




SeaD- End-to-end Text-to-SQL Generation with Schema-aware Denoising.pdf
免费下载
SeaD: End-to-end Text-to-SQL Generation with Schema-aware Denoising
Kuan Xu and Yongbo Wang and Yongliang Wang and Zujie Wen and Yang Dong
Ant Group
Hangzhou, China
{xukuan.xk,wyb269207,yongliang.wyl,zujie.wzj,doris.dy}@antgroup.com
Abstract
In text-to-SQL task, seq-to-seq models often
lead to sub-optimal performance due to limita-
tions in their architecture. In this paper, we
present a simple yet effective approach that
adapts transformer-based seq-to-seq model to
robust text-to-SQL generation. Instead of in-
ducing constraint to decoder or reformat the
task as slot-filling, we propose to train seq-
to-seq model with Schema-aware Denoising
(SeaD), which consists of two denoising ob-
jectives that train model to either recover input
or predict output from two novel erosion and
shuffle noises. These denoising objectives acts
as the auxiliary tasks for better modeling the
structural data in S2S generation. In addition,
we improve and propose a clause-sensitive ex-
ecution guided (EG) decoding strategy to over-
come the limitation of EG decoding for gen-
erative model. The experiments show that the
proposed method improves the performance of
seq-to-seq model in both schema linking and
grammar correctness and establishes new state-
of-the-art on WikiSQL benchmark
1
. The re-
sults indicate that the capacity of vanilla seq-
to-seq architecture for text-to-SQL may has
been under-estimated.
1 Introduction
Text-to-SQL aims at translating natural language
into valid SQL query. It enables layman to explore
structural database information with semantic ques-
tion instead of dealing with the complex grammar
required by logical form query. Though being a
typical seq-to-seq (S2S) task, auto-aggressive mod-
els (LSTM, Transformer, etc.) that predict target
sequence token by token fail to achieve state-of-the-
art results for text-to-SQL. Previous works attribute
the sub-optimal results to three major limitations.
First, SQL queries with different clause order may
have exact same semantic meaning and return same
results by execution. The token interchangeability
1
https://github.com/salesforce/WikiSQL
week | data | opponent | result | attendance
… | … | … | … | …
… | … | … | … | …
SeaD
SELECT ` <col0> ` from ` table ` where ` <col4> ` = ` 53,677 `
Which week had an attendance of 53,677
<col0> week <col1> data <col3> opponent …
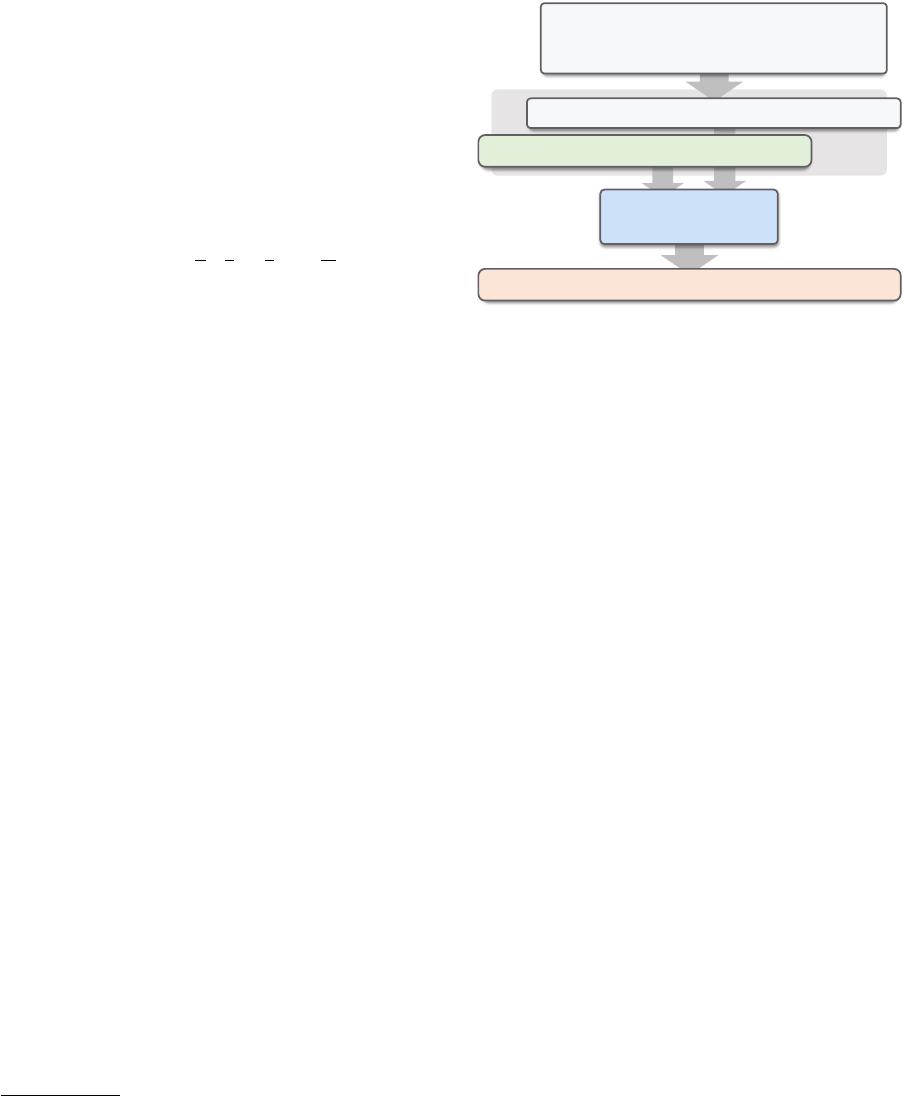
Figure 1: SeaD regards text-to-SQL as S2S generation
task. During inference, given natural language question
