1、难搞的 fielddata cache

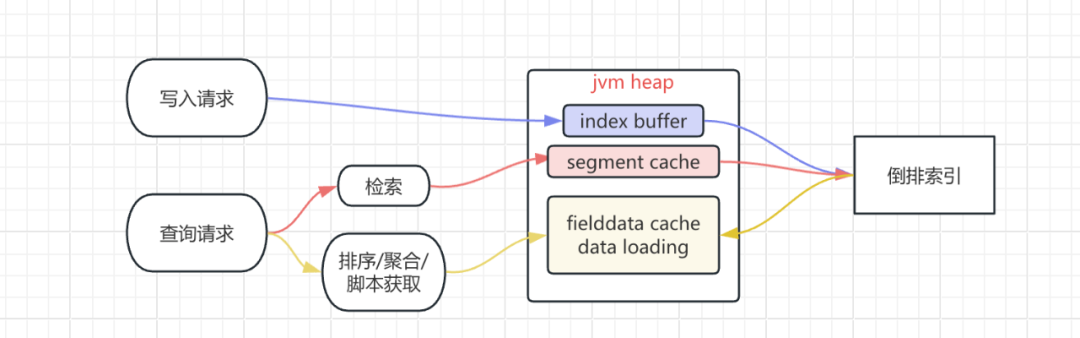
2、fielddata 内存构成
3、Text 的 fielddata 使用
4、global ordinals
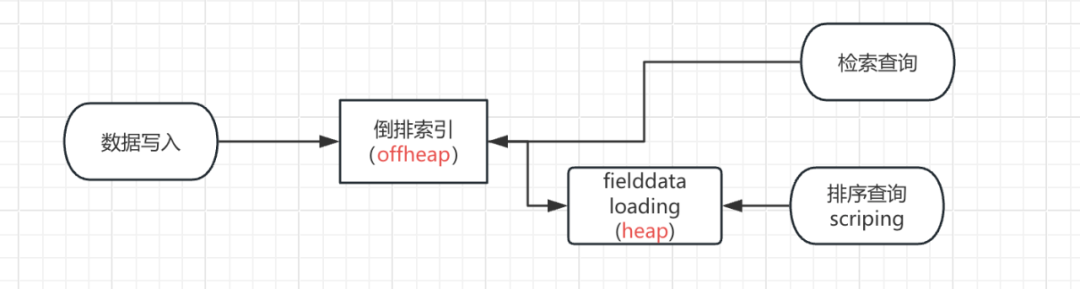
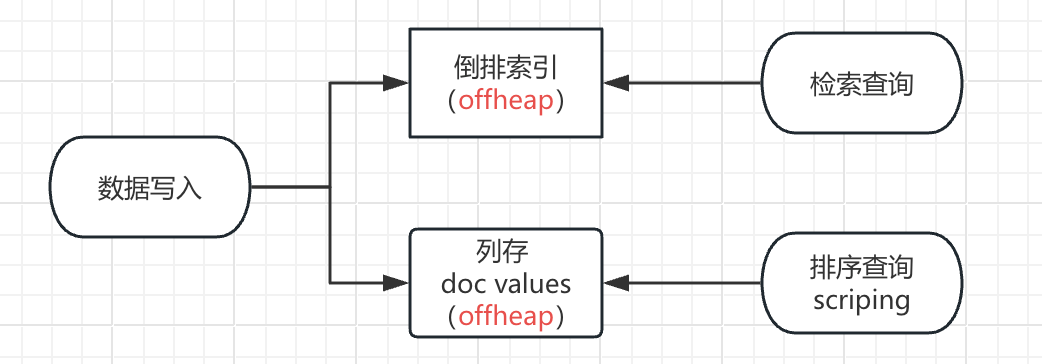
4.1 doc values 是什么
NumericDocValuesWriter (数值类型,ES 使用这个类型存储_seq_no等元数据字段) SortedNumericDocValuesWriter (多值内部排序的数值类型,被存储的字段是数值类型的数组,ES 使用这种方式存储用户定义的数值类型) SortedDocValuesWriter (排序的字符类型,保存原始值及 hash 位置) SortedSetDocValuesWriter (排序的字符数组类型,保存原始值及 hash 位置)
4.2 global ordinals 让 doc values 聚合
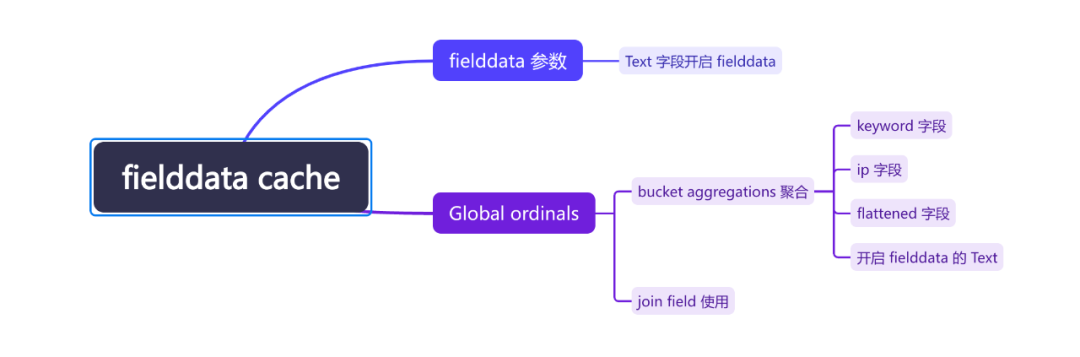
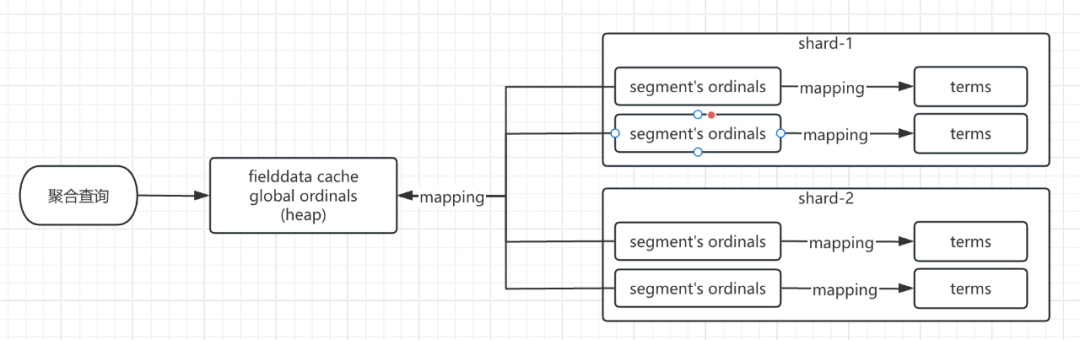
To support aggregations and other operations that require looking up field values on a per-document basis, Elasticsearch uses a data structure called doc values. Term-based field types such as keyword store their doc values using an ordinal mapping for a more compact representation. This mapping works by assigning each term an incremental integer or ordinal based on its lexicographic order. The field’s doc values store only the ordinals for each document instead of the original terms, with a separate lookup structure to convert between ordinals and terms.When used during aggregations, ordinals can greatly improve performance. As an example, the terms aggregation relies only on ordinals to collect documents into buckets at the shard-level, then converts the ordinals back to their original term values when combining results across shards.Each index segment defines its own ordinal mapping, but aggregations collect data across an entire shard. So to be able to use ordinals for shard-level operations like aggregations, Elasticsearch creates a unified mapping called global ordinals. The global ordinal mapping is built on top of segment ordinals, and works by maintaining a map from global ordinal to the local ordinal for each segment.Global ordinals are used if a search contains any of the following components:Certain bucket aggregations on keyword, ip, and flattened fields. This includes terms aggregations as mentioned above, as