




Graphix-T5- Mixing Pre-Trained Transformers with Graph-Aware Layers for Text-to-SQL Parsing.pdf
免费下载

Graphix-T5: Mixing Pre-Trained Transformers with
Graph-Aware Layers for Text-to-SQL Parsing
Jinyang Li
1,2
*
, Binyuan Hui
2
, Reynold Cheng
1,5†
, Bowen Qin
3
, Chenhao Ma
4
, Nan Huo
1
,
Fei Huang
2
, Wenyu Du
1
, Luo Si
2
, Yongbin Li
2 †
1
The University of Hong Kong
2
DAMO Academy, Alibaba Group
3
Shenzhen Institute of Advanced Technology, Chinese Academy of Sciences
4
The Chinese University of Hong Kong (Shenzhen)
5
Guangdong–Hong Kong-Macau Joint Laboratory
{jl0725,huonan,wenyudu}@connect.hku.hk, ckcheng@cs.hku.hk,
bw.qin@siat.ac.cn, machenhao@cuhk.edu.cn,
{binyuan.hby,f.huang,luo.si,shuide.lyb}@alibaba-inc.com
Abstract
The task of text-to-SQL parsing, which aims at convert-
ing natural language questions into executable SQL queries,
has garnered increasing attention in recent years, as it can
assist end users in efficiently extracting vital information
from databases without the need for technical background.
One of the major challenges in text-to-SQL parsing is do-
main generalization, i.e. , how to generalize well to un-
seen databases. Recently, the pretrained text-to-text trans-
former model, namely T5, though not specialized for text-
to-SQL parsing, has achieved state-of-the-art performance
on standard benchmarks targeting domain generalization. In
this work, we explore ways to further augment the pre-
trained T5 model with specialized components for text-to-
SQL parsing. Such components are expected to introduce
structural inductive bias into text-to-SQL parsers thus im-
proving model’s capacity on (potentially multi-hop) reason-
ing, which is critical for generating structure-rich SQLs. To
this end, we propose a new architecture GRAPHIX-T5, a
mixed model with the standard pre-trained transformer model
augmented by some specially-designed graph-aware layers.
Extensive experiments and analysis demonstrate the effec-
tiveness of GRAPHIX-T5 across four text-to-SQL bench-
marks: SPIDER, SYN, REALISTIC and DK. GRAPHIX-T5
surpass all other T5-based parsers with a significant mar-
gin, achieving new state-of-the-art performance. Notably,
GRAPHIX-T5-large reach performance superior to the orig-
inal T5-large by 5.7% on exact match (EM) accuracy and
6.6% on execution accuracy (EX). This even outperforms the
T5-3B by 1.2% on EM and 1.5% on EX.
1 Introduction
Relational database, serving as an important resource for
users to make decision in many fields, such as health care,
sports, and entertainment, has emerged frequently because
of the big data era. It is efficient for data users to access the
information from databases via structured query language,
e.g., SQL. Despite its effectiveness and efficiency, the com-
plex nature of SQLs leads to extremely expensive learning
*
Work done during an intern at Alibaba DAMO Academy.
†
Corresponding authors are Reynold Cheng and Yongbin Li.
Copyright © 2023, Association for the Advancement of Artificial
Intelligence (www.aaai.org). All rights reserved.
female
student
Student
Sex
MOD
EM
HAS
Question
Column
Table
Nature Language Question:
Find the number of dog pets that are raised by female students
!
Student
Database:
StuID
Sex
Age
Pets
PetID
PetType
Pet_age
Has_Pet
StuID
SQL:
PetID
SELECT count(*) FROM student AS T1 JOIN has_pet AS T2 ON
T1.stuid = T2.stuid JOIN pets AS T3 ON T2.petid = T3.petid
WHERE T1.sex = 'F' AND T3.pettype = 'dog'
Desired Linking
Figure 1: This is an an illustration of cross-domain text-to-
SQL challenge. The link between the target column sex
and the token female is highly desired but extremely chal-
lenging for the model to capture, especially when domain-
specific data or effective rules is absent. However, this
dilemma can be mitigated by a multi-hop reasoning path
(female
MOD
−→ student
EM
−→ Student
HAS
−→ Sex).
efforts for non-technical users. Therefore, text-to-SQL (Cai
et al. 2018; Zelle and Mooney 1996; Xu, Liu, and Song
2017; Yu et al. 2018a; Yaghmazadeh et al. 2017), aiming to
convert natural language instructions or questions into SQL
queries, has attracted remarkable attention.
