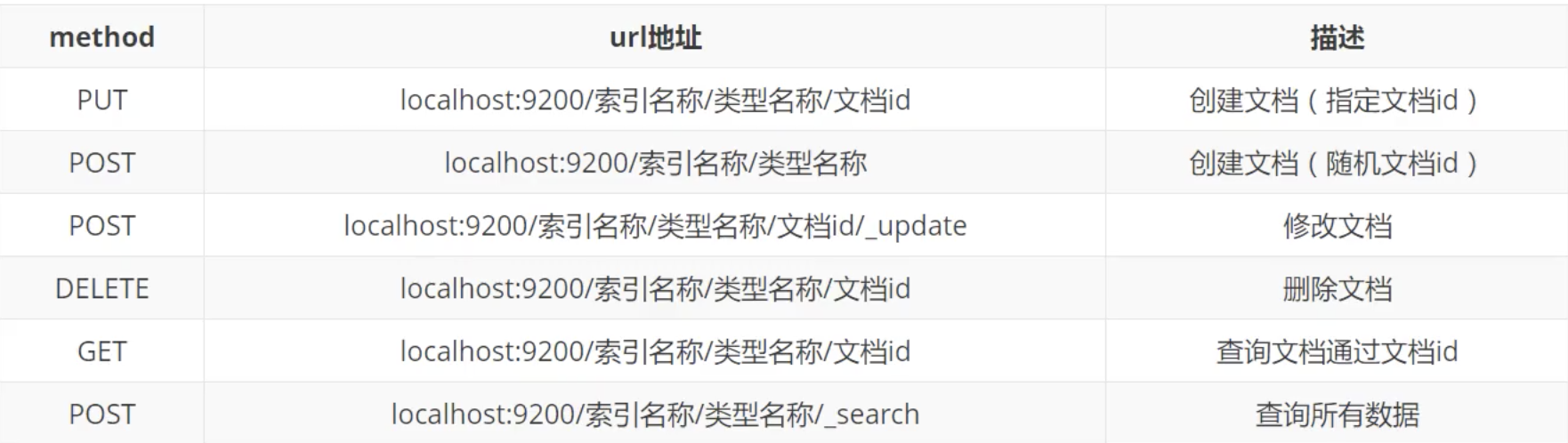
目录
一、概述
1.1、概述
一个开源的高扩展的分布式全文检索引擎,可近乎实时的存储、检索数据,可扩展性强,可处理PB级别的数据。
通过简单的Restfull API, 来隐藏Luncee的复杂性,从而让全文搜索变得简单
1.2、核心概念
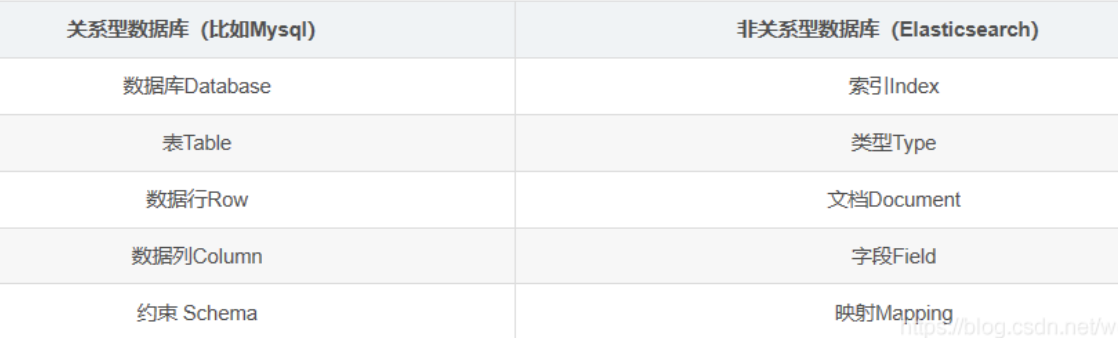
1.2.1、与传统名数据库的区别
ES只支持json格式
1.2.2、物理设计
ES会在后台把每个索引划分成多个分片,每份分片可以在集群中的不同服务间迁移
1.2.3、倒排索引
Elasticsearch是通过Lucene的倒排索引技术实现比关系型数据库更快的过滤。
首先把每个文档拆分为独立的词,然后创建一个包含所有且不重复的词条列表,然后列出每个词条出现在那个文档
这样就可以根据词条(内容)索引到包含该词条的文章,并根据文中包含搜索语句中词的个数进行排序。

-
优势
传统的搜索包含linux的文章,需要遍历所有文章内容进行like匹配
而倒排索引,搜索包含linux的文章,直接就linux这个词条,其他的直接过滤掉了,不需要进行匹配,而且不需要再匹配文章内容。
1.3、docker安装ElasticSearch
-
拉取镜像
docker pull elasticsearch:7.6.2 -
创建持久化文件
mkdir -p /elasticsearch/config mkdir -p /elasticsearch/data -
初始化配置
echo "http.host: 0.0.0.0" >> /elasticsearch/config/elasticsearch.yml -
启动镜像
docker run --name elasticsearch -p 9200:9200 -p 9300:9300 -e "discovery.type=single-node" -v /Users/yangmeng/elasticsearch/config/elasticsearch.yml:/usr/share/elasticsearch/config/elasticsearch.yml -v Users/yangmeng/elasticsearch/data:/usr/share/elasticsearch/data -v Users/yangmeng/elasticsearch/plugins:/usr/share/elasticsearch/plugins -d elasticsearch:7.6.2- p: 端口映射
- -e: 单点模式启动
- -v: 目录挂载
- -d: 后台运行
-
测试访问
localhost:9200
{ "name" : "1915d6ba7ccb", "cluster_name" : "elasticsearch", "cluster_uuid" : "E017hynLQvi28mpqUmU00w", "version" : { "number" : "7.6.2", "build_flavor" : "default", "build_type" : "docker", "build_hash" : "ef48eb35cf30adf4db14086e8aabd07ef6fb113f", "build_date" : "2020-03-26T06:34:37.794943Z", "build_snapshot" : false, "lucene_version" : "8.4.0", "minimum_wire_compatibility_version" : "6.8.0", "minimum_index_compatibility_version" : "6.0.0-beta1" }, "tagline" : "You Know, for Search" }
1.4、docker安装kibana
kibana 是 Elasticsearch 的最佳拍档
用于Query DSL的编写
-
拉取镜像
docker pull kibana:7.6.2 -
配置文件
mkdir kibana vi kibana.ymlserver.host: 0.0.0.0 elasticsearch.hosts: http://localhost:9200 -
启动
docker run --name kibana -v /Users/yangmeng/kibana/kibana.yml:/usr/share/kibana/config/kibana.yml -p 5601:5601 -d kibana:7.6.2-
