多线程模式
Java多线程编程中,常用的多线程设计模式包括:Future模式、Master-Worker模式、Guarded Suspeionsion模式、不变模式和生产者-消费者模式等
Future模式
Future模式对于多线程而言,如果线程A要等待线程B的结果,那么线程A没必要一直等待B,直到B有结果,可以先拿到一个未来的Future,等B有结果时再获取真实的结果。Future模式的核心在于:去除了主函数的等待时间,并使得原本需要等待的时间段可以用于处理其他业务逻辑。
Future模式有点类似于商品订单。在网上购物时,提交订单后,在收货的这段时间里无需一直在家里等候,可以先干别的事情。类推到程序设计中时,当提交请求时,期望得到答复时,如果这个答复可能很慢。传统的是一直持续等待直到这个答复收到之后再去做别的事情,但如果利用Future模式,其调用方式改为异步,而原先等待返回的时间段,在主调用函数中,则可以用于处理其他事务。
Future模式的应用
Future模式的应用场景非常多,比如在rxjava,guava,dubbo的client与server交互的response与request也是用future进行包装的,还有很多其他的场景中也都离不开Future的身影。下面我们顺便来看下Future在Elasticsearch中的应用。future的主要有以下几个方法:
cancel(boolean) :尝试取消任务的执行;
get():尝试获取任务执行的结果,是一个阻塞方法;
get(long,TimeUnit):获取任务执行结果的方法,阻塞到指定时间;
isDone():任务是否执行完成;
isCancelled():任务是否已经取消。
org.elasticsearch.common.util.concurrent.BaseFuture
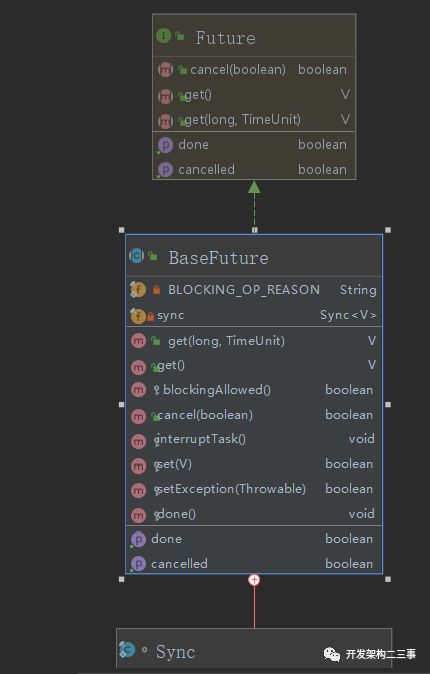
我们先来分析一下它的内部类org.elasticsearch.common.util.concurrent.BaseFuture.Sync:
/**
1. 遵循{@link AbstractQueuedSynchronizer}的约定,我们创建了一个私有子类来保存同步器。该同步器用于实现阻塞和等待调用以及以线程安全的方式处理状态更改。将来的当前状态保持为“同步”状态,并且只要状态更改为{@link #COMPLETED}或{@link #CANCELLED},就会释放锁定。
2. 为了避免进行释放和获取的线程之间的竞争,我们分两步过渡到最终状态。一个线程将成功地将CAS从RUNNING转换为COMPLETING,然后该线程将设置计算结果,然后才转换为COMPLETED或CANCELLED。
3. 我们不使用在aqs中acquire方法之间传递的整数参数,因此我们在各处传递-1来填充这个参数。
*/
static final class Sync<V> extends AbstractQueuedSynchronizer {
/* Valid states. */
static final int RUNNING = 0;// 初始状态,AQS的state默认为0
static final int COMPLETING = 1;
static final int COMPLETED = 2;
static final int CANCELLED = 4;
private V value;
private Throwable exception;
/*
* Acquisition succeeds if the future is done, otherwise it fails.
*/
@Override
protected int tryAcquireShared(int ignored) {//当future完成时获取成功,否则获取失败
if (isDone()) {// future完成
return 1;
}
return -1;
}
/*
* We always allow a release to go through, this means the state has been
* successfully changed and the result is available.
*/
@Override
protected boolean tryReleaseShared(int finalState) {// 释放
// 设置最终状态
setState(finalState);
return true;
}
/**
* Blocks until the task is complete or the timeout expires. Throws a
* {@link TimeoutException} if the timer expires, otherwise behaves like
* {@link #get()}.
*/
V get(long nanos) throws TimeoutException, CancellationException,
ExecutionException, InterruptedException {//阻塞直到任务完成或者时间超时
// Attempt to acquire the shared lock with a timeout.