and related database schema, SeaD directly generates
corresponding SQL sequence in an auto-aggressive
manner.
may confusion model that based on S2S generation.
Second, the grammar constraint induced by struc-
tural logical form is ignored during auto-aggressive
decoding, therefore the model may predict SQL
with invalid logical form. Third, schema linking,
which has been suggested to be the crux of text-to-
SQL task, is not specially addressed by vanilla S2S
model.
Recent years, there have been various works pro-
posed to improve the performance of S2S model
with sketch-based slot-filling, constraint (structural-
awared) decoder or explicitly schema linking mod-
ule, that try to mitigate these limitations respec-
tively. Though most of these works share the
same encoder-decoder architecture with S2S model,
they only consider it as a simple baseline. On the
other side, generative model exhibits huge poten-
tial in other tasks that also require structural output,
which shares similar property with text-to-SQL.
This raised the question: Is the capacity of genera-
tive model underestimated or not?
In this paper, we investigate this question based
on the Transformer architecture. Instead of build-
arXiv:2105.07911v2 [cs.CL] 30 Jan 2023
ing extra module or placing constraint on model
output, we propose novel schema-awared denois-
ing objectives trained along with the original S2S
task. These denoising objectives deal with the in-
trinsic attribute of logical form and therefore facili-
tate schema linking required for text-to-SQL task.
The inductive schema-awared noises can be cate-
gorized into two types: erosion and shuffle. Ero-
sion acts on schema input by randomly permute,
drop and add columns into the current schema set.
The related schema entity in target SQL query will
be jointly modified according to the erosion re-
sult. Shuffle is applied via randomly re-ordering
the mentioned entity and values in NL or SQL with
respect to the schema columns. During training pro-
cedure, shuffle is performed during monolingual
self-supervision that trains model to recover orig-
inal text given the noised one. Erosion is applied
to S2S task that trains model to generate corrupted
SQL sequence, given NL and eroded schema as
input. These proposed denoising objectives are
combined along with the origin S2S task to train a
SeaD model. In addition, to deal with the limitation
of execution-guided (EG) decoding, we propose a
clause-sensitive EG strategy that decide beam size
with respect to the clause token that is predicted.
We compare the proposed method with other
top-performing models on WikiSQL benchmark.