若遇到该容器已经存在,rm掉,重现启动即可
docker rm a71a11a3a30fd6bfc
-
-
访问
localhost:5601 【Kibana server is not ready yet】
-
排错
按照以上做法,访问localhost:5601会报错 【Kibana server is not ready yet】
原因是:1、ElasticSearch和kibana版本不匹配
2、kibana.yml错误
-
更改kibana.yml
server.host: 0.0.0.0 elasticsearch.hosts: http://192.168.0.102:9200 -
重启kibana
docker restart 80118c57cabc
-
二、分词
2.1、概述
ES 中处理分词的部分被称作分词器,英文是
Analyzer,它决定了分词的规则。ES 自带了很多默认的分词器,比如Standard、Keyword、Whitespace等等,默认是Standard。当我们在读时或者写时分词时,均可以指定要使用的分词器。
-
分词原理
分词器的组成如下:
- Character Filters:针对原始文本进行处理,比如去除html标签
- Tokenizer:将原始文本按照一定规则切分为单词
- Token Filters:针对Tokenizer处理的单词进行再加工,比如转小写、删除或增新等处理
-
分词器种类
-
默认分词器:standard
POST _analyze { "analyzer": "standard", "text": "往事知多少" } -
停用词分词器:stop
POST _analyze { "analyzer": "stop", "text": ["The 2 QUICK Brown Foxes jumped over the lazy dog's bone."] } -
中文分词器:ik分词器
POST _analyze { "analyzer": "ik_smart", "text": "春花秋月何时" } POST _analyze { "analyzer": "ik_max_word", "text": "往事知多少" }
-
-
示例
2.2、写入时分词
当创建文档时,ES会进行分词,用于倒排索引,存储在服务器磁盘中
-
默认写入时分词
写入时,分词默认使用的是
Standard。会将中文分成单个字当索引PUT test/_mapping/doc { "name": "春花秋月何时" } -
指定分词器
写入时,也可以指定分词器
PUT test/_mapping/doc { "name": "春花秋月何时" "analyzer": "ik_" }
2.3、搜索时分词
用户搜索时,也会对搜索词进行分词,存储在内存中(查询结束则消失)
-
默认分词器
读时分词器默认与写时分词器默认保持一致(读写采用一致的分词器,才能尽最大可能保证分词的结果是可以匹配的。)
-
指定分词器
ES 允许也读时分词器单独设置
POST test/_search { "query":{ "match":{ "msg":{ "query": "eating", "analyzer": "english" } } } }
2.4、IK分词器
对中文的分词进行了优化
2.1.1、安装IK分词器插件
-
进入ElasticSearch容器,安装插件,重启容器
需要跟ElasticSearch相同版本
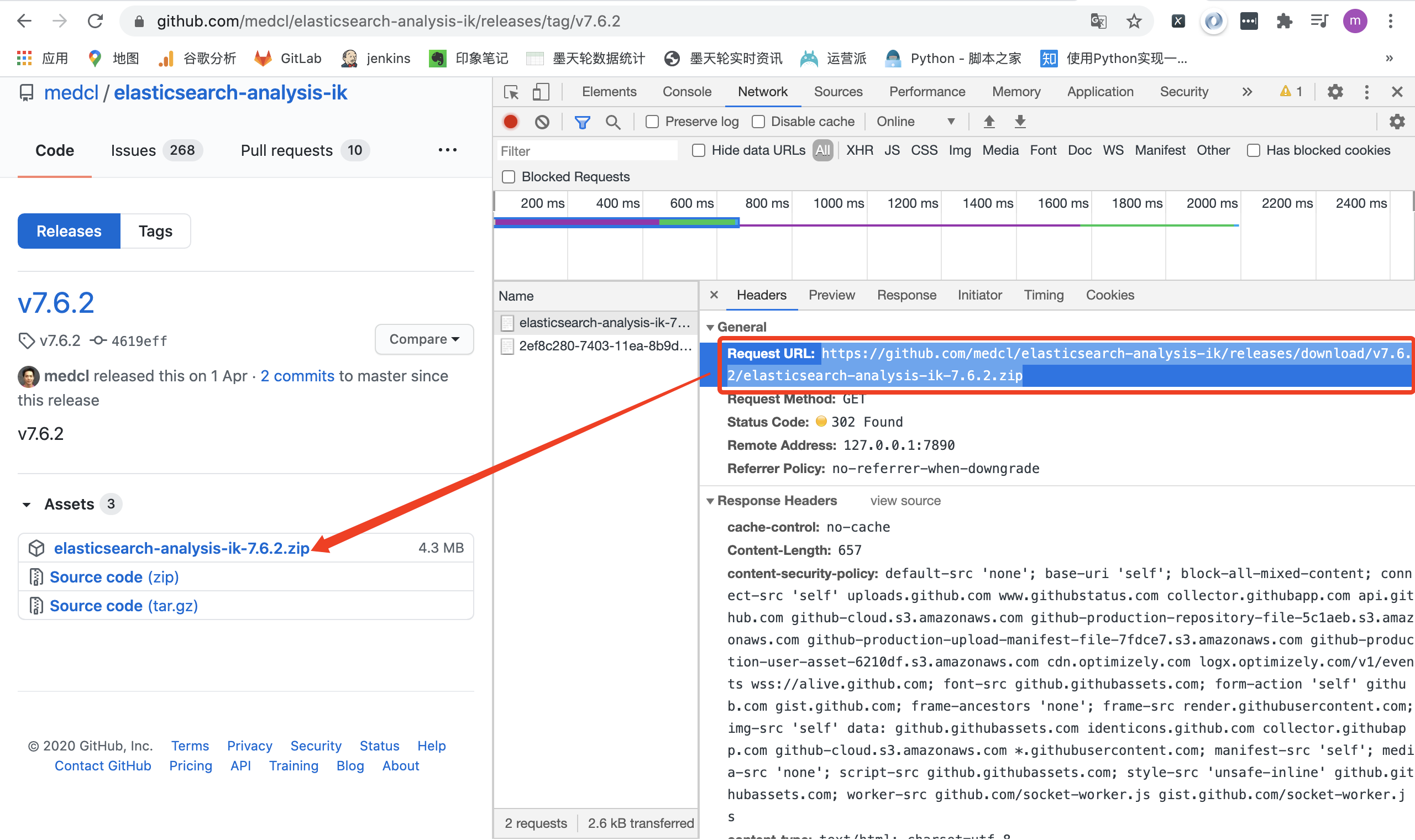
// 进入容器 docker exec -it es /bin/bash // 下载相同版本的ik插件 elasticsearch-plugin install https://github.com/medcl/elasticsearch-analysis-ik/releases/download/v7.6.2/elasticsearch-analysis-ik-7.6.2.zip // 重启容器 docker restart es
2.1.2、使用
- 基本使用
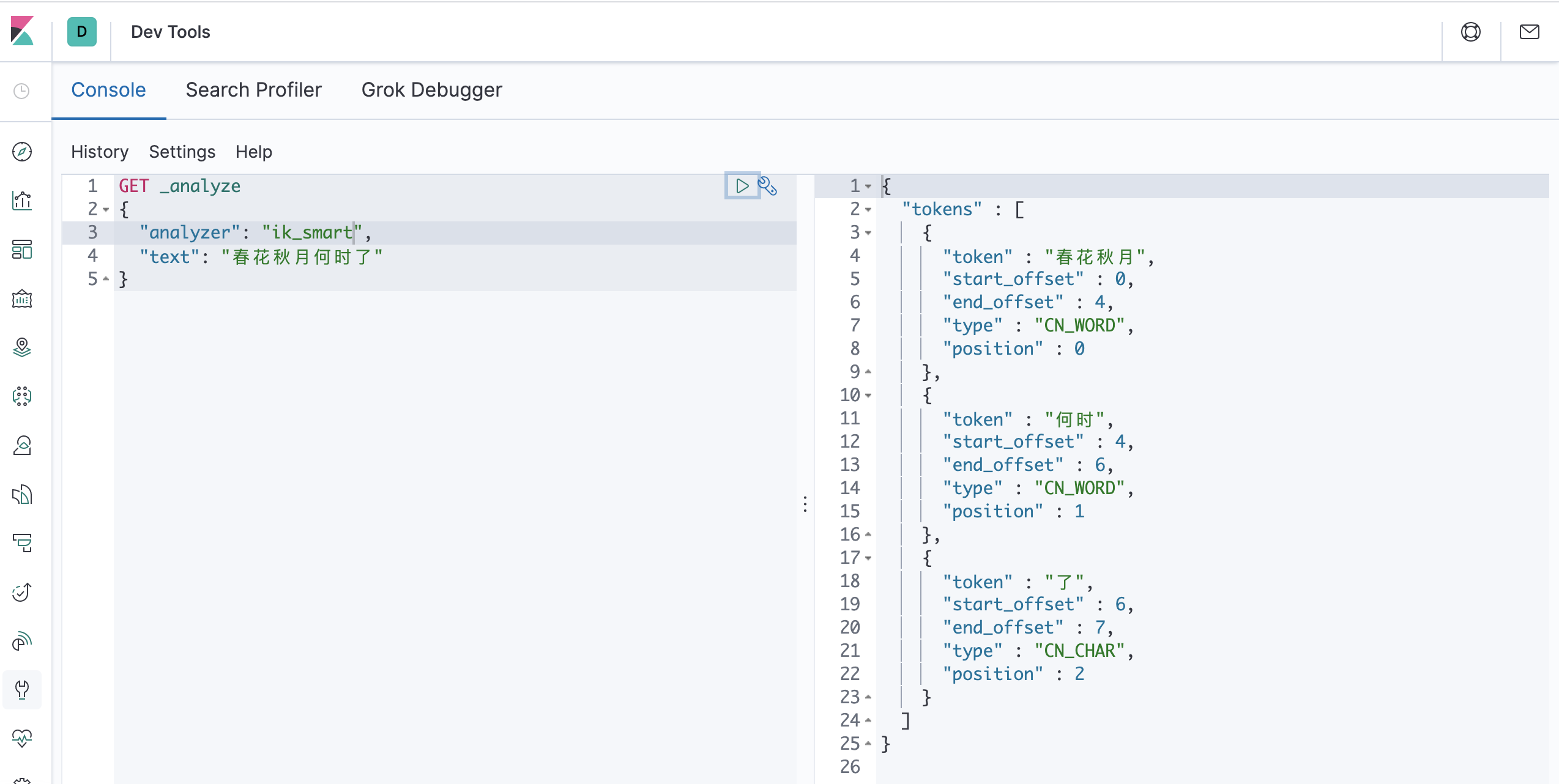
一个中文分词器插件,提供了两个分词算法:ik_smart:最小切分、ik_max_word:最小粒度划分
GET _analyze
{
"analyzer": "ik_smart",