/**
这里调用的是java.util.concurrent.locks.AbstractQueuedSynchronizer#tryAcquireSharedNanos方法
public final boolean tryAcquireSharedNanos(int arg, long nanosTimeout)
throws InterruptedException {
if (Thread.interrupted())
throw new InterruptedException();
return tryAcquireShared(arg) >= 0 ||
doAcquireSharedNanos(arg, nanosTimeout);
}
1. 这里调用的是上面的tryAcquireShared方法,在任务完成时返回1,否则返回-1,当返回1时会直接返回true,不会执行doAcquireSharedNanos方法;
2. 如果任务没有完成,则tryAcquireShared(arg) >= 0为false,那么会进入doAcquireSharedNanos方法,在该方法中会在未超时的时间内调用tryAcquireShared方法再次尝试,也是在任务执行完成时返回true,否则进行阻塞直到超时释放并返回false。当两个结果都为false时会进入下面这个判断。
*/
if (!tryAcquireSharedNanos(-1, nanos)) {
throw new TimeoutException("Timeout waiting for task.");
}
// 如果能进行到这里,证明任务已经执行完成,可以获取到结果
return getValue();
}
/**
* Blocks until {@link #complete(Object, Throwable, int)} has been
* successfully called. Throws a {@link CancellationException} if the task
* was cancelled, or a {@link ExecutionException} if the task completed with
* an error.
*/
V get() throws CancellationException, ExecutionException,
InterruptedException {
/**
这里我们看下方法:
public final void acquireSharedInterruptibly(int arg)
throws InterruptedException {
if (Thread.interrupted())
throw new InterruptedException();
if (tryAcquireShared(arg) < 0)
doAcquireSharedInterruptibly(arg);
}
1. tryAcquireShared方法在任务未完成时会返回-1,然后进入doAcquireSharedInterruptibly方法;
2. 再来看doAcquireSharedInterruptibly方法,里面会调用tryAcquireShared方法进行判断,如果任务完成则返回值为1,会直接返回,否则代表任务未完成,线程会被park,进行等待状态,直到complete方法被调用。
*/
// Acquire the shared lock allowing interruption.
acquireSharedInterruptibly(-1);
return getValue();
}
/**
* Implementation of the actual value retrieval. Will return the value
* on success, an exception on failure, a cancellation on cancellation, or
* an illegal state if the synchronizer is in an invalid state.
*/
private V getValue() throws CancellationException, ExecutionException {
int state = getState();
switch (state) {
case COMPLETED:
if (exception != null) {
throw new ExecutionException(exception);
} else {
// 返回执行结果
return value;
}
case CANCELLED:
throw new CancellationException("Task was cancelled.");
default:
throw new IllegalStateException(
"Error, synchronizer in invalid state: " + state);
}
}
/**
* Checks if the state is {@link #COMPLETED} or {@link #CANCELLED}.
*/
boolean isDone() {
// 是否执行完成
return (getState() & (COMPLETED | CANCELLED)) != 0;
}
/**
* Checks if the state is {@link #CANCELLED}.
*/
boolean isCancelled() {
// 是否处于取消状态
return getState() == CANCELLED;
}
/**
* Transition to the COMPLETED state and set the value.
*/
boolean set(@Nullable V v) {//过渡到COMPLETED状态并设置值
// 设置状态
return complete(v, null, COMPLETED);
}
/**
* Transition to the COMPLETED state and set the exception.
*/
boolean setException(Throwable t) {// 过渡到COMPLETED状态并设置异常
return complete(null, t, COMPLETED);
}
/**
* Transition to the CANCELLED state.
*/
boolean cancel() {//过渡到CANCELLED状态
return complete(null, null, CANCELLED);
}
/**
* Implementation of completing a task. Either {@code v} or {@code t} will
* be set but not both. The {@code finalState} is the state to change to
* from {@link #RUNNING}. If the state is not in the RUNNING state we
* return {@code false} after waiting for the state to be set to a valid
* final state ({@link #COMPLETED} or {@link #CANCELLED}).
*
* @param v the value to set as the result of the computation.
* @param t the exception to set as the result of the computation.
* @param finalState the state to transition to.
*/
private boolean complete(@Nullable V v, @Nullable Throwable t,
int finalState) {
// cas AQS的state从初始的RUNNING到COMPLETING
boolean doCompletion = compareAndSetState(RUNNING, COMPLETING);
if (doCompletion) {//如果cas成功了
// If this thread successfully transitioned to COMPLETING, set the value
// and exception and then release to the final state.
this.value = v;//设置结果
this.exception = t;// 设置异常
/**
public final boolean releaseShared(int arg) {
if (tryReleaseShared(arg)) {
doReleaseShared();// 在里面执行线程唤醒的任务,unparkSuccessor
return true;
}
return false;
}
*/
releaseShared(finalState);// 设置最终状态
} else if (getState() == COMPLETING) {// 如果是完成中
// If some other thread is currently completing the future, block until
// they are done so we can guarantee completion.