In this work, we explore the challenging cross-domain
setting where a text-to-SQL parser needs to achieve domain
generalization, i.e. , the ability to generalize to domains that
are unseen during training. Achieving this goal would, in
principle, contribute to a universal natural language interface
that allows users to interact with data in arbitrary domains.
The major challenge towards domain generalization (Wang
et al. 2020a; Cao et al. 2021; Wang et al. 2022; Cai et al.
2021; Hui et al. 2022) is that generating structure-rich SQLs
requires (potentially multi-hop) reasoning, i.e. the ability
to properly contextualize a user question against a given
database by considering many explicit relations (e.g., table-
column relations specified by database schema) and implicit
relations (e.g., whether a phrase refers to a column or table).
Figure 1 shows an introductory example of multi-hop rea-
soning in the text-to-SQL parsing and Figure 6 presents two
more detailed cases.
arXiv:2301.07507v1 [cs.CL] 18 Jan 2023
GNN
Graphix Layer
Question | Schema
Transformer
Transformer
Transformer
Pre-trained (T5)
Pre-trained (T5)
Graphix Layer
Graphix Layer
SQL
Transformer
Transformer
Transformer
Pre-trained (T5)
Question | Schema
Transformer
Transformer
Transformer
Pre-trained (T5)
SQL
GNN
Encoder
Decoder
Transformer
Transformer
Transformer
Pre-trained (BERT)
Question | Schema
Transformer
Transformer
Transformer
Random Init.
SQL
Transformer
Transformer
Transformer
Pre-trained (T5)
Question | Schema
Transformer
Transformer
Transformer
Pre-trained (T5)
SQL
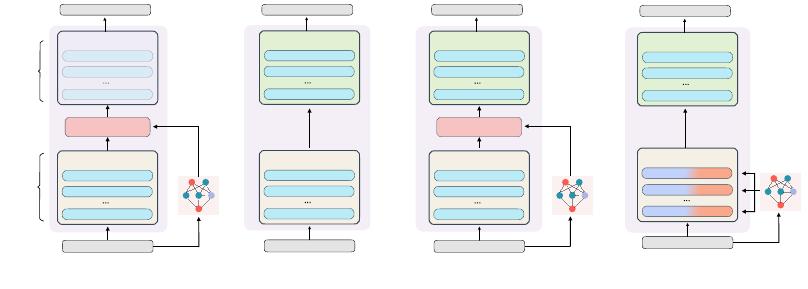
(a) RATSQL (b) T5
(c) GNN-T5 (d) Graphix-T5
Figure 2: Graphical illustration of existing methods (a) RATSQL [pre-trained BERT-encoder → graph-based module → ran-
domly initialized decoder]. (b) T5 [pre-trained T5-encoder → pre-trained T5-decoder] and the proposed variant (c) GNN-
T5 [pre-trained T5-encoder → graph-based module → pre-trained T5-decoder] (d) GRAPHIX-T5 [semi-pre-trained graphix-
module → pre-trained T5-decoder].