"text": "春花秋月何时了"
}
GET _analyze
{
"analyzer": "ik_max_word",
"text": "春花秋月何时了"
}
# 补充:curl携带body发送请求测试ik分词器
curl -X POST \
'http://127.0.0.1:9200/_analyze?pretty=true' \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
-d '{"text":"我们是软件工程师","tokenizer":"ik_smart"}'
-
增加配置
-
自定义扩展词
-
修改配置文件IKAnalyzer.cfg.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <!DOCTYPE properties SYSTEM "http://java.sun.com/dtd/properties.dtd"> <properties> <comment>IK Analyzer 扩展配置</comment> <!--用户可以在这里配置自己的扩展字典 --> <entry key="ext_dict">myself.dic</entry> <!--用户可以在这里配置自己的扩展停止词字典--> <entry key="ext_stopwords"></entry> <!--用户可以在这里配置远程扩展字典 --> <!--<entry key="remote_ext_dict">http://localhost/es_new_word.txt</entry>--> <!--用户可以在这里配置远程扩展停止词字典--> <!-- <entry key="remote_ext_stopwords">words_location</entry> --> </properties> -
编写自定义dic(myself.dic)
春花秋
-
-
2.1.3、实操
-
与默认分词器对比
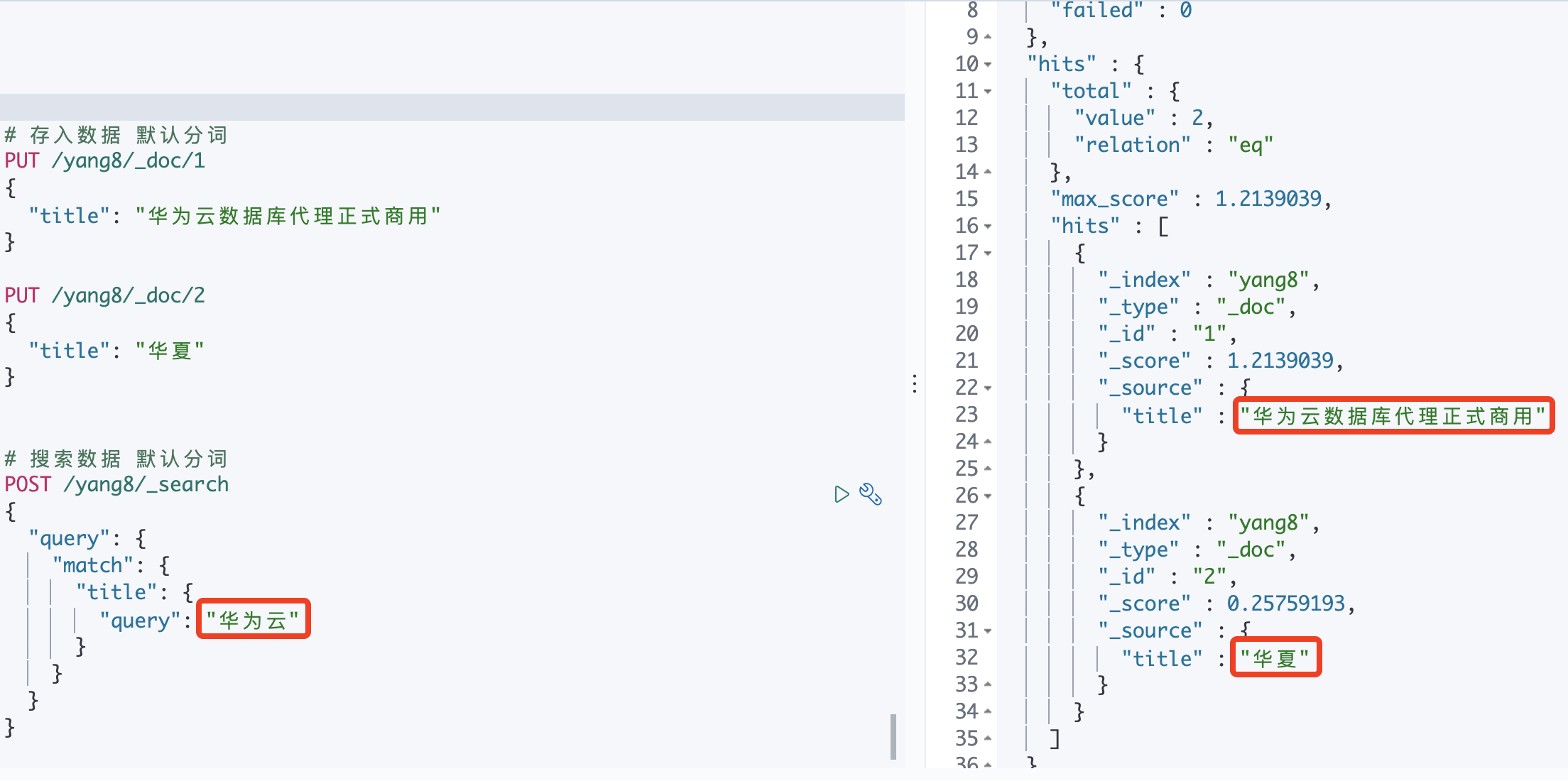
【默认分词器】
存入时:把华夏拆分为"华" “夏”
搜索时:把华为云拆分为"华" “为” “云”
因此,把华夏也匹配到了
【ik分词器】
存入时:把华夏拆分为"华夏"
搜索时:把华为云拆分为"华为" “云”
因此,不会把华夏匹配进去
-
使用ik分词器分词
-
创建索引
【注意】一定要在创建索引时指定ik分词器,才会生效
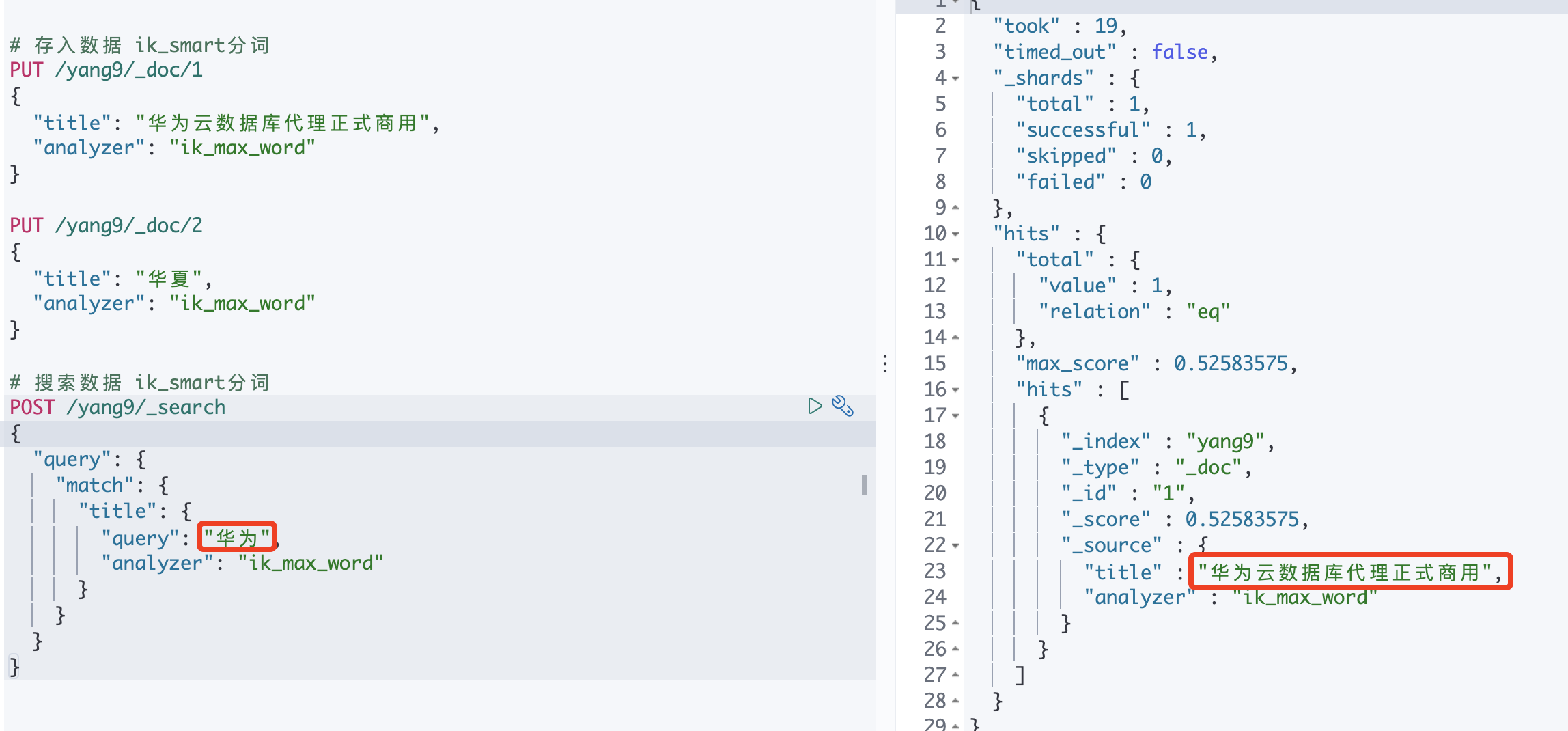
# 【一定要在创建索引时指定ik分词器,才会生效】 PUT /yang9 { "mappings": { "properties": { "title": { "type": "text", "analyzer": "ik_max_word" } } } } -
存入数据
PUT /yang9/_doc/1 { "title": "华为云数据库代理正式商用", "analyzer": "ik_max_word" # 可以省略,默认跟索引设置的分词器一致 } PUT /yang9/_doc/2 { "title": "华夏", "analyzer": "ik_max_word" # 可以省略,默认跟索引设置的分词器一致 } -
搜索数据
POST /yang9/_search { "query": { "match": { "title": { "query": "华为", "analyzer": "ik_max_word" # 可以省略,默认跟存入数据分词器一致 } } } }
-
三、ES基本操作
Rest风格操作
3.1、索引的操作
3.1.1、增删改查
-
增
-
创建一个索引(没有指定字段类型,es会默认指定相应的类型)
# PUT /索引名/类型名/文档id # {请求体} PUT /test
-
-
删
- 删除索引
DELETE /test -
改
- 修改数据
POST /test3/_doc/1/_update { "doc":{ "name": "法外之徒张三" } } -
查
- 获得指定索引的信息(不包含文档内容)
GET test-
查看有哪些索引
GET _cat/indices?v // 查看所有索引 GET _cat/indices/s*?v // 查看以s开头的所有索引
GET _cat/indices?v // 通过_cat查看默认配置(查看版本信息)
3.1.2、设置数据类型(mappings)