acquireShared(-1);// 如果有线程处于完成中,阻塞直到他们全部完成
}
// 返回结果
return doCompletion;
}
}
遵循{@link AbstractQueuedSynchronizer}的约定,我们创建了一个私有子类来保存同步器。该同步器用于实现阻塞和等待调用以及以线程安全的方式处理状态更改。将来的当前状态保持为“同步”状态,并且只要状态更改为{@link #COMPLETED}或{@link #CANCELLED},就会释放锁定。
为了避免进行释放和获取的线程之间的竞争,我们分两步过渡到最终状态。一个线程将成功地将CAS从RUNNING转换为COMPLETING,然后该线程将设置计算结果,然后才转换为COMPLETED或CANCELLED。
我们不使用在aqs中acquire方法之间传递的整数参数,因此我们在各处传递-1来填充这个参数。
get(long nanos)方法,get()方法和complete方法都是可能会阻塞的,这些可以理解成都是属于client方法,即外层的方法,具体细节参考代码注释内容。
唤醒操作依赖于 set(@Nullable V v)、setException(Throwable t)、cancel()等方法的调用,因为在这些方法中都调用了complete()方法并进行了state的更新。这些可以理解成处理任务的server端的方法,即内层通知外层任务执行完成的方法。
有一点需要注意,这里可能会存在外层多个线程同时get的情况,如果此时任务已经完成,则结果立即返回,否则多个线程都会进入阻塞,然后在complete方法的releaseShared方法中进行unpark。
BaseFuture中的属性与方法一览:
public abstract class BaseFuture<V> implements Future<V> {
private static final String BLOCKING_OP_REASON = "Blocking operation";
/**
* Synchronization control for AbstractFutures.
*/
private final Sync<V> sync = new Sync<>();
@Override
public V get(long timeout, TimeUnit unit) throws InterruptedException,
TimeoutException, ExecutionException {
assert timeout <= 0 || blockingAllowed();
// 这里调用的是sync的get(timeout)方法
return sync.get(unit.toNanos(timeout));
}
/**
* {@inheritDoc}
* <p>
* The default {@link BaseFuture} implementation throws {@code
* InterruptedException} if the current thread is interrupted before or during
* the call, even if the value is already available.
*
* @throws InterruptedException if the current thread was interrupted before
* or during the call (optional but recommended).
* @throws CancellationException {@inheritDoc}
*/
@Override
public V get(long timeout, TimeUnit unit) throws InterruptedException,
TimeoutException, ExecutionException {
assert timeout <= 0 || blockingAllowed();
// 调用的是sync的get(timeout)方法
return sync.get(unit.toNanos(timeout));
}
/*
* Improve the documentation of when InterruptedException is thrown. Our
* behavior matches the JDK's, but the JDK's documentation is misleading.
*/
/**
* {@inheritDoc}
* <p>
* The default {@link BaseFuture} implementation throws {@code
* InterruptedException} if the current thread is interrupted before or during
* the call, even if the value is already available.
*
* @throws InterruptedException if the current thread was interrupted before
* or during the call (optional but recommended).
* @throws CancellationException {@inheritDoc}
*/
@Override
public V get() throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException {
assert blockingAllowed();
return sync.get();
}
// protected so that it can be overridden in specific instances
protected boolean blockingAllowed() {// 用于es集群状态、处理线程等的校验,可以被使用的地方重写
return Transports.assertNotTransportThread(BLOCKING_OP_REASON) &&
ThreadPool.assertNotScheduleThread(BLOCKING_OP_REASON) &&
ClusterApplierService.assertNotClusterStateUpdateThread(BLOCKING_OP_REASON) &&
MasterService.assertNotMasterUpdateThread(BLOCKING_OP_REASON);
}
@Override
public boolean isDone() {
return sync.isDone();
}
@Override
public boolean isCancelled() {
return sync.isCancelled();
}
@Override
public boolean cancel(boolean mayInterruptIfRunning) {
if (!sync.cancel()) {
return false;
}
done();
if (mayInterruptIfRunning) {
interruptTask();
}
return true;
}
// 模板方法
protected void interruptTask() {
}
/**
* Subclasses should invoke this method to set the result of the computation
* to {@code value}. This will set the state of the future to
* {@link BaseFuture.Sync#COMPLETED} and call {@link #done()} if the
* state was successfully changed.
*
* @param value the value that was the result of the task.
* @return true if the state was successfully changed.
*/
protected boolean set(@Nullable V value) {
boolean result = sync.set(value);
if (result) {
done();
}
return result;
}
可以看到BaseFuture中的方法大都依赖于Sync来实现的。
总结
全篇设计的最妙的地方是用Sync包装了Future的方法,然后对tryAcquireShared方法和tryReleaseShared方法的重写也是整个设计的核心。以上纯属个人观点,不当之处还请指正。