well as composite, diversified_sampler, and significant_terms.Bucket aggregations on text fields that require fielddata to be enabled.Operations on parent and child documents from a join field, including has_child queries and parent aggregations.The global ordinal mapping uses heap memory as part of the field data cache. Aggregations on high cardinality fields can use a lot of memory and trigger the field data circuit breaker.
聚合涉及每个分片每个segment数据的汇总计算。 以词项数据为主的字段类型(或者说字符串数据,比如 keyword 类型)的 doc values 使用一种紧凑的数据结构 ordinals 来映射原始 terms 的值,ordinals 能加速聚合查询。 global ordinal 是对每个 segment oridnals 的 map 映射。 global ordinal mapping 使用了 fielddata cache 的内存。
Term-based field types,涉及的是 keyword/ip/flattened 这三个类型。其他类型比如 long/int 等使用聚合则并不会使用 global ordinals。
org.apache.lucene.index.OrdinalMap类,欢迎指正。
5、 fielddata内存监控与清理
5.1 设置限制
indices.fielddata.cache.size
(Static) The max size of the field data cache, eg 38% of node heap space, or an absolute value, eg 12GB. Defaults to unbounded. If you choose to set it, it should be smaller than Field data circuit breaker limit.
indices.breaker.fielddata.limit
(Dynamic) Limit for fielddata breaker. Defaults to 40% of JVM heap.
5.2 监控与清理
GET _cat/fielddata?v
#查看索引的fielddata
GET _stats/fielddata?level=indices
#查看主机级别
GET _nodes/stats/indices/fielddata?fields=*
#查看主机上index级别字段级别
GET _nodes/stats/indices/fielddata?level=indices&fields=*
POST /my-index-000001/_cache/clear?fielddata=true
6、 小结和建议

合理设置 indices.fielddata.cache.size 避免对 text 直接使用 fielddata,利用 doc values 替代其使用场景。 建立模型,清洗数据,利用合适的字段进行排序聚合。比如 数字类型数据双字段,聚合使用 long,查询匹配使用 keyword。 terms/sampler/significant_terms 这些聚合方法中将 execution_hint 设置为 map,一般基数在百万以下的改为 map 方式会更优(字段值特别长的例外)。 可以考虑对没有更新的历史数据进行 forcemerge,将 segment 数量减少到最小。 尽量减少 ES 执行聚合的复杂度,超大数据体量多层次的聚合还是对系统资源的一次考验。 做好对 fielddata 内存的监控和及时的处理,有必要时直接清理
7、 参考资料
更多推荐

更短时间更快习得更多干货!
和全球超2000+ Elastic 爱好者一起精进!
elastic6.cn——ElasticStack进阶助手

文章转载自铭毅天下Elasticsearch,如果涉嫌侵权,请发送邮件至:contact@modb.pro进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,墨天轮将立刻删除相关内容。