- 常见数据类型

- 示例
PUT /test2
{
"mappings": {
"properties": {
"name": {
"type": "text"
},
"age": {
"type": "long"
},
"birthday": {
"type": "date"
}
}
}
}
-
区分字符串类型的text与keywords
text :会被分词器分割
keyword:不会分词器被分割
PUT /yang2/_doc/1 { "mappings": { "properties":{ "name": { "type": "text" }, "desc": { "type": "keyword" } } } }
3.2、文档的操作
3.2.1、增删改
-
添加数据
PUT /yang/user/1 { "name": "yang", "age": 25, "desc": "一波操作猛如虎,一看工资2500", "tags": ["积极", "向上"] } -
删除数据
-
删除指定数据
POST /yang/user/_delete_by_query { "query": { "match": { "name": "张三" } } } -
删除全部数据(不删结构)
POST /yang/user/_delete_by_query { "query": { "match_all": {} } }
-
-
更新数据
POST /yang/user/1/_update { "doc": { "name": "张三" } }也可以直接使用PUT/POST, 但是不能做到部分update,没有传入的值会被置空
3.1.2、查询
-
基本查询
-
全表
select * from ...;GET yang/user/1GET /yang/user/_search { "query": { "match_all": {} } } -
选择字段
Select name, desc from ..;GET /yang/user/_search { "_source": ["name", "desc"] }
-
-
条件查询
-
where
Select * from .. where name like "%张三%";GET /yang/user/_search { "query": { "match": { "name": { "query": "张三" } } } } -
order by
Select * from .. order by age desc; --降序GET /yang/user/_search { "sort": { "age": { "order": "desc" } } } -
limit分页
Select * from .. limit 0, 10; --从第0个开始,一页10条数据GET /yang/user/_search { "from": 0, "size": 10 }
-
-
多条件查询
-
and
select * from .. where name like "%张三%" and age = 19;GET /yang/user/_search { "query": { "bool": { # 多条件 "must": [ # 相当于and { "match": { "name": { "query": "张三" } } }, { "match": { "age": 19 } } ] } } } -
or
select * from .. where name like "%张三%" or age = 19;GET /yang/user/_search { "query": { "bool": { # 多条件 "should": [ # 相当于or { "name": { "query": "张三" } } }, { "match": { "age": 19 } } ] } } } -
not
select * from .. where name not like "%张三%";GET /yang/user/_search { "query": { "bool": { # 多条件 "must_not": [ # 相当于not { "name": { "query": "张三" } } } ] } } }
-
-
范围过滤
-
范围