From the modeling perspective, there are two critical di-
mensions along which we can differentiate current text-to-
SQL parsers. The first is how to effectively imbue rela-
tional structures (both explicit and implicit) in the form of
graphs into neural networks, and the second is how to take
the most advantage of pre-trained models (e.g.T5 (Raffel
et al. 2020)). These two dimensions are inter-connected and
form a spectrum of methods. On one end of the spectrum,
PICARD (Scholak, Schucher, and Bahdanau 2021) uses
the original pre-trained T5 model by linearizing database
schemas into sequences, hoping that T5 can successfully
capture the underlying relational structures. On the other
end of the spectrum, RAT-SQL (Wang et al. 2020a) only uti-
lizes pre-trained encoders (e.g., BERT (Devlin et al. 2019))
and explicitly captures desired relations via specialized
relation-aware models. However, more powerful encoder-
decoder based pre-trained models are not exploited in this
framework, but relational structures are accommodated at
most. In this work, we explore the cross zone where the
encoder-decoder based pre-trained models (specifically T5)
and relation-aware encodings are deeply coupled in favor of
better domain generalization. We first observe that naively
adding a relational graph-based module in the middle of T5,
resulting in a ‘T5-encoder → graph-based module → T5-
decoder architecture’ (see also Figure 2(c), namely GNN-
T5), does not work very well on standard benchmarks. Pre-
sumably, the deficiency comes from the middle graph-based
modules breaking the original information flow inside T5.
In order to address this problem, we present a novel ar-
chitecture called GRAPHIX-T5 that is capable of effectively
modelling relational structure information while maintain-
ing the powerful contextual encoding capability of the pre-
trained T5. First, we design a GRAPHIX layer that simul-
taneously encodes a mixture of semantic and structural in-
formation. Concretely, hidden states of inputs composed by
questions and databases are modelled by contextualized se-
mantic encoding, and the structural representation is injected
in each transformer layer using a relational GNN block
that enhances multi-hop reasoning through message passing
(Fang et al. 2020; Velickovic et al. 2018) to capture explicit
and implicit relations. Second, we construct a new encoder
by stacking the GRAPHIX layers and replacing the origi-
nal T5 encoder. In each GRAPHIX layer, the parameters of
the semantic block are still initialized by T5, in an attempt
to maintain the contextualized encoding power of the pre-
training. In contrast to the severed GNN-T5 (Figure 2.(c)),
the GRAPHIX-T5 (Figure 2.(d)) will allow intensive interac-
tion between semantic and structure from the starting layers.
We empirically show the effectiveness of GRAPHIX-T5
on several cross-domain text-to-SQL benchmarks, i.e. , SPI-
DER, SYN, DK and REALISTIC. On these datasets, the
proposed model achieves new state-of-the-art performance,
substantially outperforming all existing models by large
margins. Specifically, GRAPHIX-T5-large surprisingly beats
the vanilla T5-3B. Furthermore, we verified that GRAPHIX-
T5 can also achieve the significant improvement in the low-
resource and compositional generalization obviously thanks
to the introduction of structural bias. It should be noticed that
though we only focus on text-to-SQL parsing in this work,
we believe that the general methodology of GRAPHIX-T5
can be extended to structured knowledge grounding tasks,
e.g., TableQA (Pasupat and Liang 2015), Data-to-text (Nan
et al. 2021) and KBQA (Talmor and Berant 2018).
2 Task Formulation and Notations
2.1 Task Definition
Given a natural language question Q =
q
1
, ..., q
|Q|
with
its corresponding database schemas D = hC, T i, where C =
c
1
, ..., c
|C|
and T =
t
1
, ..., t
|T |
represent columns and
tables, |C| and |T | refer to the number of columns and tables
in each database respectively. The goal of text-to-SQL is to
generate the corresponding SQL query y.
2.2 Vanilla T5 Architecture
Model Inputs The most canonical and effective format of
inputs to T5 performing text-to-SQL task is PeteShaw (Shaw
et al. 2021), which unifies natural language questions Q and
of 10
免费下载
【版权声明】本文为墨天轮用户原创内容,转载时必须标注文档的来源(墨天轮),文档链接,文档作者等基本信息,否则作者和墨天轮有权追究责任。如果您发现墨天轮中有涉嫌抄袭或者侵权的内容,欢迎发送邮件至:contact@modb.pro进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,墨天轮将立刻删除相关内容。
下载排行榜


评论