem optimization and large scale data-driven ap-
plications since 1970s, which are closely related to
the first two factors. It is natural to think about
the relationships between databases and deep learn-
ing. First, are there any insights that the database
community can offer to deep learning? It has been
shown that larger training datasets and a deeper
model structure improve the accuracy of deep learn-
ing models. However, the side effect is that the
training becomes more costly. Approaches have been
proposed to accelerate the training speed from both
the system perspective [12, 42, 18, 80, 2] and the
theory perspective [120, 27]. Since the database
community has rich experience with system opti-
mization, it would be opportune to discuss the ap-
plicability of database techniques for optimizing deep
learning systems. For example, distributed com-
puting and memory management are key database
technologies also central to deep learning.
Second, are there any deep learning techniques
that can be adapted for database problems? Deep
learning emerged from the machine learning and
computer vision communities. It has been success-
fully applied to other domains, like NLP [28]. How-
ever, few studies have been conducted using deep
learning techniques for traditional database prob-
lems. This is partially because traditional database
problems — like indexing, transaction and storage
management — involve less uncertainty, whereas
deep learning is good at predicting over uncertain
events. Nevertheless, there are problems in databases
like knowledge fusion [21] and crowdsourcing [79],
which are probabilistic problems. It is possible to
apply deep learning techniques in these areas. We
will discuss specific problems like querying interface,
knowledge fusion, etc. in this paper.
The previous version [108] of this paper has ap-
peared in SIGMOD Record. In this version, we ex-
tend it to include the recent developments in this
field and references to recent work.
arXiv:1906.08986v2 [cs.DB] 19 Jan 2020
initialize
parameters
compute
gradients
update
parameters
read mini-
batch data
Figure 1: Stochastic Gradient Descent.
The rest of this paper is organized as follows: Sec-
tion 2 provides background information about deep
learning models and training algorithms; Section 3
discusses the application of database techniques for
optimizing deep learning systems. Section 4 de-
scribes research problems in databases where deep
learning techniques may help to improve perfor-
mance. Some final thoughts are presented in Sec-
tion 5.
2. BACKGROUND
Deep learning refers to a set of machine learn-
ing models which try to learn high-level abstrac-
tions (or representations) of raw data through mul-
tiple feature transformation layers. Large training
datasets and deep complex structures [8] enhance
the ability of deep learning models for learning ef-
fective representations for tasks of interest. There
are three popular categories of deep learning models
according to the types of connections between lay-
ers [57], namely feedforward models (direct connec-
tion), energy models (undirected connection) and
recurrent neural networks (recurrent connection).
Feedforward models, including Convolution Neural
Network (CNN), propagate input features through
each layer to extract high-level features. CNN is
the state-of-the-art model for many computer vi-
sion tasks. Energy models, including Deep Belief
Network (DBN) are typically used to pre-train other
models, e.g., feedforward models. Recurrent Neu-
ral Network (RNN) is widely used for modeling se-
quential data. Machine translation and language
modeling are popular applications of RNN.
Before deploying a deep learning model, the model
parameters involved in the transformation layers
need to be trained. The training turns out to be a
numeric optimization procedure to find parameter
values that minimize the discrepancy (loss function)
between the expected output and the real output.
Stochastic Gradient Descent (SGD) is the most widely
used training algorithm. As shown in Figure 1,
SGD initializes the parameters with random val-
ues, and then iteratively refines them based on the
computed gradients with respect to the loss func-
tion. There are three commonly used algorithms
for gradient computation corresponding to the three
model categories above: Back Propagation (BP),
Contrastive Divergence (CD) and Back Propaga-
Approach B
• TBD
input
inner-
product
sigmoid
loss
DB
W
b
data
data
gradient
gradient
data
data
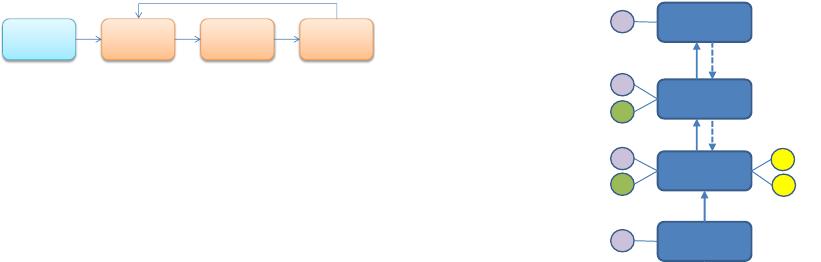
Figure 2: Data flow of Back-Propagation.
tion Through Time (BPTT). By regarding the lay-
ers of a neural net as nodes of a graph, these algo-
rithms can be evaluated by traversing the graph in
certain sequences. For instance, the BP algorithm
is illustrated in Figure 2, where a simple feedfor-
ward model is trained by traversing along the solid
arrows to compute the data (feature) of each layer,
and along the dashed arrows to compute the gradi-
ent of each layer and each parameter (W and b).
3. DATABASES TO DEEP LEARNING
In this section, we discuss the optimization tech-
niques used in deep learning systems, and research
opportunities from the perspective of databases.
3.1 Stand-alone Training
Currently, the most effective approach for im-
proving the training speed of deep learning mod-
els is using Nvidia GPU with the cuDNN library.
Researchers are also working on other hardware,
e.g. FPGA [56]. Besides exploiting advancements
in hardware technology, operation scheduling and
memory management are two important components
to consider.
3.1.1 Operation Scheduling
Training algorithms of deep learning models typ-
ically involve expensive linear algebra operations as
shown in Figure 3, where the matrix W 1 and W 2
could be larger than 4096∗4096. Operation schedul-
ing is to first detect the data dependency of oper-
ations and then place the operations without de-
pendencies onto executors, e.g., CUDA streams and
CPU threads. Taking the operations in Figure 3 as
an example, a1 and a2 in Figure 3 could be com-
puted in parallel because they have no dependen-
cies. The first step could be done statically based
on dataflow graph or dynamically [10] by analyzing
the orders of read and write operations. Databases
also have this kind of problems in optimizing trans-
of 10
10墨值下载
【版权声明】本文为墨天轮用户原创内容,转载时必须标注文档的来源(墨天轮),文档链接,文档作者等基本信息,否则作者和墨天轮有权追究责任。如果您发现墨天轮中有涉嫌抄袭或者侵权的内容,欢迎发送邮件至:contact@modb.pro进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,墨天轮将立刻删除相关内容。
下载排行榜


评论