select * from .. where age >= 10 and age <= 100;GET /yang/user/_search { "query": { "bool": { "filter": { "range": { "age": { "gte": 10, "lte": 100 } } } } } } -
in
select * from .. where "男" in tags or "技术" in tags;GET /yang/user/_search { "query": { "match": { "tags": { "query": "男 技术" # 空格隔开即可(tags:["技术宅", "男性", "唱歌"])【模糊匹配】 } } } }
-
-
精确查询
match: 对搜索词进行分词,然后匹配倒排索引
term:不分词,直接匹配倒排索引
match_phrase:对搜索词进行分词,然后匹配倒排索引「所有的分词必须同时出现在文档中」
# 存在name:春花秋月何时了 (默认分词器会分为 春 花 秋 月 何 时 了) GET /yang2/_doc/_search { "query": { "term": { # 啥也查不到 "name": "春花秋月" # term不能用query:"春花秋月" } } } GET /yang2/_doc/_search { "query": { "match": { # 可以查到 "name": { "query": "春花冬月" } } } } GET /yang2/_doc/_search { "query": { "match_phrase": { # 查不到 "name": { "query": "春花冬月" } } } } -
高亮查询
-
默认倾斜
GET /yang/user/_search { "query": { "match": { "name": "张三" } }, "highlight": { "fields": { "name": {} } } }<em>张三<em> -
自定义高亮样式
GET /yang/user/_search { "query": { "match": { "name": "张三" } }, "highlight": { "pre_tags": "<a class='hehe'>", "post_tags": "</a>", "fields": { "name": {} } } }<a class='hehe'>张三</a>
-
四、集成SpringBoot
4.1、导入依赖
<!--这边配置下自己对应的版本-->
<properties>
<java.version>1.8</java.version>
<elasticsearch.version>7.6.2</elasticsearch.version>
</properties>
<!--es客户端-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.elasticsearch.client</groupId>
<artifactId>elasticsearch-rest-high-level-client</artifactId>
<version>7.6.2</version>
</dependency>
<!--springboot的elasticsearch服务-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-elasticsearch</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!--fastjson-->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba</groupId>
<artifactId>fastjson</artifactId>
<version>1.2.73</version>
</dependency>
4.2、编写配置文件
@Configuration
public class ElasticSearchClientConfig {
@Bean
public RestHighLevelClient restHighLevelClient(){
RestHighLevelClient client = new RestHighLevelClient(
RestClient.builder(new HttpHost("localhost",9200,"http"))
);
return client;
}
}
4.3、使用
