我与客户分别做了一个相同的实验:
create table test2 as select * from dba_objects;
create table test3 as select * from dba_objects;
create index idx_test2_id on test2(object_id);
create index idx_test2_name on test2(object_name,owner);
create index idx_test3_id on test3(object_id);
执行sql语句:
select *
from (select temp.*,rownum rn
from (select object_name,owner from test2 t2 where t2.object_name is not null and exists (select 1 from test3 t3 where t3.object_id=t2.object_id)
order by t2.object_name,t2.owner) temp where rownum<=10) temp1
where rn>0;
发现执行计划是不同的,然后我注意到我用的是scott用户,他用的是sys用户。
scott用户下将rownum<=10推入到内层查询,使用了test2的索引(object_name,owner)进行排序,而sys用户下则进行了全表扫。
执行计划分别如下:
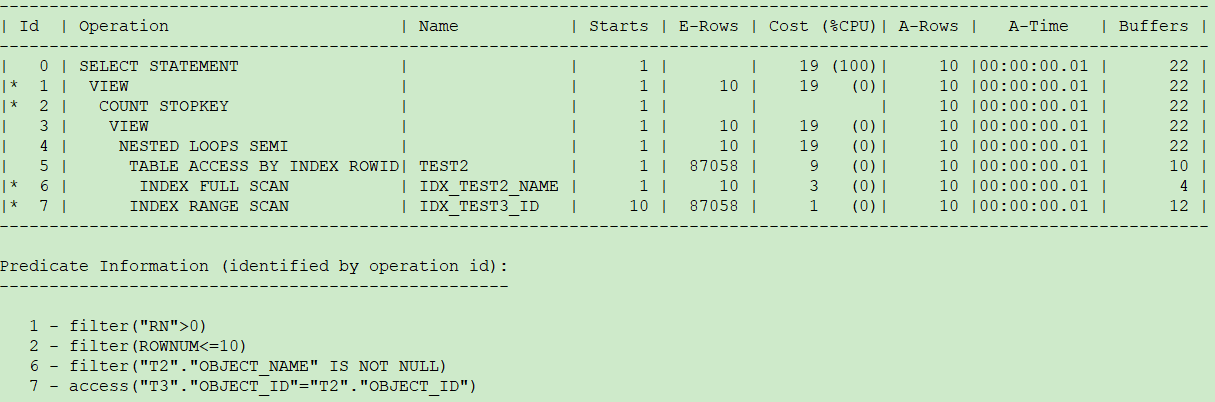
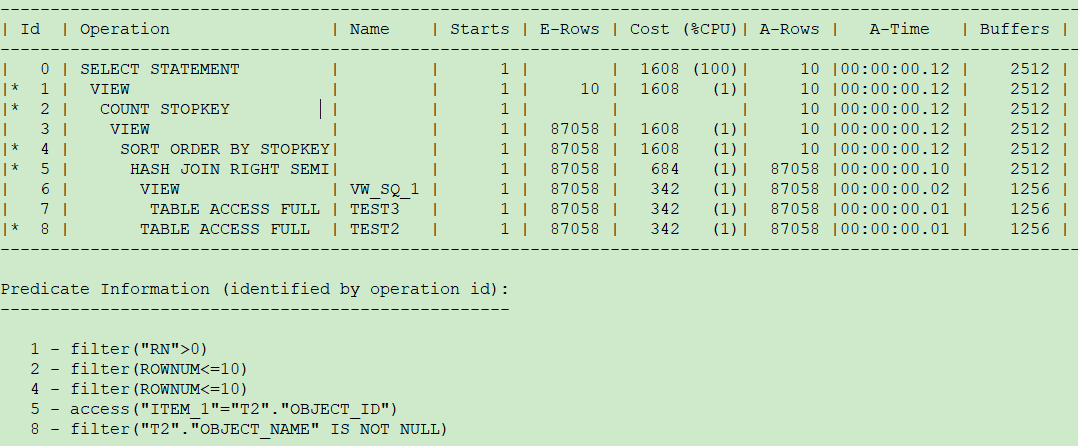
用10053跟踪了一下:
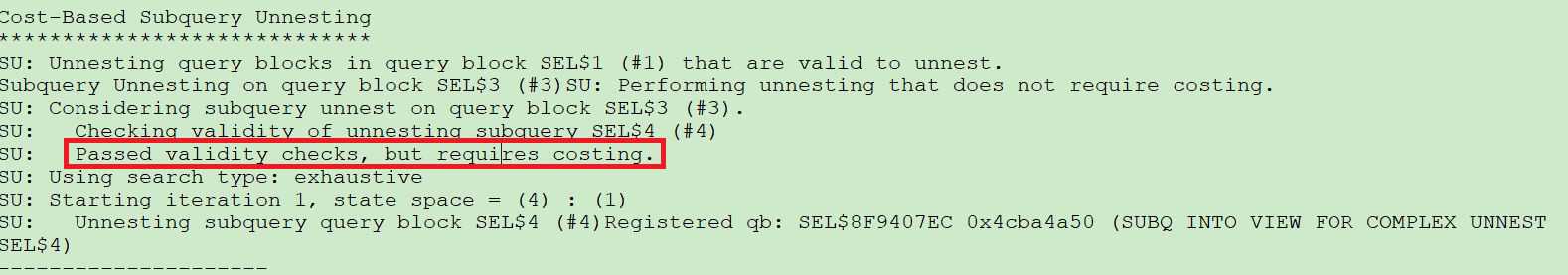
sys下子查询展开通过检查,仍然要costing
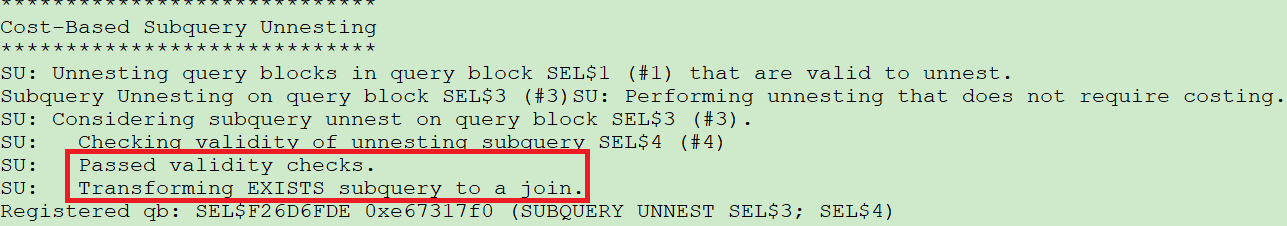
scott下将exists转换为join:
请问:访问属主为sys用户的表与普通用户的表有什么不同吗,执行计划为什么不一样?
 墨值悬赏
墨值悬赏



 评论
评论