The results show that the performance of our model
surpasses previous work and establish new state-of-
the-art for WikiSQL. It demonstrate the effective-
ness of the schema-aware denoising approach and
also shad lights on the importance of task-oriented
denoising objective.
2 Related Work
Semantic Parsing
The problem of mapping natu-
ral language to meaningful executable programs
has been widely studied in natural language pro-
cessing research. Logic forms (Zettlemoyer and
Collins, 2012; Artzi and Zettlemoyer, 2011, 2013;
Cai and Yates, 2013; Reddy et al., 2014; Liang
et al., 2013; Quirk et al., 2015; Chen et al., 2016)
can be considered as a special instance to the more
generic semantic parsing problem. As a sub-task
of semantic parsing, the text-to-SQL problem has
been studied for decades. (Warren and Pereira,
1982; Popescu et al., 2003; Li et al., 2006; Giordani
and Moschitti, 2012; Bodik). Slot-filling model
(Hwang et al., 2019; He et al., 2019a; Lyu et al.,
2020) translates the clauses of SQL into subtasks,
(Ma et al., 2020) treat this task as a two-stage se-
quence labeling model. However, the convergence
rate between subtasks is inconsistent or the inter-
action between multiple subtasks may lead to the
model may not converge well. Like lots of previ-
ous work (Dong and Lapata, 2016; Lin et al., 2018;
Zhong et al., 2017; Suhr et al., 2020; Raffel et al.,
2019), we treat text-to-SQL as a translation prob-
lem, and taking both the natural language question
and the DB as input.
Hybrid Pointer Networks
Proposed by (Vinyals
et al., 2015), copying mechanism (CM) uses atten-
tion as a pointer to copy several discrete tokens
from input sequence as the output and have been
successfully used in machine reading comprehen-
sion (Wang and Jiang, 2016; Trischler et al., 2016;
Kadlec et al., 2016; Xiong et al., 2016), interactive
conversation (Gu et al., 2016; Yu and Joty, 2020;
He et al., 2019b), geometric problems (Vinyals
et al., 2015) and program generation (Zhong et al.,
2017; Xu et al., 2017; Dong and Lapata, 2016; Yu
et al., 2018; McCann et al., 2018; Hwang et al.,
2019). In text-to-SQL, CM can not only facilitate
the condition value extraction from source input,
but also help to protect the privacy of the database.
In this paper, We use a Hybrid Pointer Generator
Network which is similar to (Jia and Liang, 2016;
Rongali et al., 2020) to generate next step token.
Denoising Self-training
Language model pretrain-
ing (Devlin et al., 2018; Yang et al., 2019; Liu et al.,
2019; Lan et al., 2019) has been shown to improve
the downstream performance on many NLP tasks
and brought significant gains. (Radford et al., 2018;
Peters et al., 2018; Song et al., 2019) are benefi-
cial to S2S task, while they are problematic for
some tasks. While (Lewis et al., 2019) is a denois-
ing S2S pre-training model, which is effective for
both generative and discriminative tasks, reduces
the mismatch between pre-training and generation
tasks. Inspired by this, we propose a denosing self-
training architecture in training to learn mapping
corrupted documents to the original.
3 Methodology
Given natural language question
Q
and a schema
S
,
our goal is to obtain the corresponding SQL query
Y
. Here the natural question
Q = {q
1
, ..., q
|Q|
}
denotes a word sequence, the schema
S =
{c
1
, ..., c
|S|
}
is composed of a set of columns,
where each column
c
i
= {c
1
, ..., c
|c
i
|
}
is a se-
quence of words.
Y = y
1
, ..., y
|Y |
denotes the
of 9
免费下载
【版权声明】本文为墨天轮用户原创内容,转载时必须标注文档的来源(墨天轮),文档链接,文档作者等基本信息,否则作者和墨天轮有权追究责任。如果您发现墨天轮中有涉嫌抄袭或者侵权的内容,欢迎发送邮件至:contact@modb.pro进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,墨天轮将立刻删除相关内容。
下载排行榜


评论