4.3.1、索引操作
-
创建索引
// 这两个包不要导错 import org.elasticsearch.client.indices.CreateIndexRequest; import org.elasticsearch.client.indices.CreateIndexResponse; @SpringBootTest // 一定要写 public class TestSearch { @Autowired @Qualifier("restHighLevelClient") private RestHighLevelClient client; // 创建索引 @Test void testCreateIndex() throws IOException { //1.创建索引的请求 CreateIndexRequest request = new CreateIndexRequest("springboot_index"); //2客户端执行请求,请求后获得响应 CreateIndexResponse response = client.indices().create(request, RequestOptions.DEFAULT); System.out.println(response); } } -
删除索引
//删除索引 @Test void testDeleteIndex() throws IOException { DeleteIndexRequest request = new DeleteIndexRequest("springboot_index"); AcknowledgedResponse delete = client.indices().delete(request,RequestOptions.DEFAULT); System.out.println("删除索引--------"+delete.isAcknowledged()); } -
查询索引是否存在
//查询索引是否存在 @Test void testExistIndex() throws IOException { //1.创建索引的请求 GetIndexRequest request = new GetIndexRequest("springboot_index"); //2客户端执行请求,请求后获得响应 boolean exist = client.indices().exists(request, RequestOptions.DEFAULT); System.out.println("测试索引是否存在-----"+exist); }
4.3.2、文档操作
先创建一个model用于存储对象
@Data
@AllArgsConstructor
@NoArgsConstructor
@Builder
public class User {
private String name;
private Integer age;
private String desc;
}
-
增
- 新增单条
//添加文档 @Test void testAddDocument() throws IOException { User user = new User("yang", 25, "一波操作猛如虎,一看工资2500"); IndexRequest request = new IndexRequest("springboot_index"); // 设置id request.id("1"); //设置超时时间 request.timeout("1s"); //将数据放到json字符串 request.source(JSON.toJSONString(user), XContentType.JSON); //发送请求 IndexResponse response = client.index(request,RequestOptions.DEFAULT); System.out.println("添加文档-------"+response.toString()); System.out.println("添加文档-------"+response.status()); }-
批量新增
//测试批量添加文档 @Test void testBulkAddDocument() throws IOException { ArrayList<User> userList=new ArrayList<User>(); userList.add(new User("cyx1",5, "描述1")); userList.add(new User("cyx1",15, "描述2")); userList.add(new User("cyx1",25, "描述3")); userList.add(new User("cyx1",35, "描述4")); userList.add(new User("cyx1",45, "描述5")); //批量操作的Request BulkRequest request = new BulkRequest(); request.timeout("1s"); //批量处理请求 for (int i = 0; i < userList.size(); i++) { request.add( new IndexRequest("springboot_index") .id(""+(i+2)) .source(JSON.toJSONString(userList.get(i)),XContentType.JSON) ); } BulkResponse response = client.bulk(request, RequestOptions.DEFAULT); //response.hasFailures()是否是失败的 System.out.println("测试批量添加文档-----"+response.hasFailures()); }
-
删
// 删除文档 @Test void testDeleteDocument() throws IOException { DeleteRequest request= new DeleteRequest("springboot_index","1"); request.timeout("1s"); DeleteResponse response = client.delete(request, RequestOptions.DEFAULT); System.out.println("测试删除文档------"+response.status()); } -
改
// 修改文档 @Test void testUpdateDocument() throws IOException { User user = new User(); user.setName("张三"); //修改是id为1的 UpdateRequest request= new UpdateRequest("springboot_index","1"); request.timeout("1s"); request.doc(JSON.toJSONString(user),XContentType.JSON); UpdateResponse response = client.update(request, RequestOptions.DEFAULT); System.out.println("测试修改文档-----"+response); System.out.println("测试修改文档-----"+response.status()); } -
查
基础查询
-
查整条数据
select * from springboot_index where id = 1;// 查看文档 @Test void testGetDocument() throws IOException { GetRequest request= new GetRequest("springboot_index","1"); GetResponse response = client.get(request, RequestOptions.DEFAULT); System.out.println("测试获取文档-----"+response.getSourceAsString()); System.out.println("测试获取文档-----"+response); }
复杂查询
@Test void searchDocument() throws IOException { SearchRequest searchRequest = new SearchRequest("springboot_index"); // 构建搜索条件【用于放body】 SearchSourceBuilder sourceBuilder = new SearchSourceBuilder(); // 【body】 // "query" : bool, match, term TermQueryBuilder termQueryBuilder = QueryBuilders.termQuery("name", "cyx1"); // "highlight" : pre_tags, post_tags, field 【高亮】 HighlightBuilder highlight = new HighlightBuilder(); highlight.preTags("<a class='hehe'>").postTags("</a>").field("name"); // 【放body】 sourceBuilder.query(termQueryBuilder); sourceBuilder.highlighter(highlight); sourceBuilder.timeout(new TimeValue(1, TimeUnit.MINUTES)); searchRequest.source(sourceBuilder); SearchResponse response = client.search(searchRequest, RequestOptions.DEFAULT); System.out.println(response); for (SearchHit documentFields : response.getHits().getHits()) { System.out.println(documentFields.getSourceAsMap()); } } -
4.4、模仿京东搜索小项目
五、结合SpringCloud
5.1、优势
直接使用SpringBoot整合
- 需要导入与服务器上ElasticSearch相同版本的ElasticSearch依赖
- 需要编写ElasticSearchClientConfig用于生成client
- 需要调用ElasticSearch的各个类的各种方法,实现ElasticSearch的各种操作(不能使用ElasticSearch语法)
结合使用SpringCloud的@FeignClient发起跨服务http请求
- 不需要导入依赖
- 不需要编写ElasticSearchClientConfig
- 直接使用原生的ElasticSearch语法发起跨服务http请求
5.2、原理

5.3、使用
-
【EasticSearchApi】使用@FeignClient
@FeignClient(name = "elasticsearchApi", url = "${feign.url}") public interface ElasticSearchApi { //搜索 @RequestLine("POST /{index}/_doc/_search") @Headers("Content-Type: application/json") @Body("body") SearchResponse search(SearchRequest body, @Param("index") String index); //创建索引 @RequestLine("POST /{index}/_doc/{id}") @Headers("Content-Type: application/json") @Body("body") void build(@Param("index") String index, @Param("id") String id, Source body); //...等等(根据需求按照原生ElasticSearch语法编写接口)... } -
【EasticSearchService】操作索引&文档
public SearchResponse search(Long pageNum, Long pageSize, String index,...) { //根据入参构造查询体body body = SearchRequestBody(...) //传入参数,调用ElasticSearchApi查询ElasticSearch数据 response = elasticSearchApi.search(body, index); return response; } -
【EasticSearchController】
当做一个微服务提供给别的微服务调用
代码略
-
【EasticSearchDAO】
编写查询数据库的接口,用户Service层调用,查询数据库数据,并调用EasticSearchApi存入EasticSearch
代码略